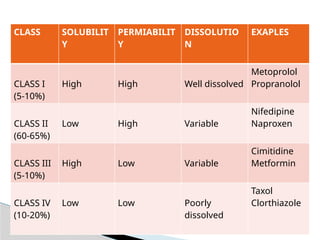
The Biopharmaceutical Classification System (BCS) categorizes drugs based on their solubility, permeability, and dissolution rate to predict in-vivo pharmacokinetics, enabling efficient screening for oral drug products. BCS divides compounds into four classes, with Class I exhibiting high solubility and permeability, while Class IV shows limitations in both. This framework aids in drug development and regulatory processes by guiding formulation strategies and predicting the bioavailability of drug substances.




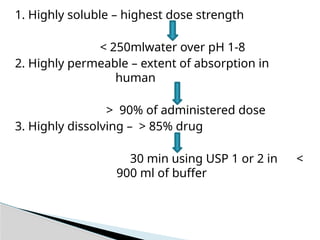


![ It is process in which solid substance solubilises in given
solvent i.e mass transfer from solid surface to liquid
phase.
Using USP apparatus I at 100 rpm or USP apparatus II at
50 rpm.
Dissolution Media [900ml],
1. 1.0.1 N HCl or simulated gastric fluid (pH 1.2) without
enzyme.
2. 2.pH 4.5 buffer & pH 6.8 buffer.
3. 3.Simulated intestinal fluid without enzyme.
Dissolution](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bcsclassificationppt-241122063413-dd35f793/85/Industrial-Pharmacy-unit-I-BCS-Classification-8-320.jpg)