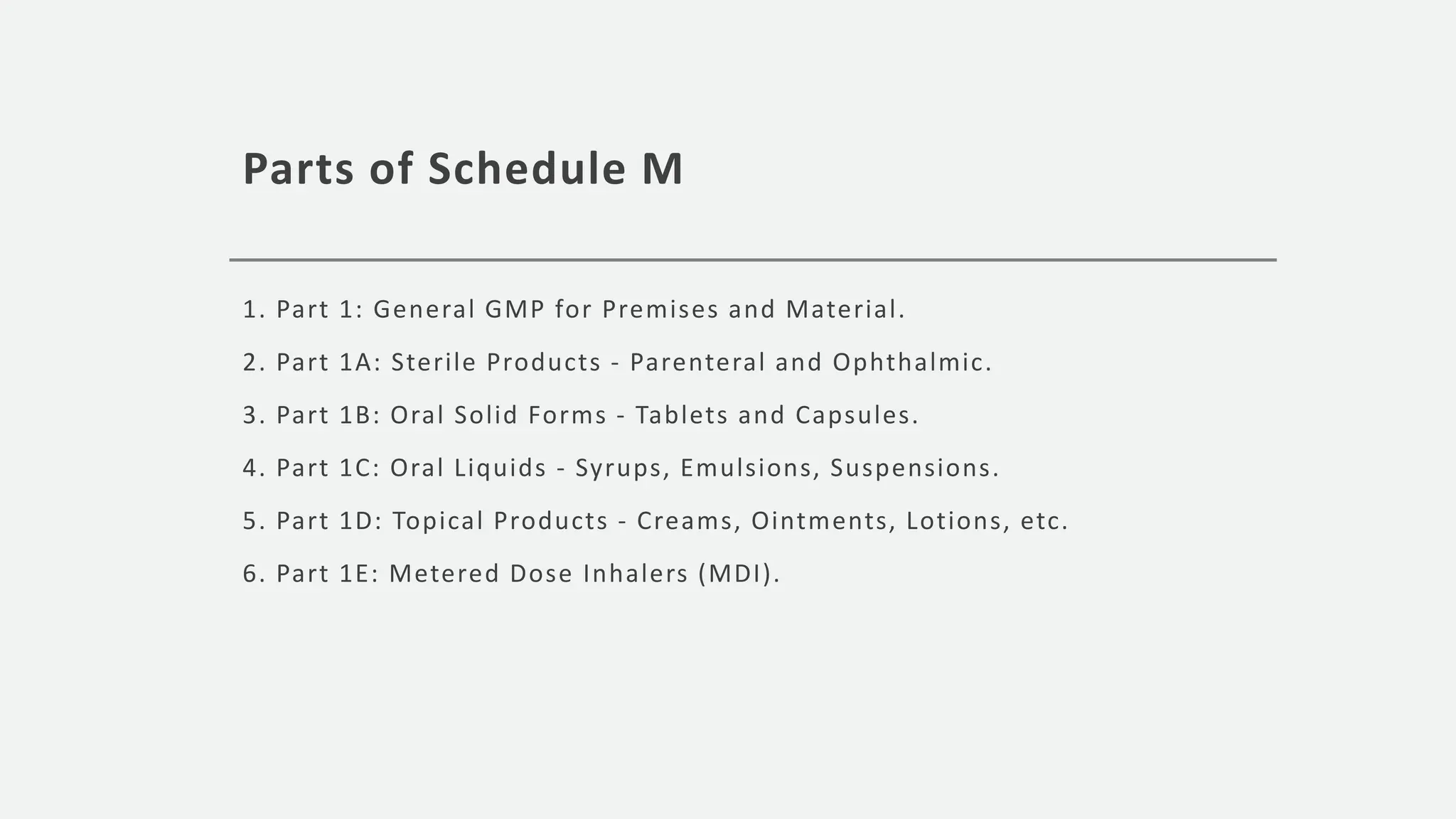
The document outlines various schedules and regulations under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act 1940 and its rules 1945, including classifications for hormonal preparations, prescription medications, good manufacturing practices (GMP), and requirements for pharmacies. It details the specific guidelines for the manufacture and sale of different drug categories, emphasizing safety, labeling, and documentation to ensure quality control and compliance in the pharmaceutical industry. Additionally, it includes regulations for blood banks, clinical trials, and restrictions on advertising certain drugs and remedies.