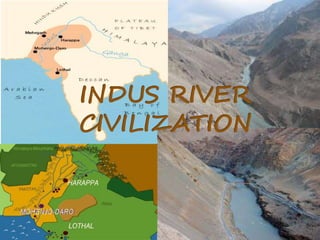
The Indus Valley civilization began around 2500 BC in the northwestern region of the Indian subcontinent. It covered parts of modern day Pakistan and northwest India. The civilization is known for its large, well-planned urban centers like Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro which had populations over 10,000. They developed advanced sanitation systems with sewers and drainage. The Indus Valley civilization relied on agriculture along the Indus River system and trade. It developed a system of uniform weights and measures and produced goods like pottery, beads, and figurines.