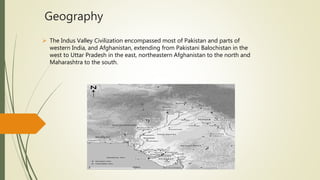
The Indus Valley civilization was one of the earliest civilizations in world history, located in northwest India from 3300-1300 BCE. It featured large, well-planned urban centers like Harappa and Mohenjo Daro with populations of tens of thousands. The cities had advanced architecture, sanitation systems, and extensive trade networks. Though over 400 symbols have been found, the meaning of the Indus script remains unknown. The civilization grew wheat, barley, and other crops and had a diet including meat and fruits. Figurines suggest the worship of mother goddesses and animal deities. After 1900 BCE, the cities were rapidly abandoned due to unknown catastrophic events like migrations or assaults.