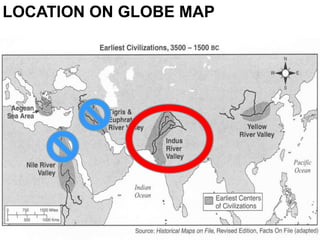
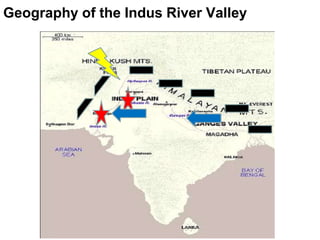
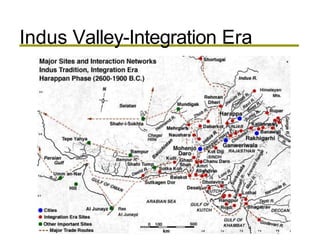
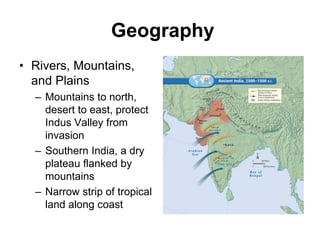
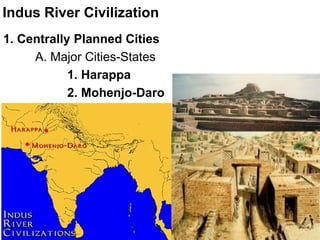
1. The Indus River Valley Civilization consisted of two major cities, Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro, which were centrally planned with fortresses, a grid layout, and advanced infrastructure like baked brick homes, water and sewage systems, and granaries.
2. Both cities displayed a uniform culture and advanced architecture, agriculture, crafts and trade networks, though the language remains undeciphered, suggesting a highly organized society and economy.
3. The civilization began declining around 1750 BCE due to environmental factors, and was ultimately replaced by Aryan groups entering the region by 1500 BCE.