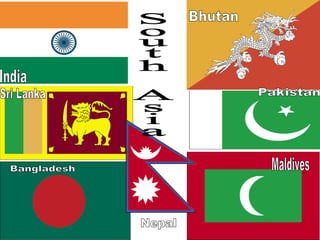
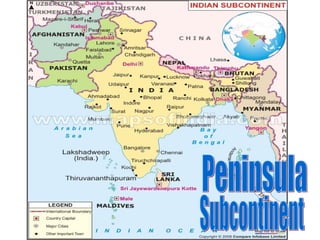
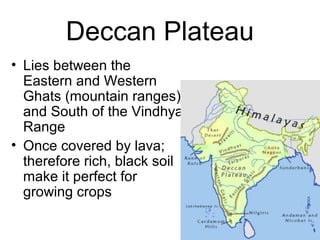
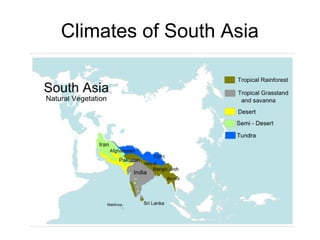
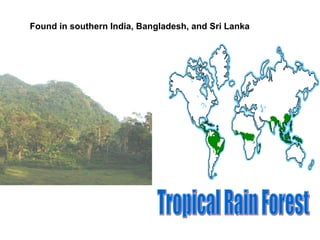
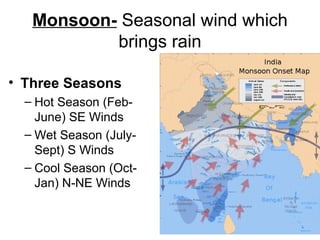
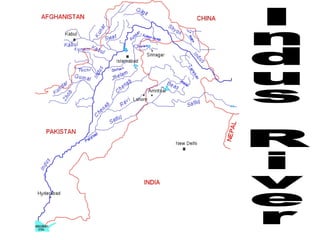
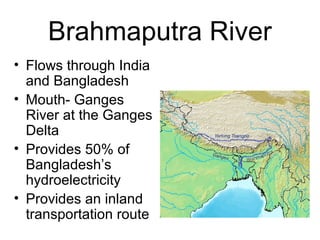
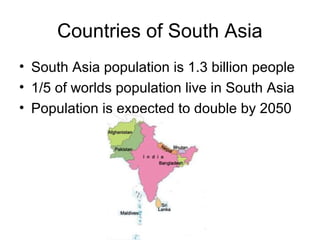
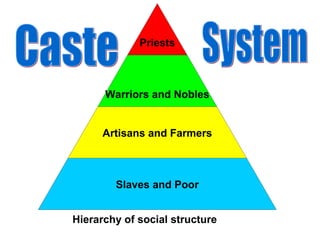
The document provides information on the physical geography, climate, transportation routes, cities, countries, religions, and history of South Asia. It notes that South Asia was created by the collision of the Indian plate with Asia, forming mountain ranges like the Himalayas. South Asia has a population of over 1.3 billion people who mainly practice religions like Hinduism, Buddhism, Islam. Major rivers include the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra. Large cities facing overpopulation issues include Mumbai, Delhi, Dhaka, and Karachi. The region has a variety of climates and was influenced by ancient civilizations and leaders like Gandhi.