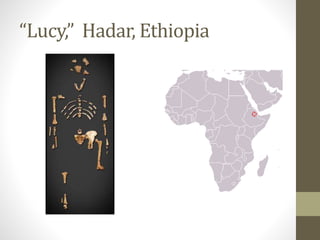
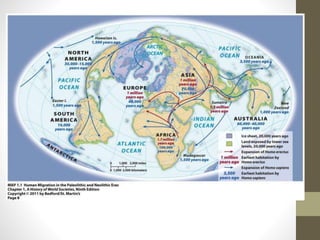
1. Early humans evolved in Africa and migrated throughout the world over millions of years, developing larger brains and culture.
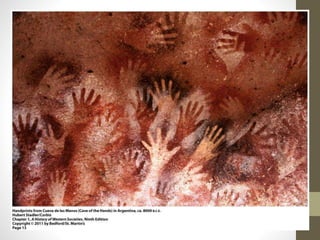
2. During the Paleolithic period from 250,000 to 9,000 BCE, humans lived in hunter-gatherer societies and developed art, music, tools, and spiritual beliefs.
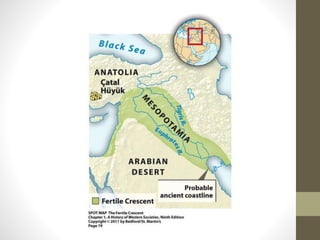
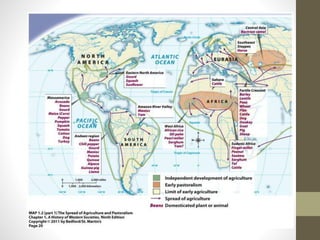
3. Around 9,000 BCE, the Agricultural Revolution began as humans in the Fertile Crescent domesticated plants and animals, leading to permanent settlements and specialized labor, as well as growing social hierarchies and complexity.