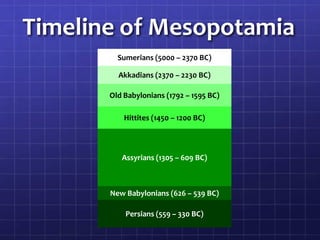
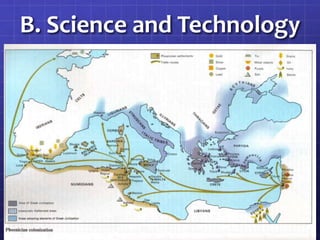
The document outlines the contributions of various Mesopotamian civilizations, including the Sumerians, Akkadians, Old Babylonians, Hittites, Assyrians, New Babylonians, and Persians, over different historical periods. Significant developments in law, government, society, economy, science, technology, art, architecture, religion, and literature are highlighted, such as Hammurabi's Code and the first written epic, the 'Epic of Gilgamesh.' Additionally, it emphasizes cultural diffusion and the establishment of systems that facilitated trade and communication across vast empires.