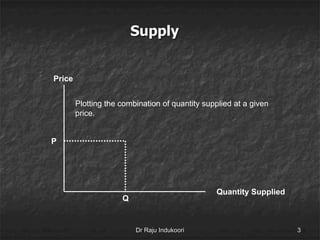
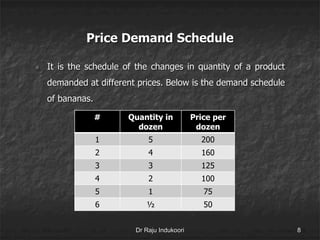
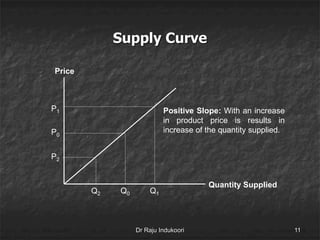
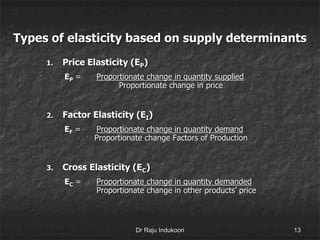
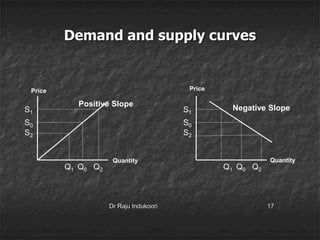
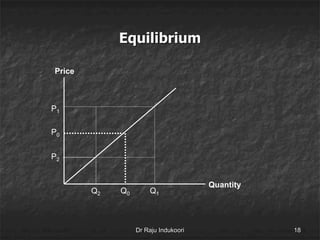
This document discusses supply, the supply function, determinants of supply, and the law of supply. It defines supply as the quantity of a product offered for sale at a given price in a given time period. The supply function defines the quantity supplied (Sx) as a function of price (Px) and other determinants, including production costs, prices of related goods, technology, taxes, subsidies, and external factors. The law of supply states that as price increases, suppliers will offer a larger quantity, and as price decreases, suppliers will offer a smaller quantity.