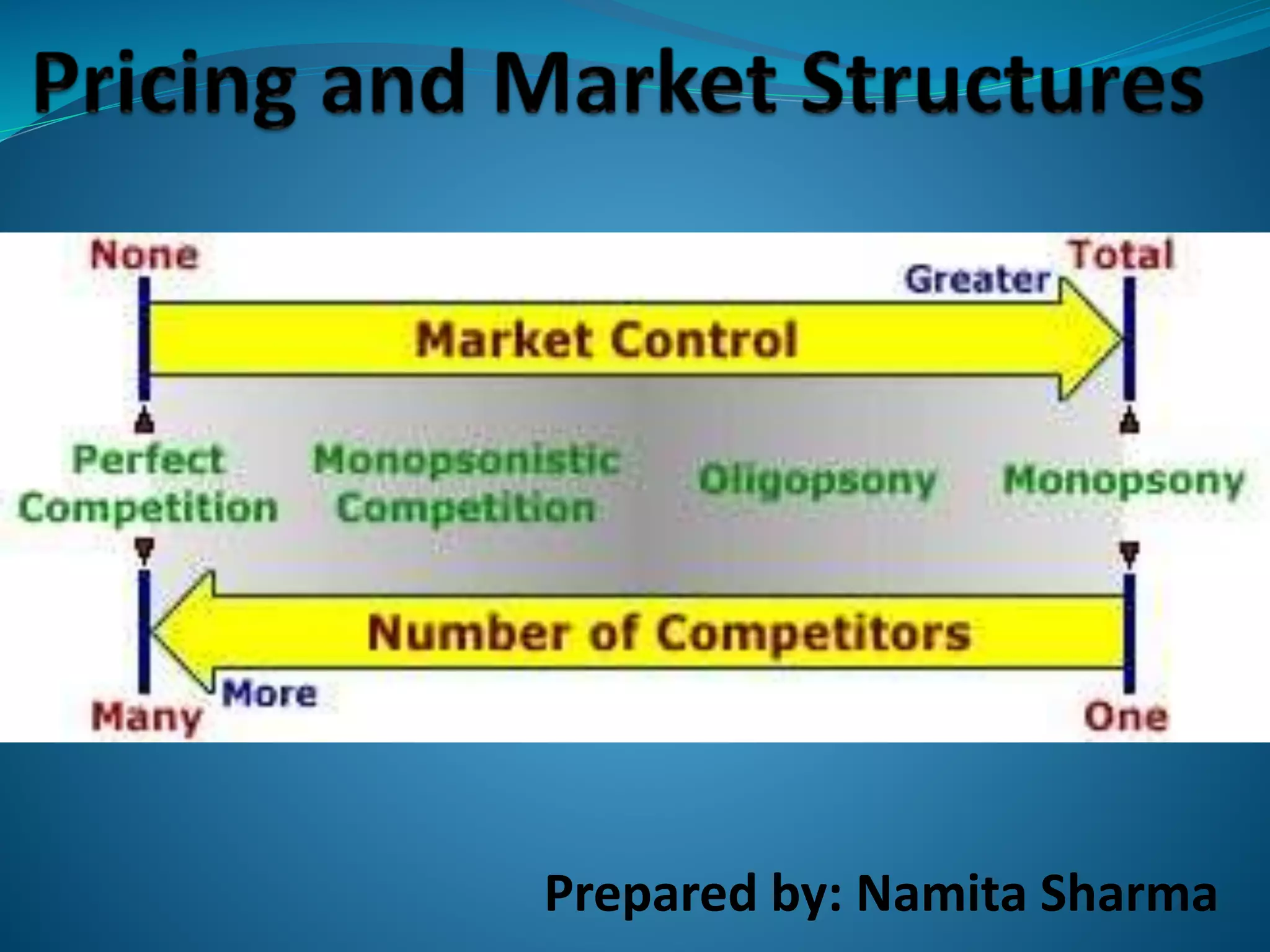
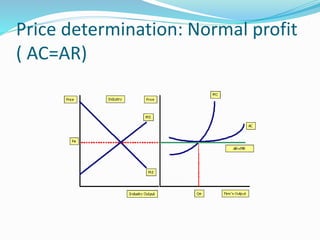
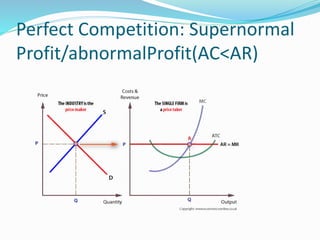
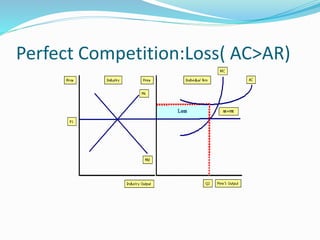
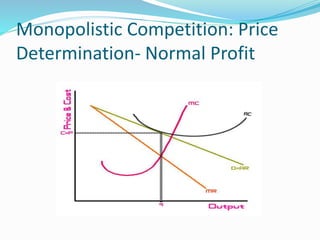
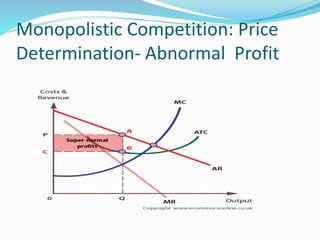
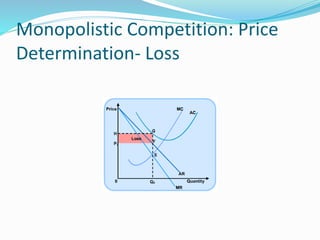
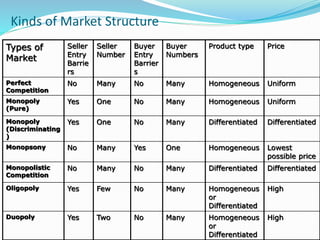
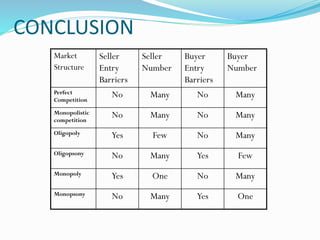
The document discusses different types of markets, including perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. Perfect competition is defined as having many small firms and sellers producing homogeneous goods, with no single firm influencing price. A monopoly exists when there is only one seller of a unique product without close substitutes. Monopolistic competition involves differentiated products and free entry/exit. Oligopoly is characterized by a small number of large firms that interact strategically and can engage in price wars or collusion.