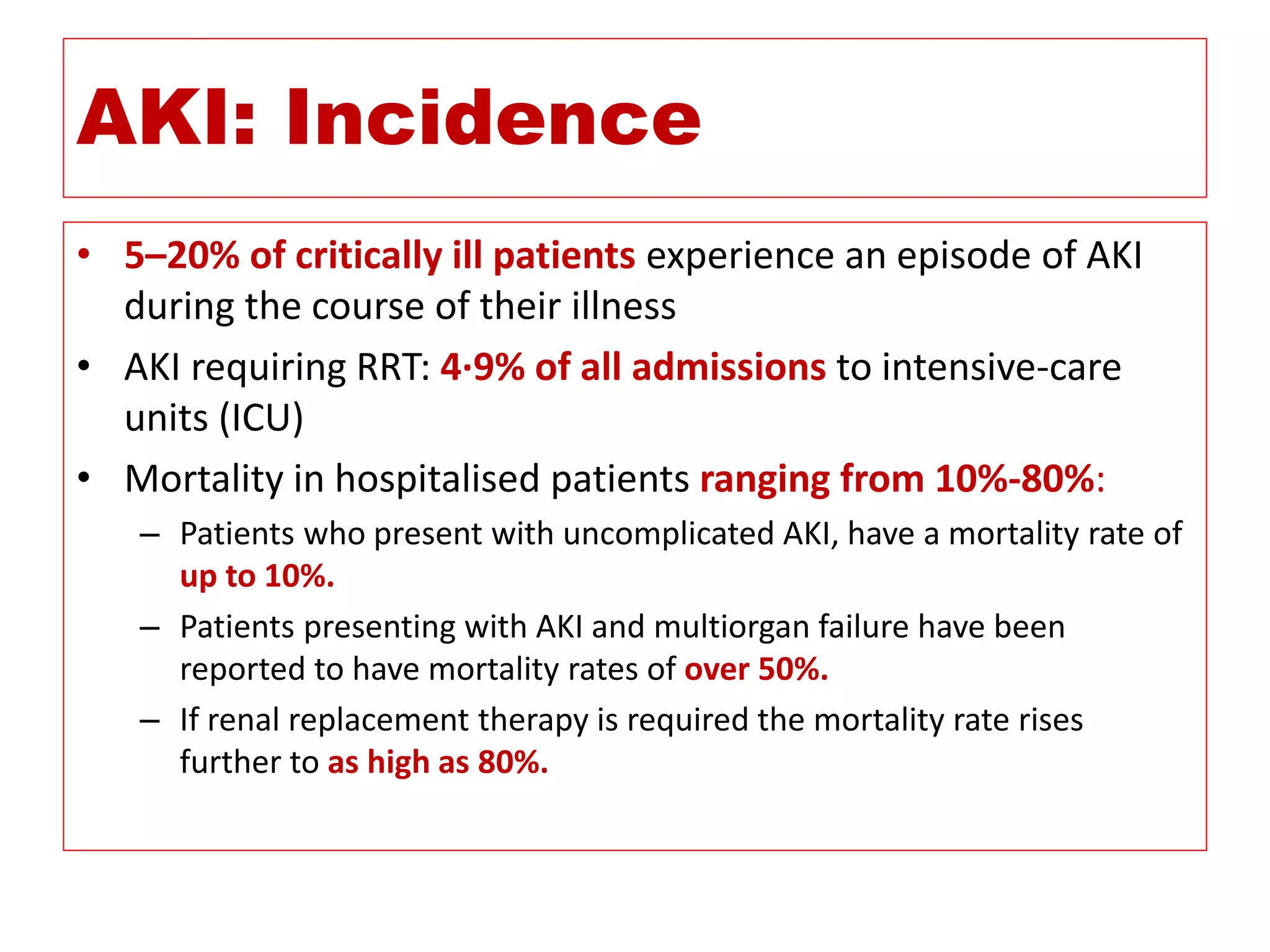
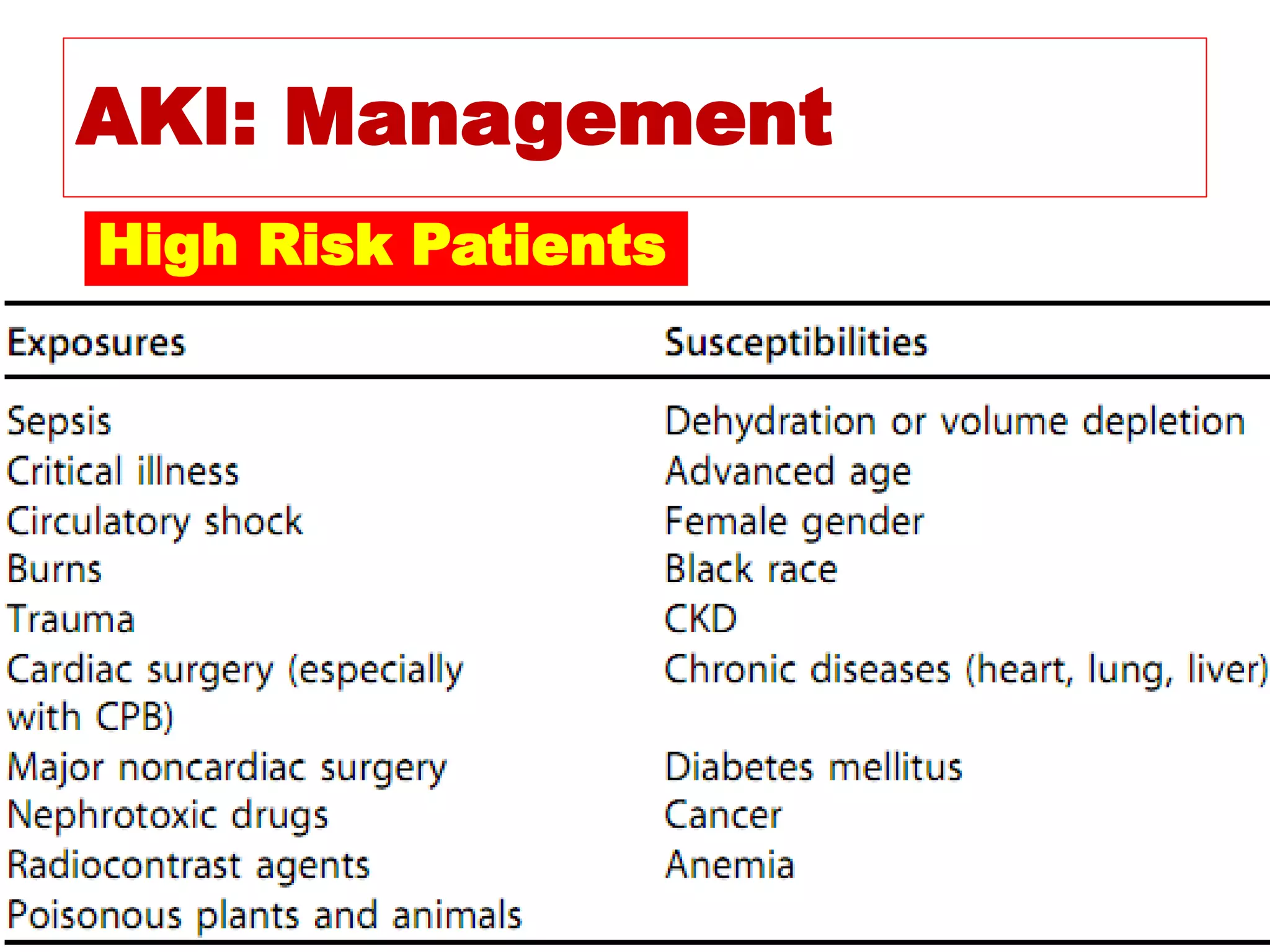
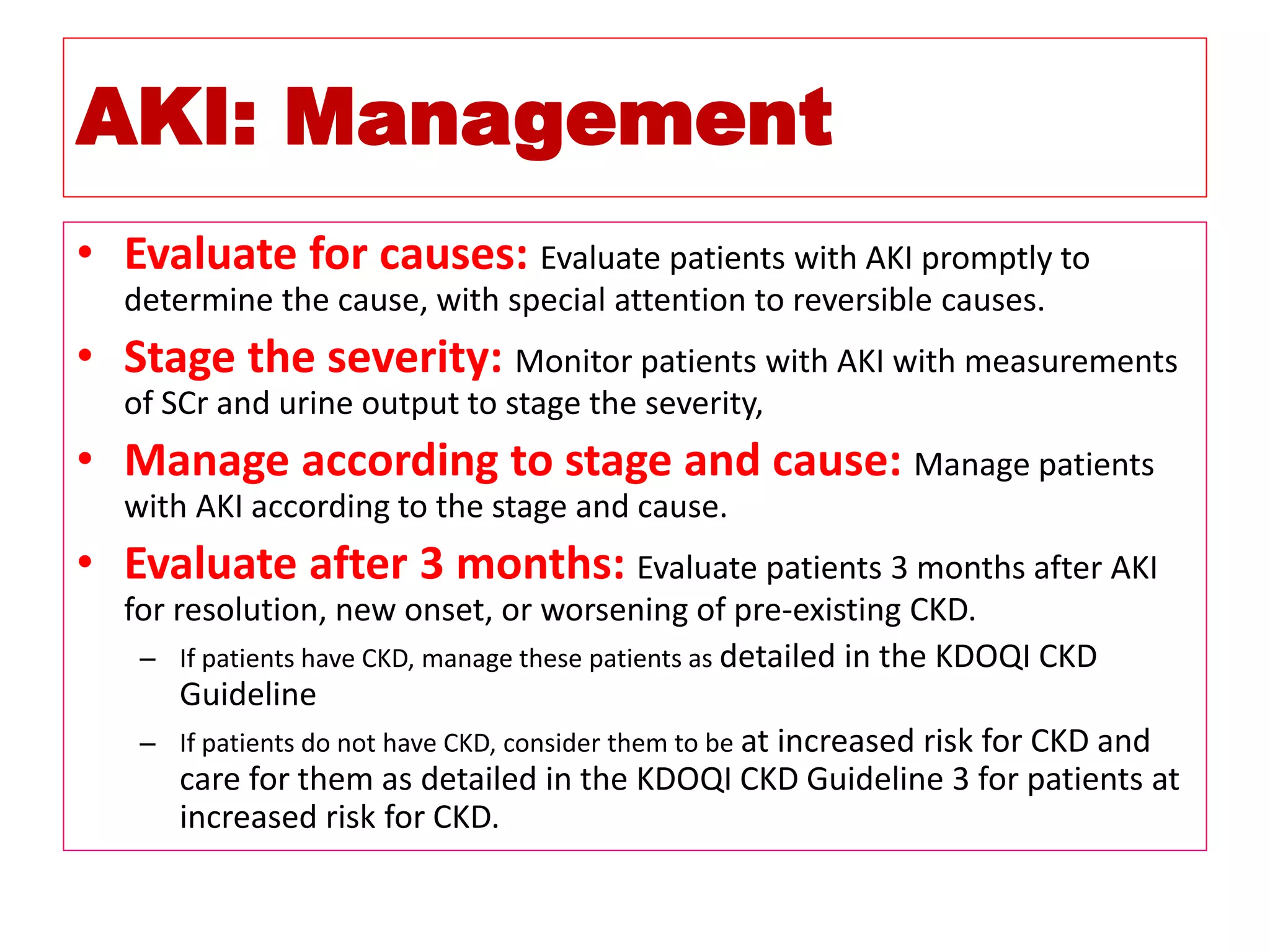
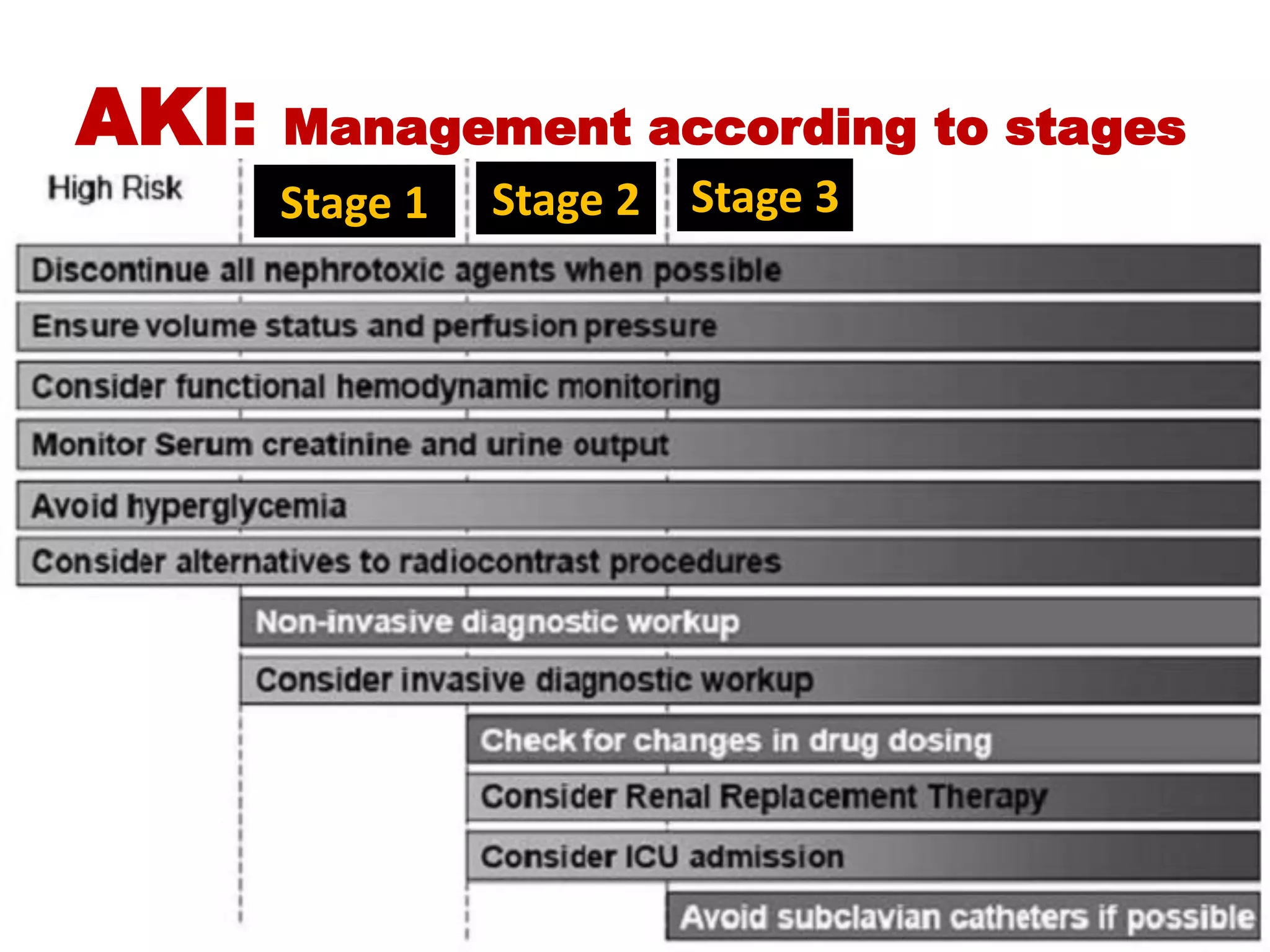
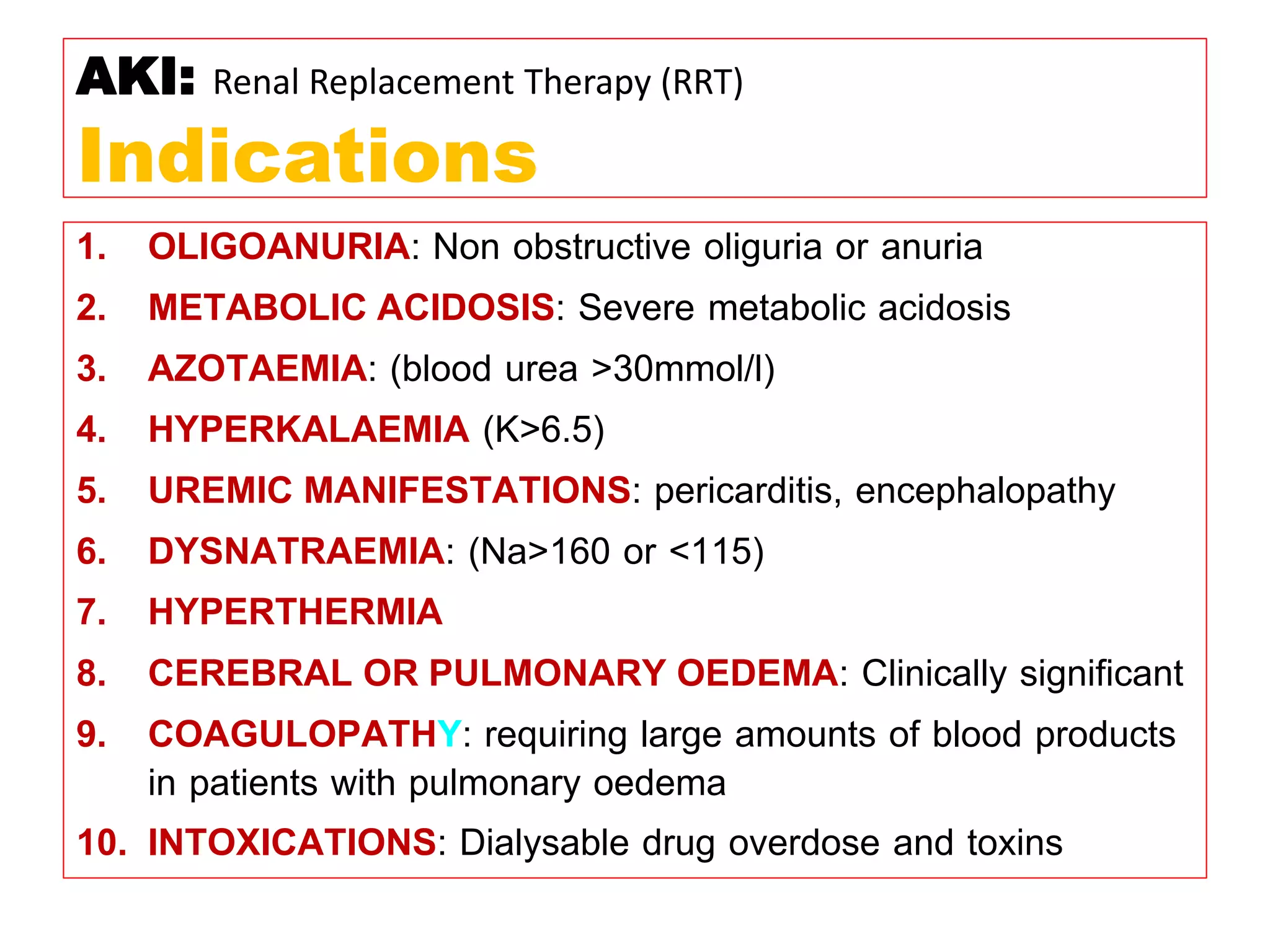
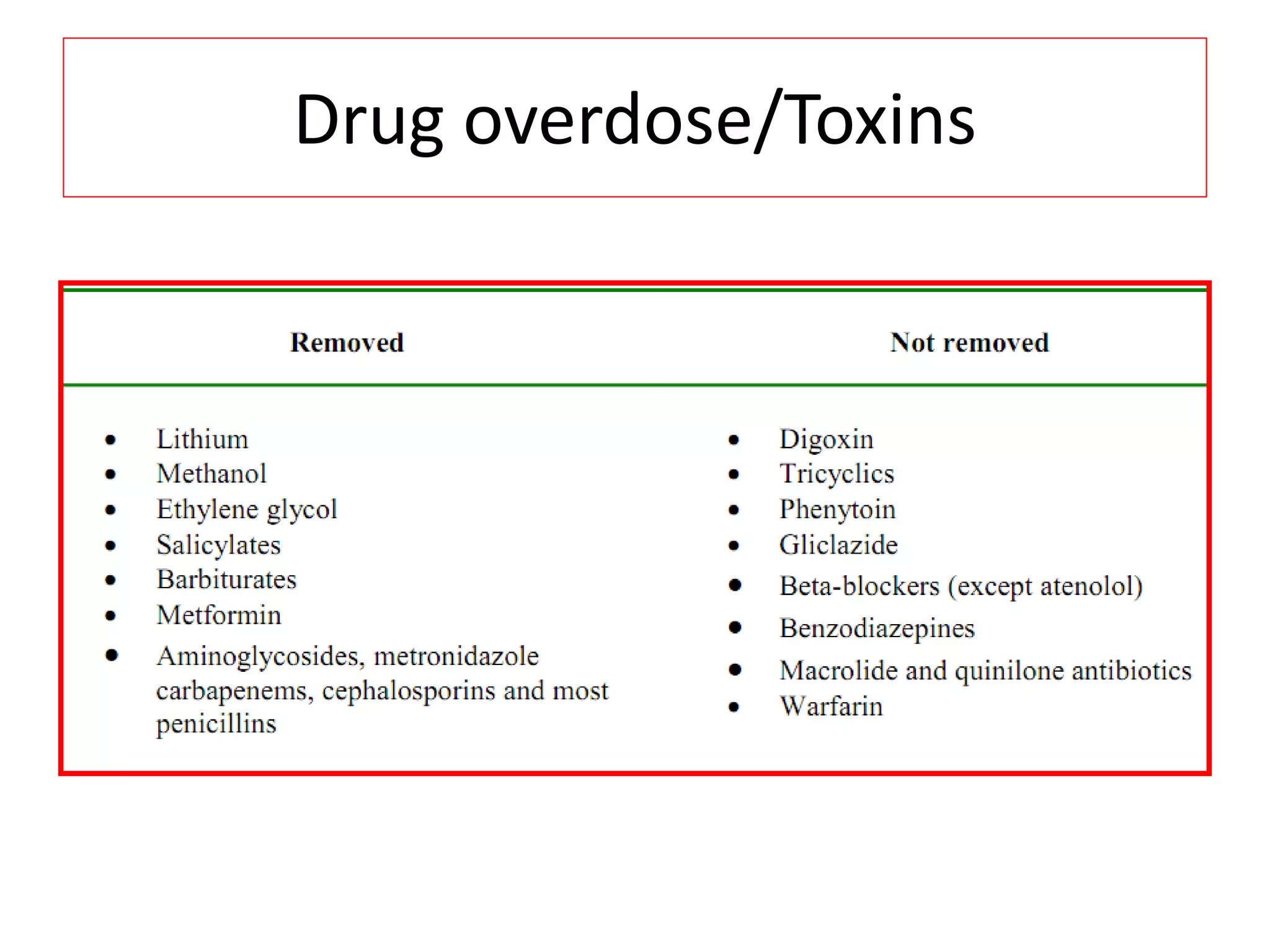
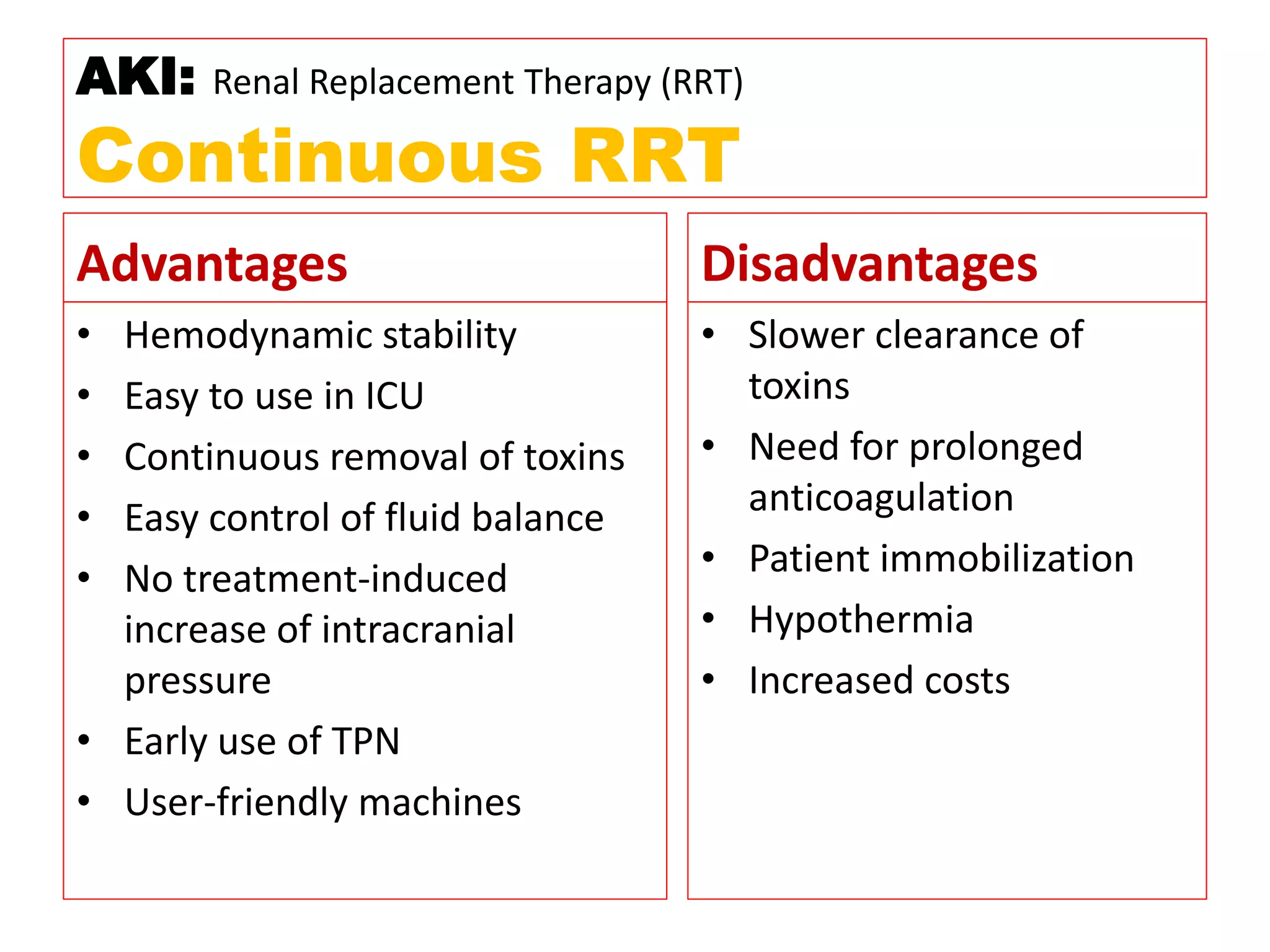
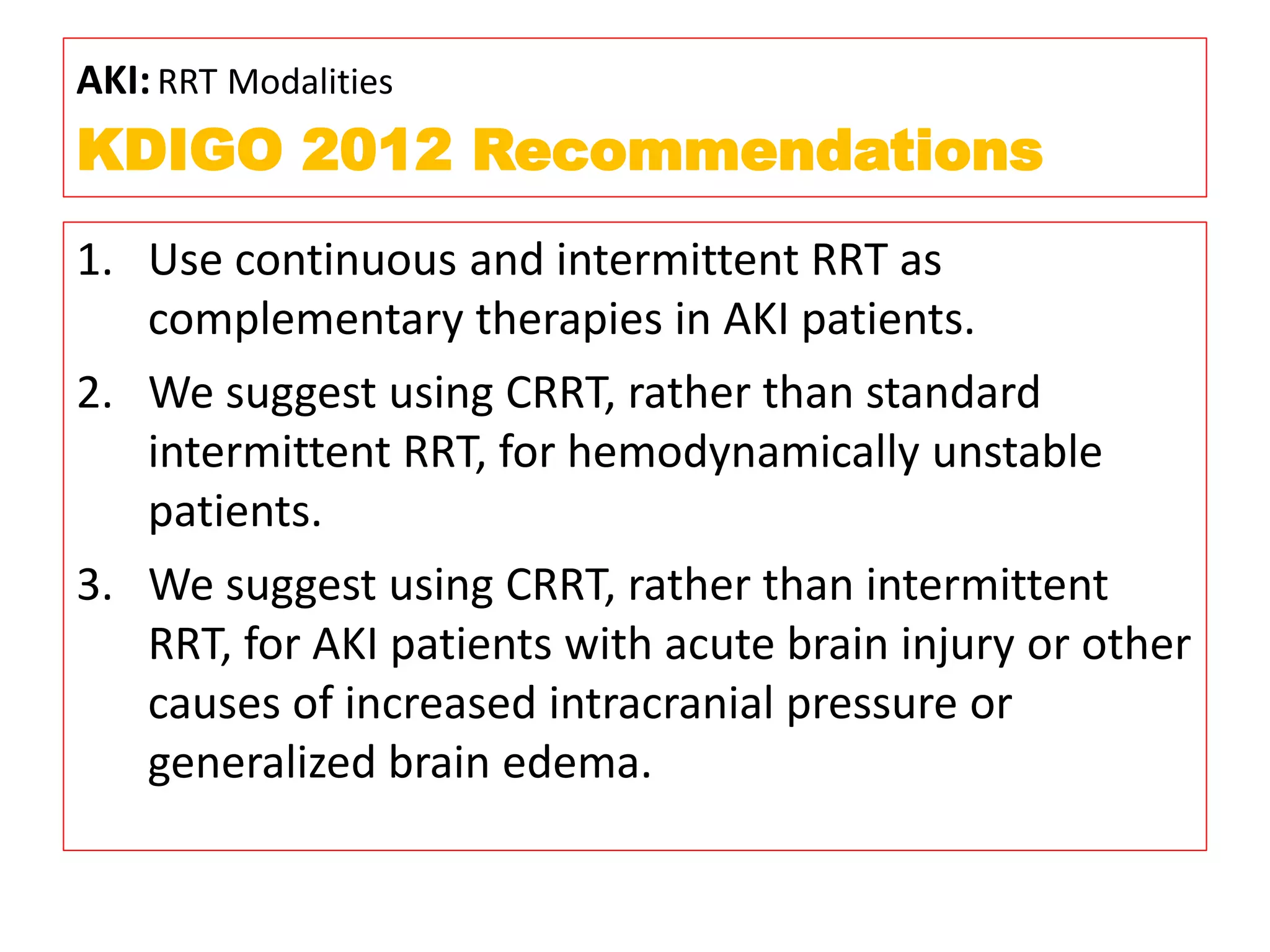
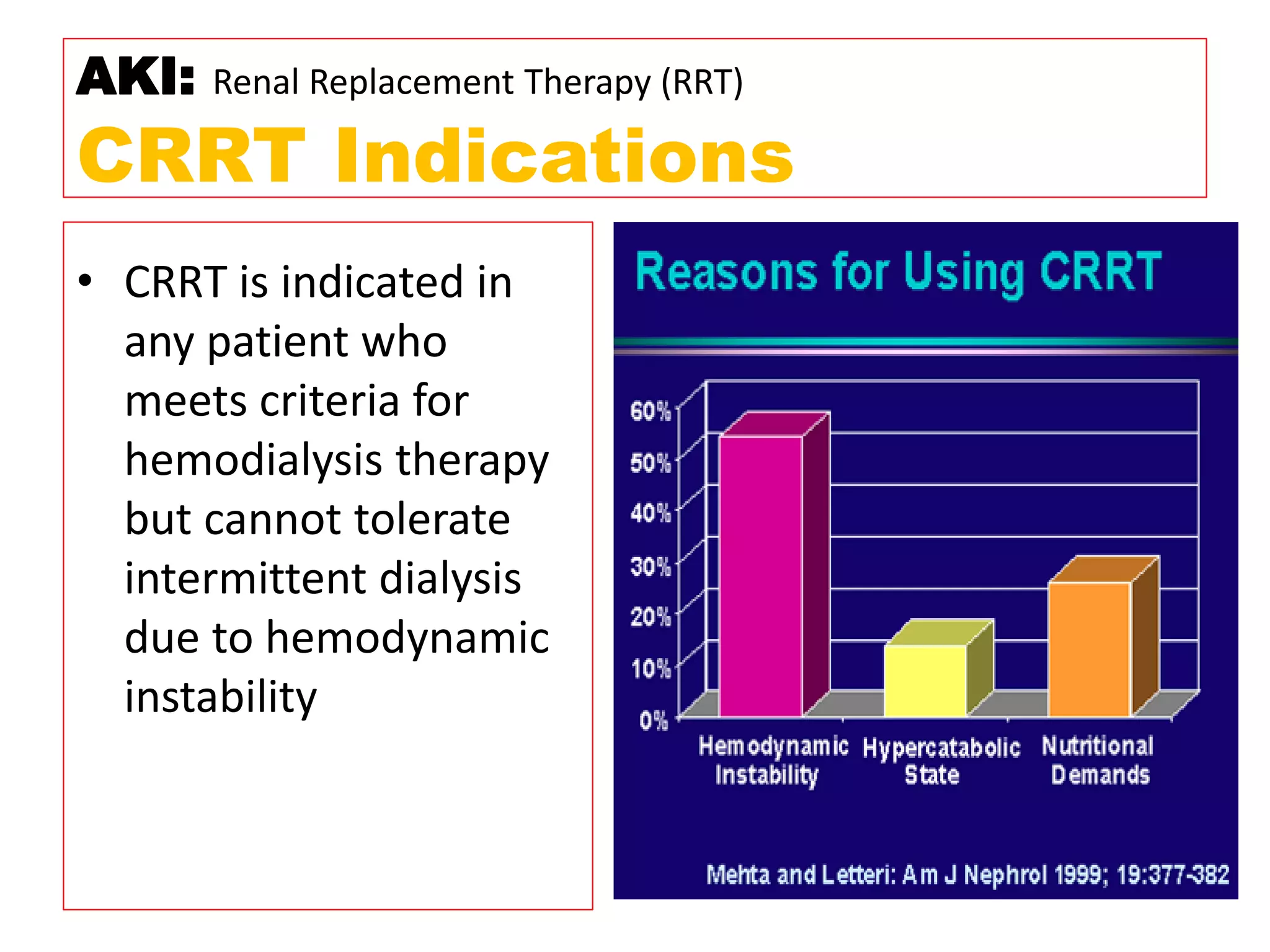
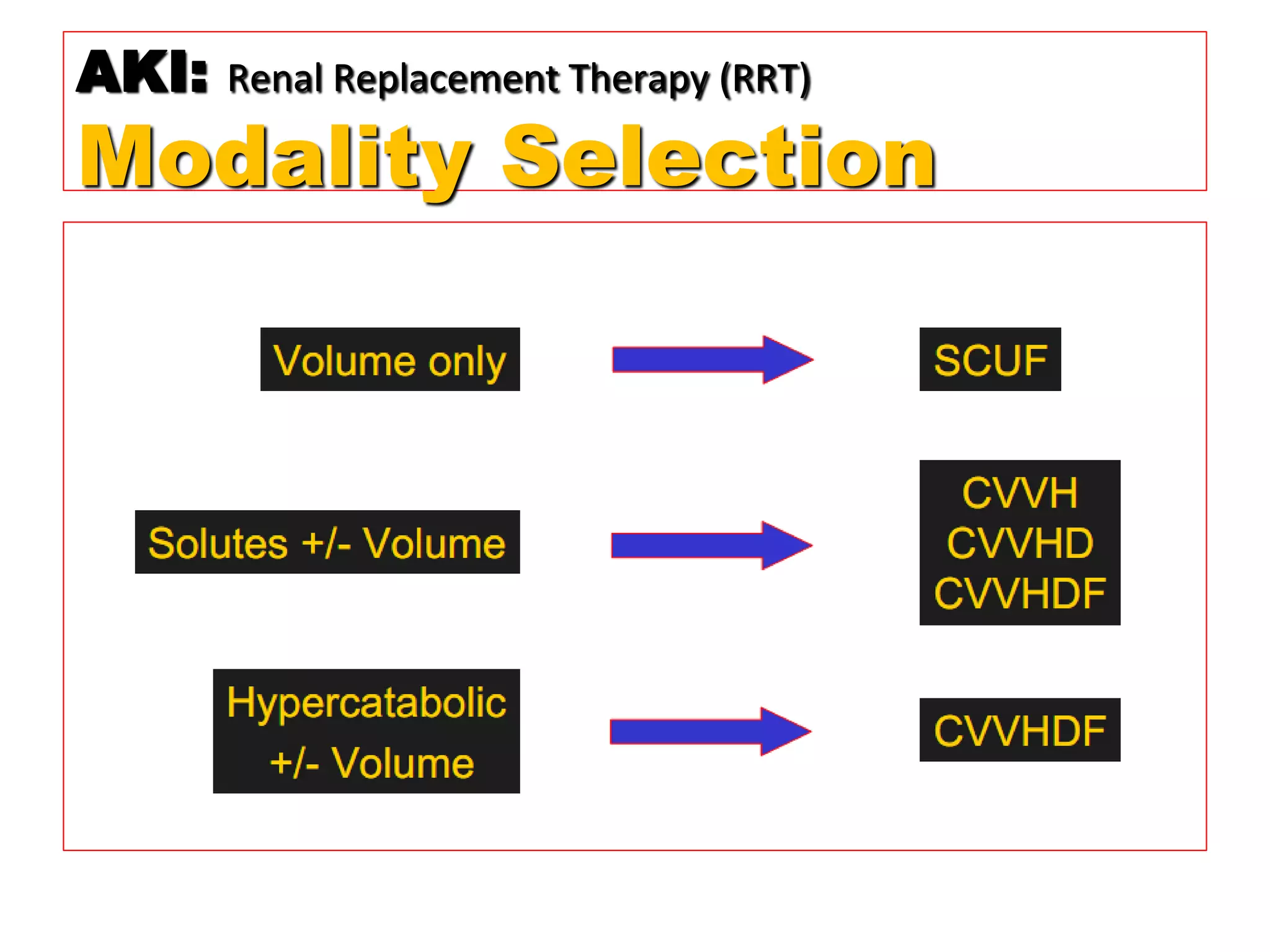
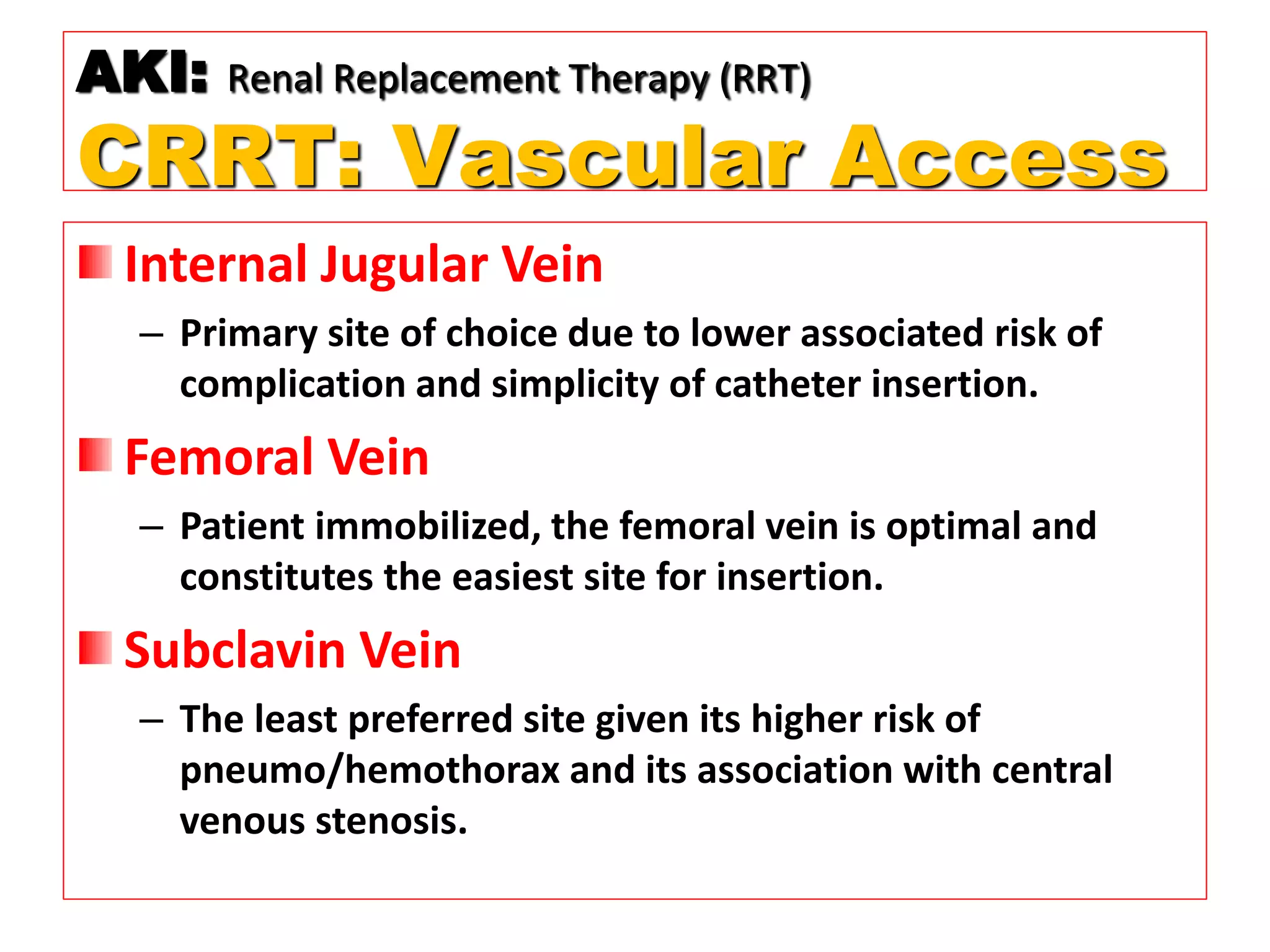
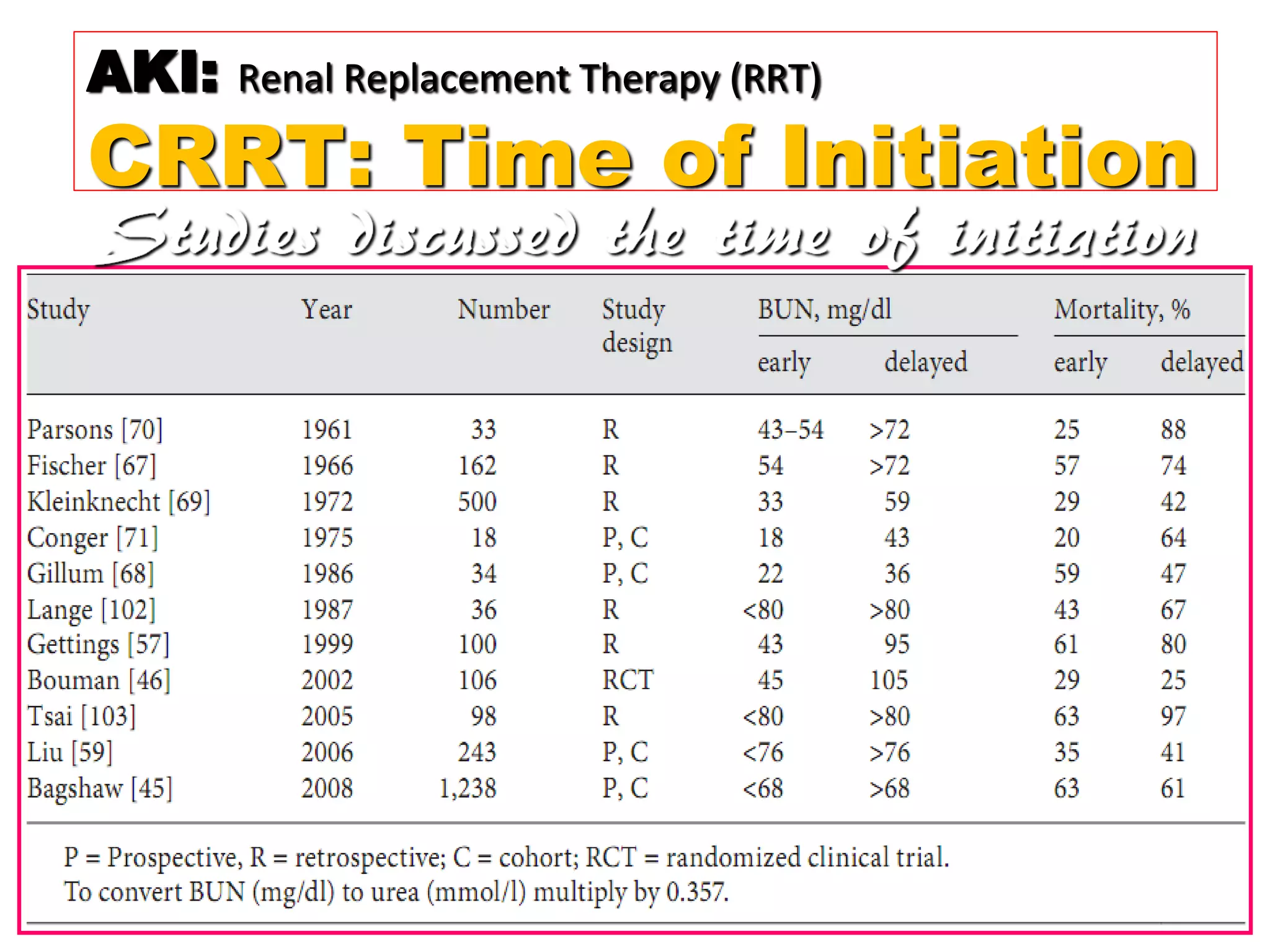
* Pt weight: 60 kg
* Required dose: 35 ml/kg/hr
* Pt weight in kg: 60 kg
* Dose per kg: 35 ml/kg/hr
* Dose for pt: 60 kg x 35 ml/kg/hr = 2100 ml/hr
* Fluid removal: 100 ml/hr
* So required dialysate flow: 2100 - 100 = 2000 ml/hr
Therefore, the required dialysate flow is 2000 ml/hr.