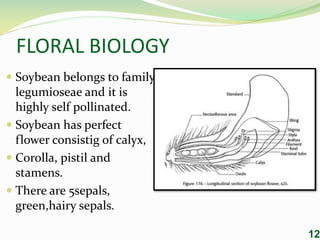
Soybean is an important legume crop originating from China. It is grown in over 35 countries with the largest producers being the United States, Brazil, China, and Argentina. Soybean seeds are high in protein (40%) and oil (20%) and are used to produce meal, flour, and oil for food and industrial applications. Soybean is a diploid species with 40 chromosomes and is highly self-pollinated. Techniques for selfing and crossing soybean plants are described. The document provides information on the taxonomy, uses, cytology, floral biology, and research of soybean.