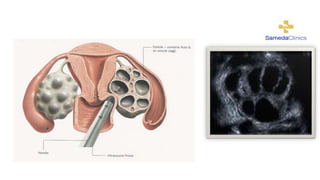
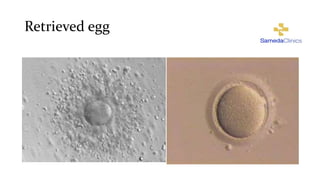
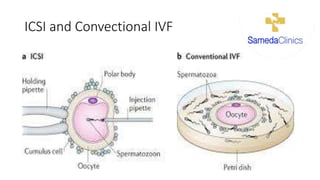
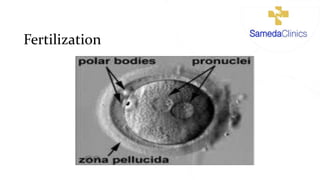
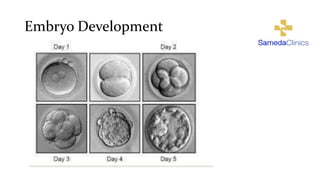
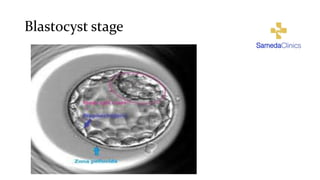
In Vitro fertilization (IVF) involves monitoring and stimulating a woman's ovaries, removing eggs and fertilizing them with sperm in a lab dish. IVF is indicated for blocked or damaged fallopian tubes, sperm abnormalities, advanced maternal age, unsuccessful intrauterine insemination, endometriosis, uterine problems, or unexplained infertility. Eggs are retrieved 34-36 hours after an HCG injection under anesthesia. Sperm is then injected into eggs or mixed with eggs, and embryos are selected for transfer into the uterus 2-5 days later. Side effects may include soreness, nausea, mood swings and fatigue. Success rates are 25-30% but vary depending on maternal age, sperm and