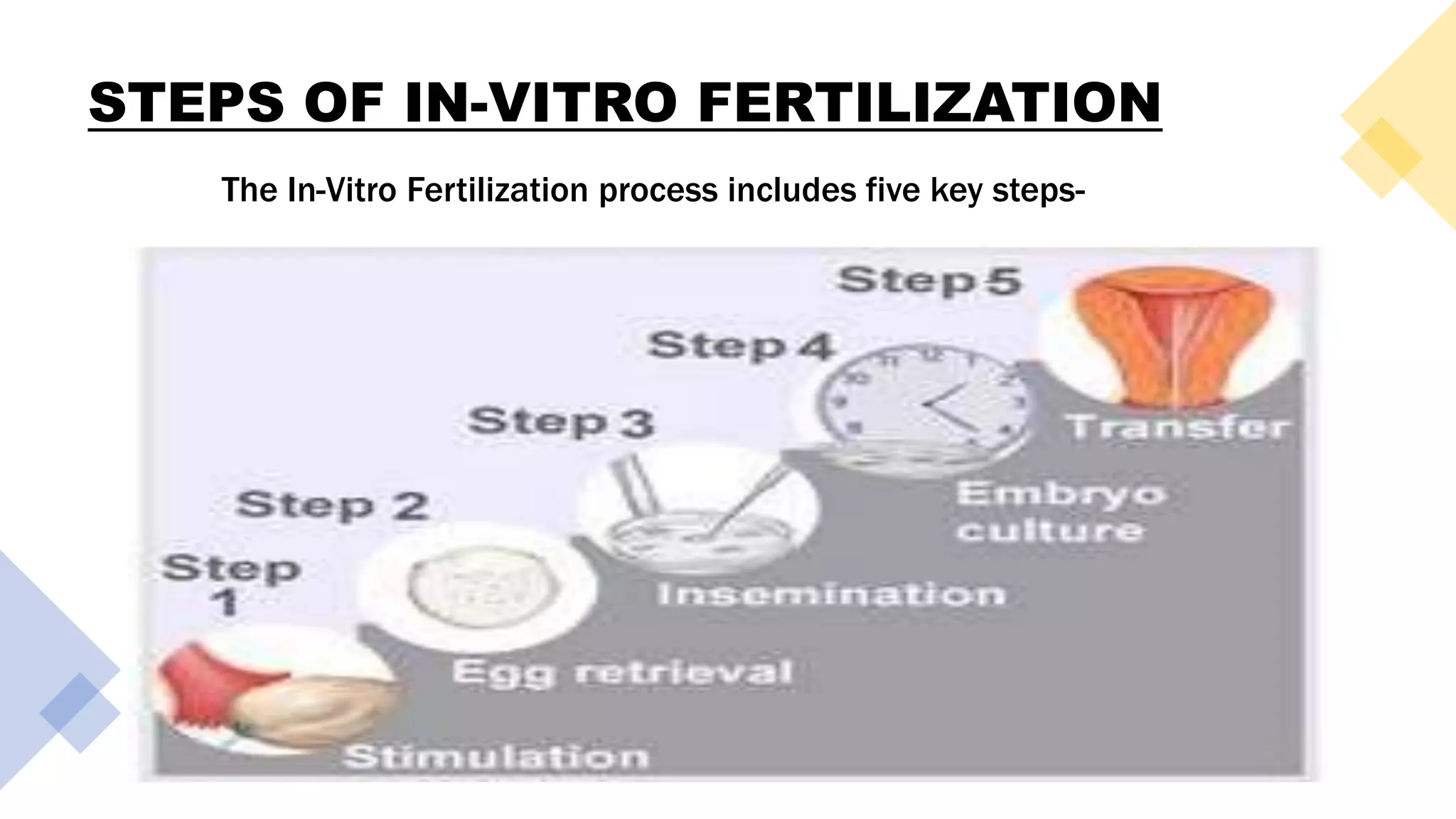
The document provides an overview of in-vitro fertilization (IVF) and embryo transfer, explaining key terms, causes of infertility treatable by IVF, and the steps involved in the IVF process. IVF is described as a form of assisted reproductive technology aimed at enabling couples facing certain infertility challenges to conceive, with its first successful case occurring in 1987. It outlines factors affecting IVF success, along with advantages and disadvantages of the procedure.