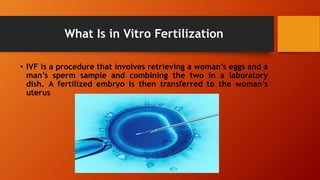
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment that involves retrieving eggs and sperm to create an embryo outside the body before transferring it to a woman's uterus. The history of IVF dates back over 50 years, leading to ethical controversies and varying legal statuses worldwide. The success of IVF is influenced by factors such as the patient's age, with higher rates of live births for those under 35.