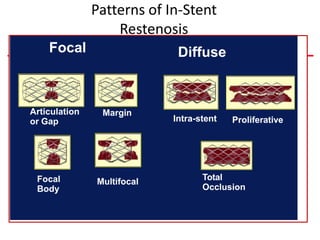
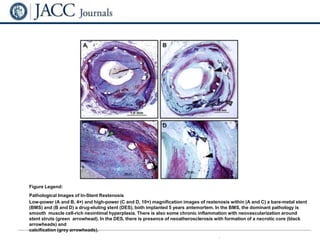
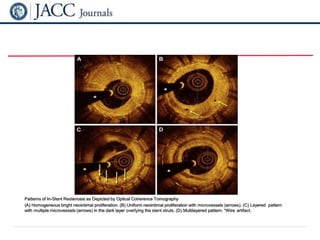
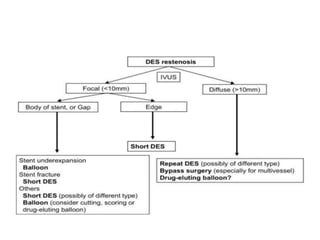
This document discusses in-stent restenosis (ISR), including definitions, incidence rates, pathogenic mechanisms, risk factors, classification, treatment options, and outcomes. Some key points:
- ISR is defined as a renarrowing of the artery after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with or without stent implantation. It can be angiographic or clinical.
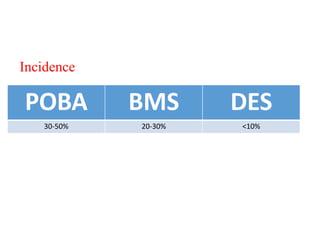
- Incidence is higher with balloon angioplasty (30-50%) compared to bare-metal stents (20-30%) and drug-eluting stents (<10%).
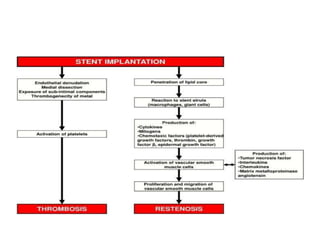
- Pathogenic mechanisms include early elastic recoil, vascular remodeling, and neointimal hyperplasia.
- Risk factors include diabetes,
























![ Thrombocyte Activity Evaluation and Effects of Ultrasound Guidance in Long
IntracoronaryStent Placement (TULIP) STUDYAND The Angiography Versus
Intravascular Ultrasound- Directed (AVID) STUDY.
Showed that there was definite benefit in lowering binary restenosis and TLR at
rate at angiographic follow-up in IVUS guided arm . [lower binary restenosis rate at 6-
months angiographic follow-up (23% vs. 46%, p=0.0082) and a subsequent
decrease in TLR (4% vs. 14%, p=0.037)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/instentrestenosissayee-201012024105/85/Instent-restenosis-31-320.jpg)