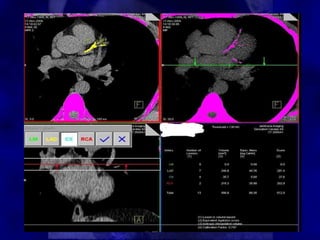
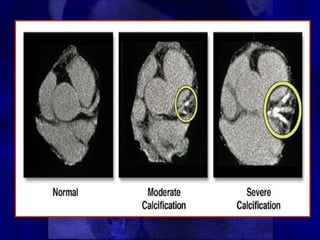
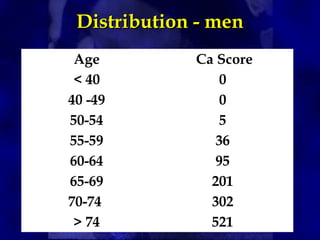
CT calcium scoring can detect asymptomatic coronary artery disease by identifying coronary artery calcification. Calcium starts accumulating early in atherosclerosis and increases as the disease progresses. While a calcium score of zero does not rule out disease, it is associated with a very low risk of cardiac events. Higher calcium scores correlate with increased risk. CT calcium scoring provides individualized risk assessment and can guide aggressive risk factor modification in high-risk patients.







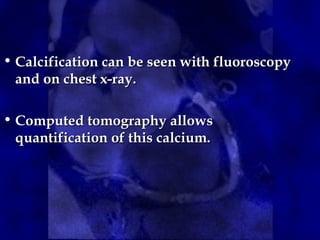





![• The method is based on the maximum x-ray
attenuation coefficient, or CT number
(measured in Hounsfield units [HU]), and
the area of calcium deposits.
• First, calcified lesions are identified on CT
images by applying a threshold of 130 HU
to the entire image set; tissues with
densities equal to or greater than the
threshold are considered to correspond to
calcium.
Agatston ScoreAgatston Score](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ctcalciumscoring1-190130102035/85/Ct-calcium-scoring-1-14-320.jpg)