Embed presentation
Download as PDF, PPTX


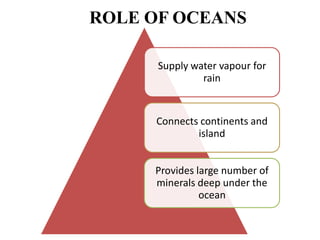
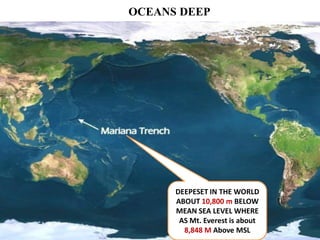

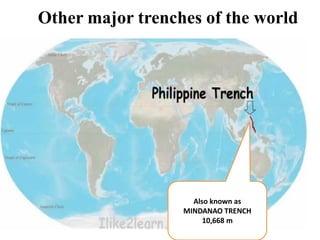
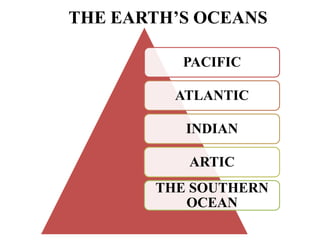
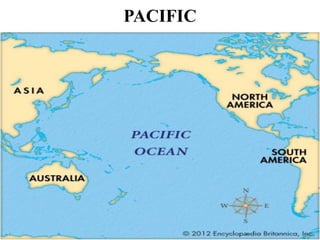


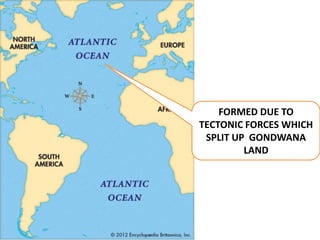

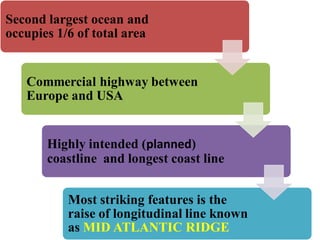
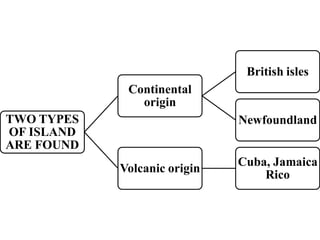
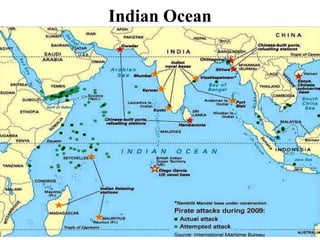
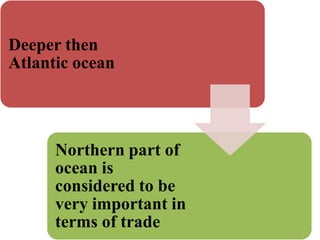
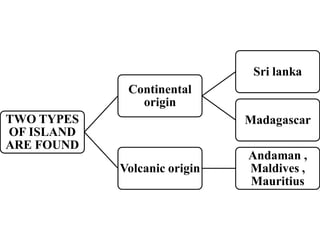
Oceanography is the study of oceans and formally began with a British expedition in 1873-1876. The oceans play an important role by supplying water vapor for rain, connecting continents and islands, and providing minerals from the ocean floor. The deepest part of the ocean is the Mariana Trench, which is about 10,800 meters below sea level, deeper than Mount Everest is tall. The Earth's major oceans are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Arctic, and Southern oceans. The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest ocean, occupying one third of the total ocean area.

















