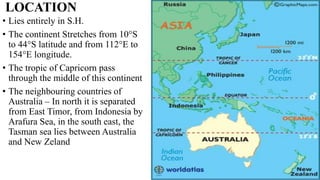
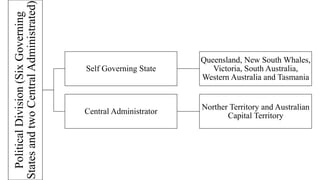
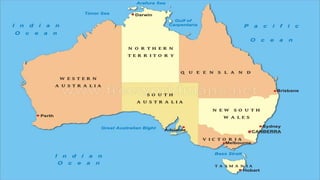
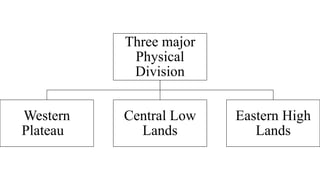
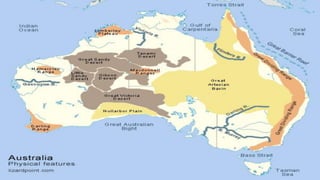
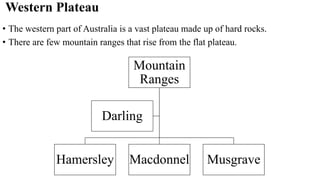
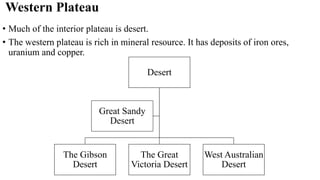
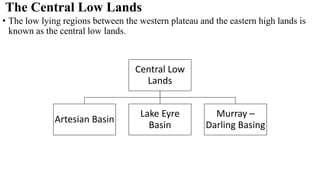
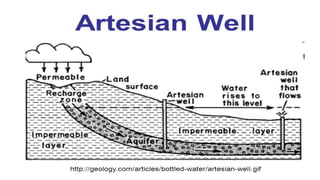
Australia is an island continent located in the Southern Hemisphere between 10°S and 44°S latitude and 112°E and 154°E longitude. It was first sighted by Dutch navigator William Janszoon in 1606 and claimed for Britain by Captain James Cook in 1770, who named it New South Wales. The six colonies federated in 1901 to form the Commonwealth of Australia. Physically, Australia is mostly flat lowlands with the highest point only 300 meters. It can be divided into the Western Plateau of hard rocks and deserts rich in minerals, the Central Low Lands containing the Great Artesian Basin, and the Eastern High Lands.