Gingival Connective Tissue Structure and Cells
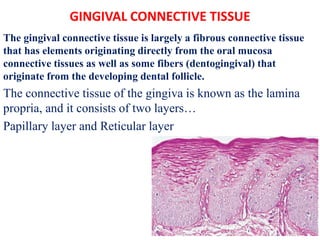
- 1. GINGIVAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE The gingival connective tissue is largely a fibrous connective tissue that has elements originating directly from the oral mucosa connective tissues as well as some fibers (dentogingival) that originate from the developing dental follicle. The connective tissue of the gingiva is known as the lamina propria, and it consists of two layers… Papillary layer and Reticular layer
- 2. Connective tissue contains- Collagen fibers (about 60% by Volume) Schluger et al. 1977 Fibroblasts (5%) Matrix (about 35%) Vessels and nerves
- 3. The different types of cell present in the connective tissue are: Fibroblasts Mast cells Macrophages Inflammatory cells
- 4. Fibroblast Gingival connective tissue fibroblasts originate from perifollicular mesenchyme, a derivative of the stomodeal mesoderm. The fibroblast is a spindle‐shaped or stellate cell with an oval‐shaped nucleus containing one or more nucleoli.
- 5. • The cytoplasm contains a well‐developed granular endoplasmic reticulum with ribosomes. The Golgi complex is usually of considerable size and the mitochondria are large and numerous.
- 6. • Fibroblasts are the predominant cells of connective tissue • They are responsible for the formation and maintenance of the fibrous components and the ground substance of connective tissue. • The resting fibroblast is an elongated cell with little cytoplasm and a dark-staining, flattened nucleus containing condensed chromatin • Active fibroblasts have an oval shaped,pale-staining nucleus and a greater amount of cytoplasm
- 8. • The degree of synthetic and secretory capacity of fibroblasts is evidenced by the amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum, secretory granules, and mitochondria, and the extent of the Golgi complex in their cytoplasm. • Fibroblasts exhibit motility and contractility, which are important during connective tissue formation and remodeling and during wound repair
- 9. Mast cell • Mast cells are important in the primary response to injury because they are located in tissues. • The cytoplasm is characterized by the presence of a large number of vesicles of varying size. These vesicles contain biologically active substances such as proteolytic enzymes, histamine, and heparin. Mast cells express on their surface the receptor (FcεRI) that binds the Fc portion of IgE antibody.
- 10. TNF release from mast cells has been found to be crucial for neutrophil recruitment and pathogen clearance. On activation from stimuli including allergen binding, infection, and trauma, mast cells produce histamine, cytokines, eicosanoids, proteases,and chemokines, which leads to vasodilatation, capillary leakage, and immunocyte recruitment. Mast cells are thought to be important cosignaling effector cells of the immune system via the release of IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-6, IL-10, IL-13, and IL-14, as well as macrophage migration–inhibiting factor. ----Bachelet I, Levi-Schaffer F, 2007
- 11. Macrophage Macrophages are tissue cells derived from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow and from progenitors in the embryonic yolk sac and fetal liver during early development. Circulating cells of this lineage are known as monocytes.
- 12. • There are two major pathways of macrophage activation, called classical and alternative pathway • Classical one, designed to destroy the offending agents, and this is followed by alternative activation, which initiates tissue repair by angiogenesis, activate fibroblasts, and stimulate collagen synthesis.
- 13. Function of Macrophages are:- Ingest and eliminate microbes and dead tissues. Initiate the process of tissue repair and are involved in scar formation and fibrosis. Macrophages display antigens to T lymphocytes and respond to signals from T cells, thus setting up a feedback loop that is essential for defense against many microbes by cell-mediated immune responses.
- 14. Inflammatory cells The neutrophilic granulocytes, also called polymorphonuclear leukocytes. A. The nucleus is lobulated and numerous B. lysosomes containing lysosomal enzymes, are found in the cytoplasm. The lymphocytes Plasma cells
- 15. Collagen fibers Predominate in the gingival connective tissue and constitute the most essential components of the periodontium The synthesis and the composition of collagen fibers produced by fibroblasts The smallest unit, the collagen molecule, is often referred to as tropocollagen is approximately 3000 Å long and has a diameter of 15 Å.
- 16. • Collagen are composed of three polypeptide alpha chains coiled around each other to form the typical collagen triple-helix configuration • Each chain contains about 1000 amino acids • The amino acid glycine in every third position (Gly-X-Y repeating sequence), of hydroxyproline and hydroxylysine
- 17. Collagen synthesis Tropocollagen synthesis takes place inside the fibroblast from which the tropocollagen molecule is secreted into the extracellular space. Thus, the polymerization of tropocollagen molecules to collagen fibers takes place in the extracellular compartment Tropocollagen molecules are aggregated longitudinally to form protofibrils which are subsequently laterally aggregated parallel to collagen fibrils (CFR).
- 19. • In the tissue, the fibers are usually arranged in bundles. As the collagen fibers mature, covalent cross‐links are formed between the tropocollagen molecules, resulting in an age‐related reduction in collagen solubility • Cementoblasts and osteoblasts are cells which also possess the ability to produce collagen
- 21. • Collagen type I forms the bulk of the lamina propria and provides the tensile strength to the gingival tissue. (Narayanan and Page, 1983a) • Type III collagen is also a principal component of the gingival connective tissues and together with type I collagen is uniformly distributed throughout the connective tissue (Rao et al, 1979; Wang et al, 1980; Chavrier et al, 1984; Narayanan et al, 1985; Romanos et al, 1991)
- 22. • Type I:III ratio of 7:1 (Nathan et al 1979) • Type IV collagen (argyrophilic reticulum fiber) branches between the collagen type I bundles, and it is continuous with fibers of the basement membrane and the blood vessel walls.{main collagenous component of basement membrane (Chavrier et al 1981).
- 23. • Healthy human gingival connective tissue appears to be arranged in two patterns of organization at the ultrastructural level: Pattern I (PI) and Pattern II (PII) • PI is dense pattern of organization mainly constituted of large, dense bundles of thick collagen fibers • PII is a loose pattern of organization, mainly constituted of short, thin collagen fibers mixed with a fine reticular network, especially located under or around basement membrane.
- 24. • Ultrastructural immunoperoxidase labelling of types I, III, and IV collagen demonstrates that gingival connective tissue is made of an intricate pattern of type I and III collagen where type I collagen fibers are preferentially organized in large dense bundles in PI, whereas a fibrous and fibrillar type III collagen network is predominant in PII. • Type IV collagen appears to be the main collagenous component of the basement membranes. --C.chavrier et al 1984
- 25. • Pattern I is mainly composed of dense type I collagen bundles. • Pattern II is composed of both types I and III collagen but shows a predominance of type III collagen. • Gingival fibroblasts of pattern I tissue should be able to synthesize both types I and III collagen with a high type I/III ratio whereas gingival fibroblasts of pattern II could produce both type I and type III collagen with a lower type l/III collagen ratio. --(C. chavrier et al 1984)
- 26. • Ultrastructural fibrous feature of type I collagen is in agreement with the notion of stability (Peyrol & Grimaud, 1981) while the fibrillar nature of type III collagen is in agreement with the notion of remodelling ability. (C. chavrier et al 1984)
- 27. Reticulin fibers • Seen in the photomicrograph,exhibit argyrophilic staining properties and are numerous in the tissue adjacent to the basement membrane. Composed of type III collagen, secreted by reticular cells. • Reticulin fibers are present at the epithelium– connective tissue and the endothelium– connective tissue interfaces
- 28. Oxytalan fibers • Fullmer & Lillie (1958) named the fibers oxytalan in recognition of their resistance to solubility in acid, which contrasts with collagen. • Scarce in the gingiva but numerous in the periodontal ligament • Composed of long thin fibrils with a diameter of approximately 150 Å(Carmichael &Fullmer 1966, Sheetz et al. 1973).
- 29. These connective tissue fibers can be demonstrated under light microscopy only after previous oxidation with peracetic acid
- 30. Elastin fibers • Elastin is a minor constituent of gingival connective tissue, accounting for approximately 6% of the total tissue protein (Chavrier, 1990). • Cell surface receptors for elastin have been identified and may be associated with cell chemotaxis (Senior et al, 1980). • Elastin is present in relatively small amounts in the fixed, inflexible attached gingiva but it is more prominent in the submucosal tissues of the more movable and flexible alveolar mucosa (Bartold. 1991).
- 31. Ground substance • It is composed of proteoglycans (mainly hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate) and glycoproteins (mainly fibronectin) • By definition, a proteoglycan is composed of a single protein core to which one or more glycosaniinoglycan side chains are covalently bound (Hardingham and Fosang,1992) • The proteins bound covalently to glycosaminoglycans are called “core proteins.”
- 32. • The amount of carbohydrate in a proteoglycan is usually much greater than that found in a glycoprotein and may comprise up to 95% of its weight. • There are at least seven GAGs: hyaluronic acid (hyaluronan), chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfates I and II, heparin, heparan sulfate, and dermatan sulfate. • GAGs are unbranched polysaccharides made up of repeating disaccharides, one component of which is always an amino sugar(hexosamine ) • The other component of the repeating disaccharide (except in the case of keratan sulfate) is a uronic acid,
- 33. Proteoglycans
- 34. GLYCOPROTEINS • The glycoproteins are proteins that contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently bound to amino acids • Fibronectin binds fibroblasts to the fibers and many other components of the intercellular matrix, thereby helping to mediate cell adhesion and migration. • Laminin (glycoprotein found in the basal lamina of about 850 kDa and 70 nm length) serves to attach it to epithelial cells
- 35. • Fibronectin binds to cells via a transmembrane receptor protein which belongs to the integrin class of proteins . • Integrins are heterodimers, containing various types of α and β polypeptide chains.
- 36. Gingival Fibers • These fibers consist of Type I collagen • The gingival fibers have the following functions . To brace the marginal gingiva firmly against the tooth . To provide the rigidity necessary to withstand the forces of mastication without being deflected away from the tooth surface To unite the free marginal gingiva with the cementum of the root and the adjacent attached gingiva
- 37. Circular fibers fiber bundles which run their course in the free gingiva and encircle the tooth in a cuff‐ or ring‐like fashion. Dentogingival fibers embedded in the cementum of the supra‐alveolar portion of the root and project out from the cementum in a fan‐like configuration into the free gingival tissue of the facial, lingual, and interproximal surfaces. Dentoperiosteal fibers embedded in the same portion of the cementum as the dentogingival fibers, but run their course apically over the vestibular and lingual bone crest and terminate in the tissue of the attached gingiva.
- 38. Trans‐septal fibers Extend between the supra‐alveolar cementum of approximating teeth. It run straight across the interdental septum and are embedded in the cementum of adjacent teeth.
- 39. Repair of gingival connective tissue • Because of the high turnover rate, the connective tissue of the gingiva has remarkably good healing and regenerative capacity. • It generally shows little evidence of scarring after surgical procedure.
- 40. Function of gingival connective tissue • The gingival connective tissue serves primarily to protect the root surface and alveolar bone from the external oral environment • Support and fixation of teeth within their alveolar housing and provides adequate support for the epithelial tissue • The gingival connective tissue provide the stage upon which the host response acts out its role of surveillance, interception and removal of foreign material.
- 41. Blood Supply • The gingiva receives its blood supply mainly through supraperiosteal blood vessels which are terminal branches of the sublingual artery (a.s.), the mental artery (a.m.), the buccal artery (a.b.), the facial artery (a.f.), the greater palatine artery (a.p.), the infra orbital artery (a.i.), and the posterior superior dental artery (a.ap.).
- 42. Gingiva receives its blood supply from (1) supraperiosteal blood vessels, (2) the blood vessels of the periodontal ligament, and (3) the blood vessels of the alveolar bone.
- 43. Lymphatic system • It progresses into the collecting network external to the periosteum of the alveolar process and then moves to the regional lymph nodes, particularly the submaxillary group • lymphatics just beneath the junctional epithelium extend into the periodontal ligament and accompany the blood vessels • The labial and lingual gingiva of the mandibular incisor region is drained to the submental lymph nodes
- 44. • The palatal gingiva of the maxilla is drained to the deep cervical lymph nodes
- 45. Nerves • Within the gingival connective tissues, most nerve fibers are myelinated and closely associated with the blood vessels • Gingival innervation is derived from fibers that arise from nerves in the periodontal ligament and from the labial, buccal,and palatal nerves.
- 46. INNERVATION
- 47. RECEPTORS: Meshwork Of Terminal Argyrophilic Fibres Meissner’s Corpuscles – Tactile Sensaion Krause-type End Bulbs – Temperaure (Coiled Terminals) Encapsulated Spindle Receptors Free Nerve Endings
