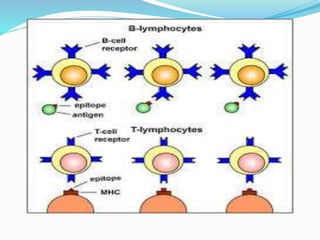
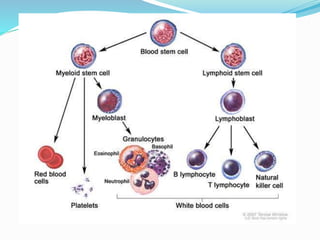
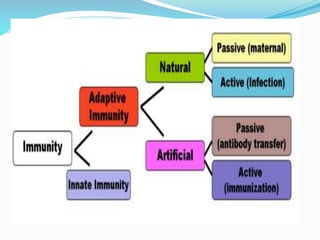
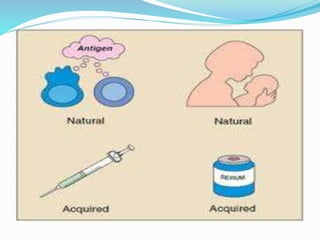
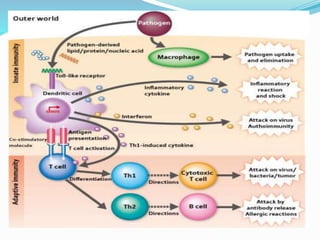
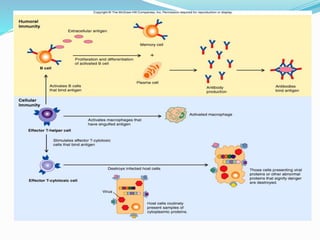
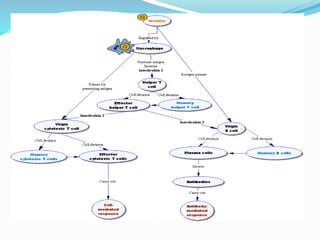
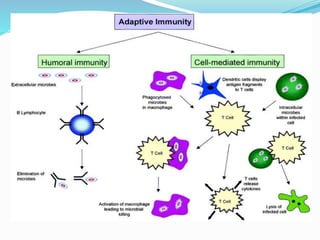
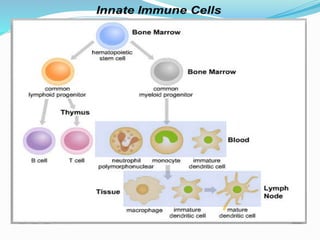
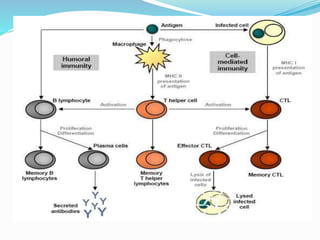
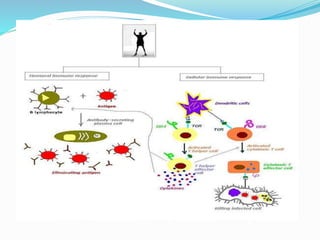
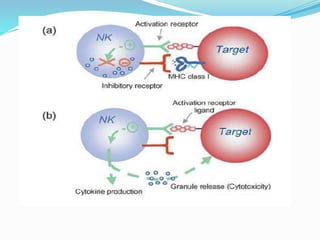
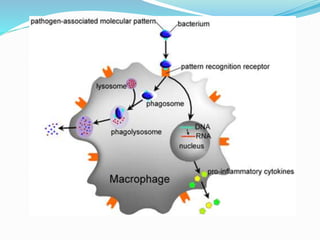
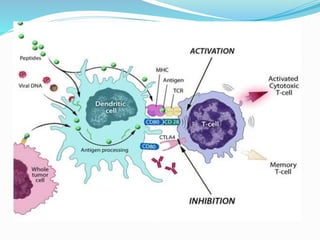
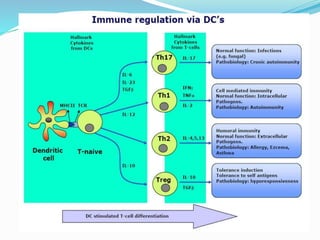
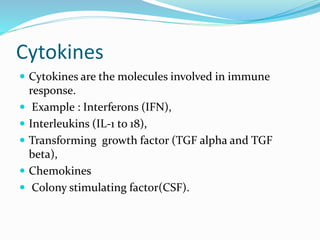
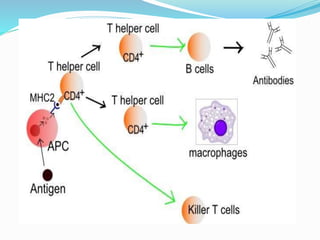
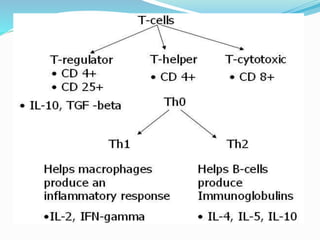
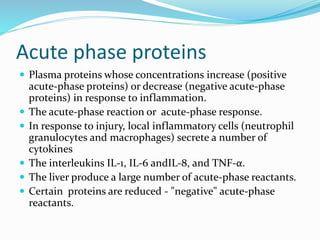
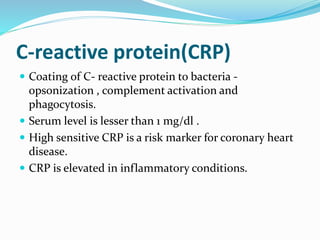
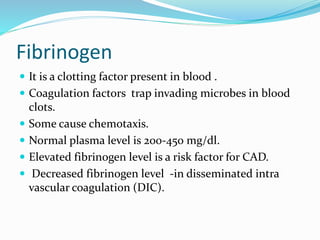
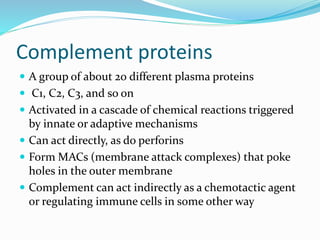
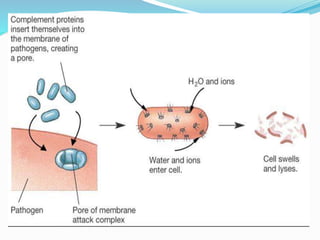
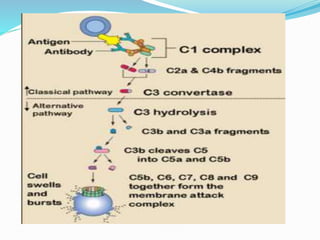
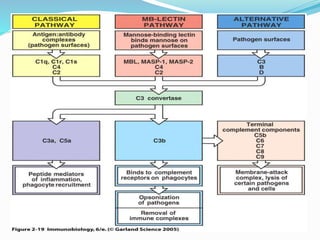
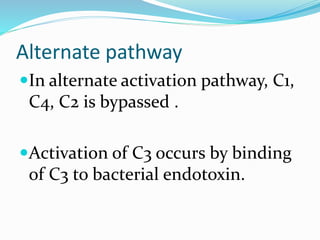
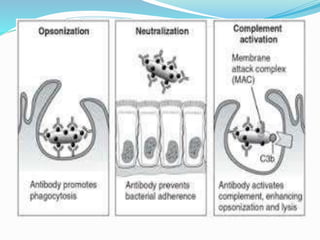
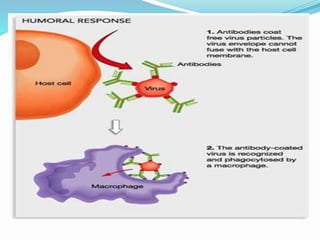
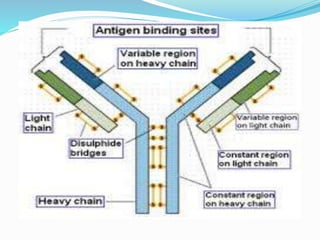
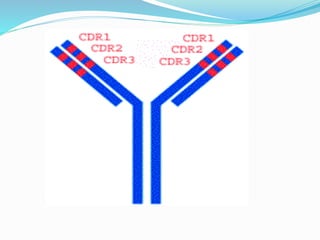
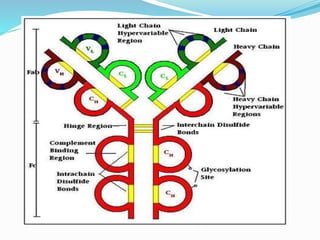
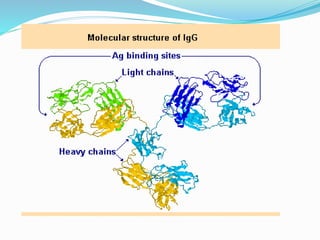
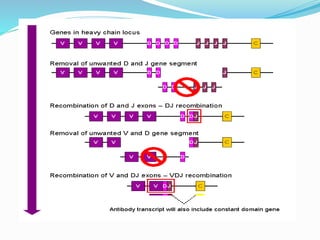
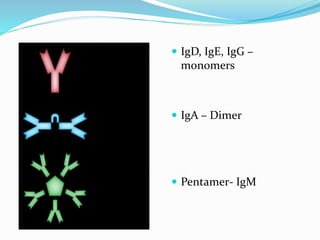
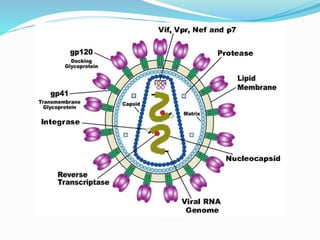
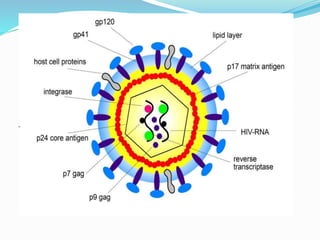
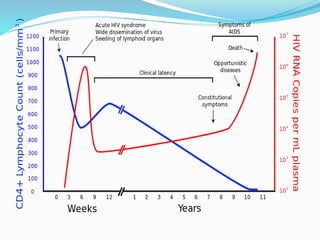
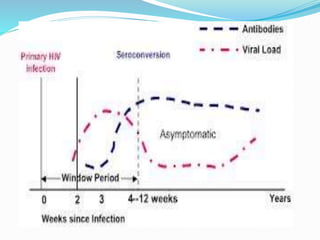
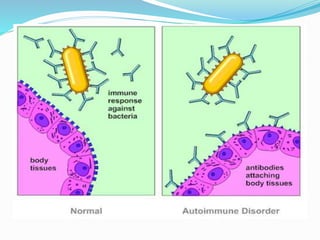
The immune system functions to eliminate non-self molecules like microbes, cancer cells, and transplanted tissues. It contains central organs like the bone marrow and thymus that produce immune cells, secondary lymphoid tissues that develop these cells, and soluble factors like cytokines. The innate immune system provides non-specific defenses like physical barriers and phagocytes. The adaptive immune system mounts specific responses through B cells and antibodies or T cells. Antibodies mediate humoral immunity against pathogens.