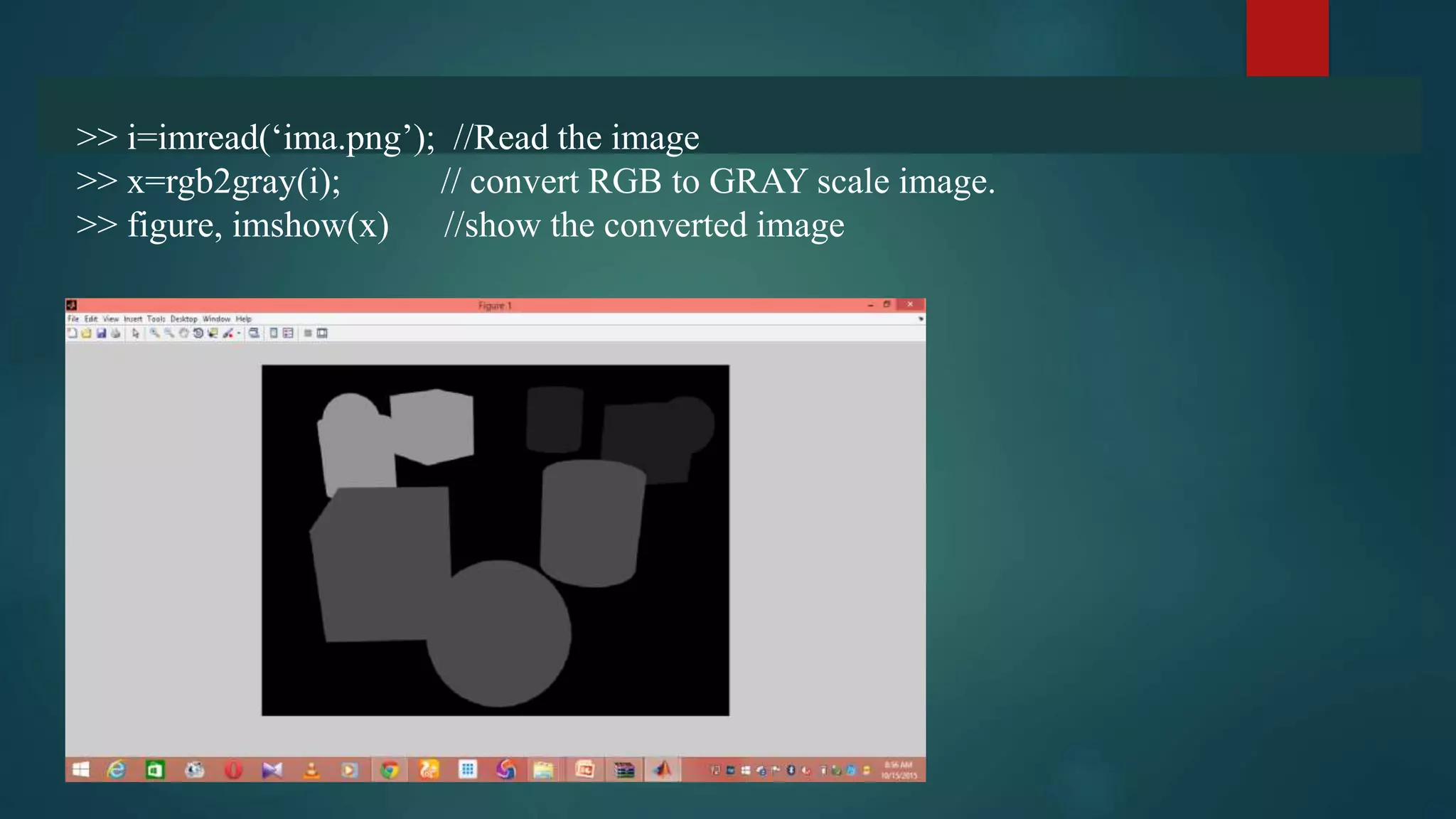
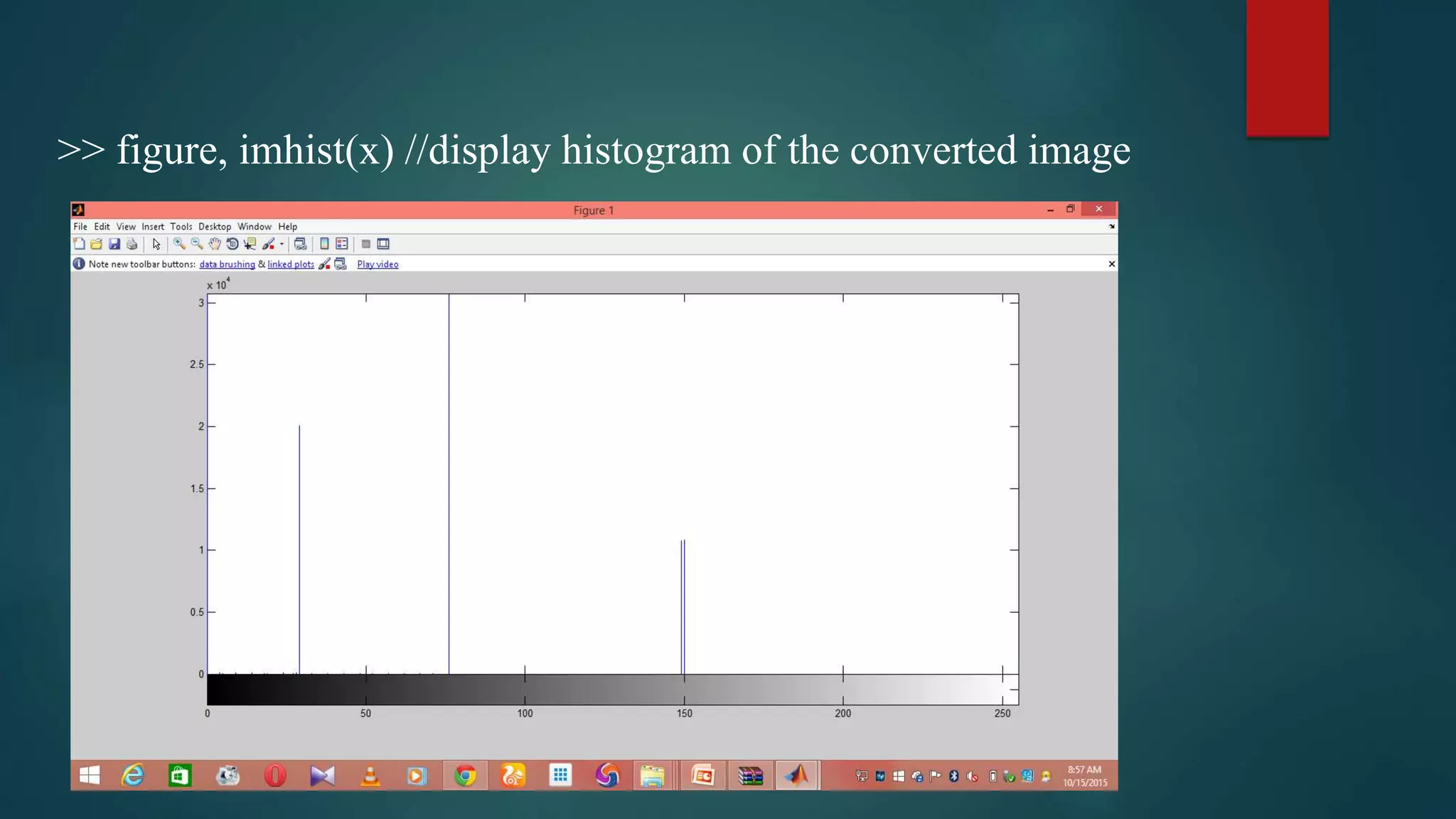
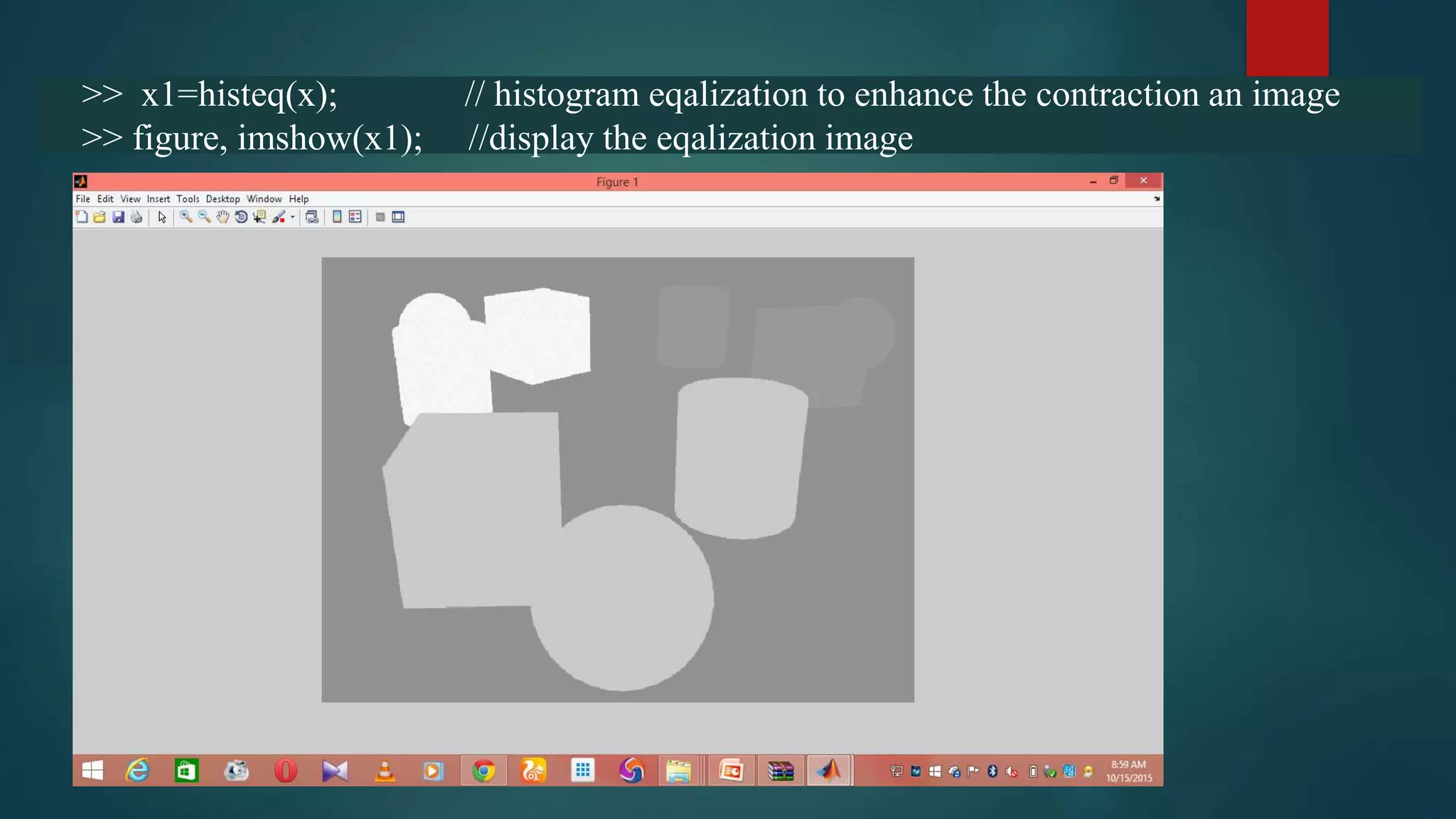
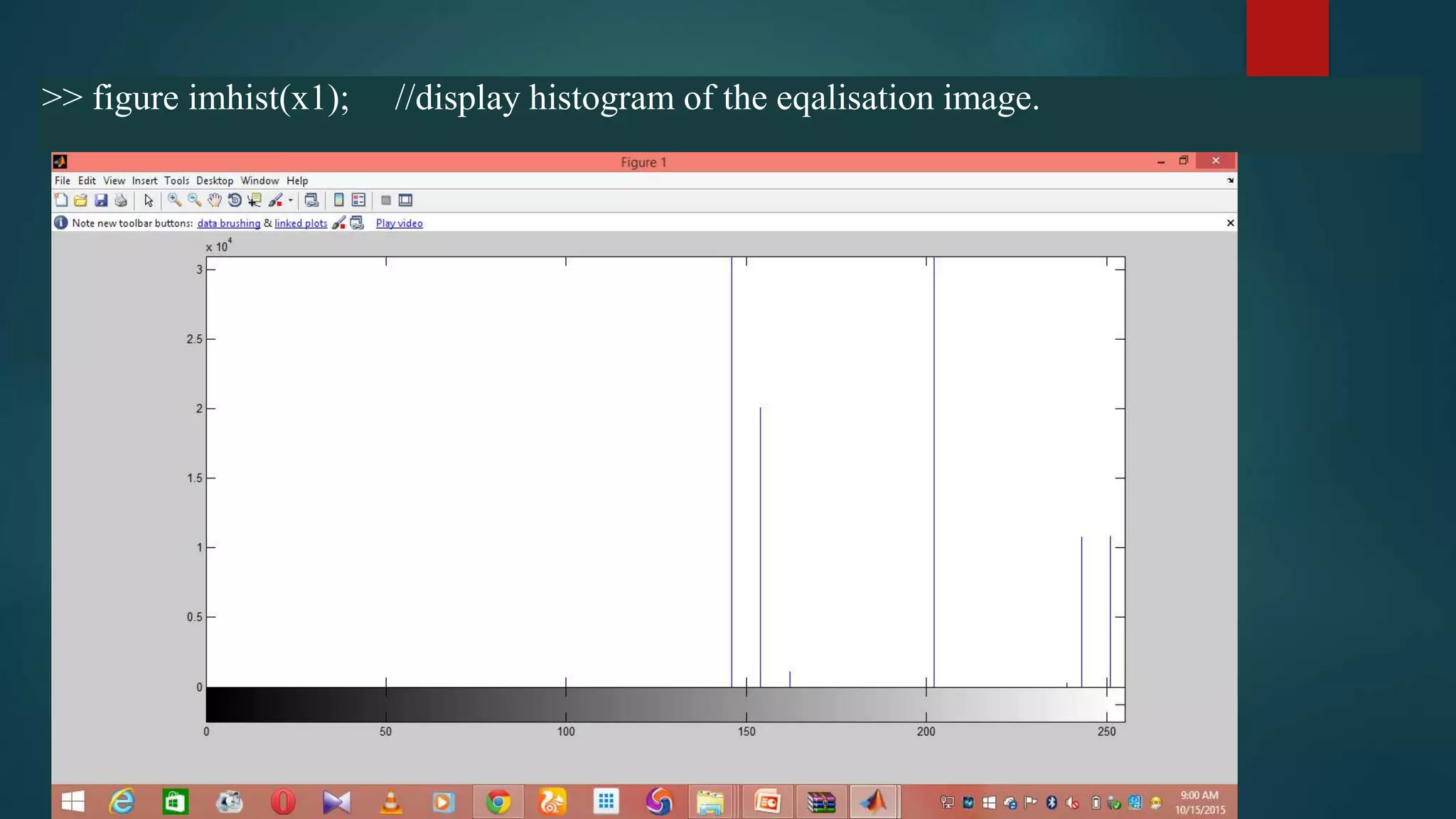
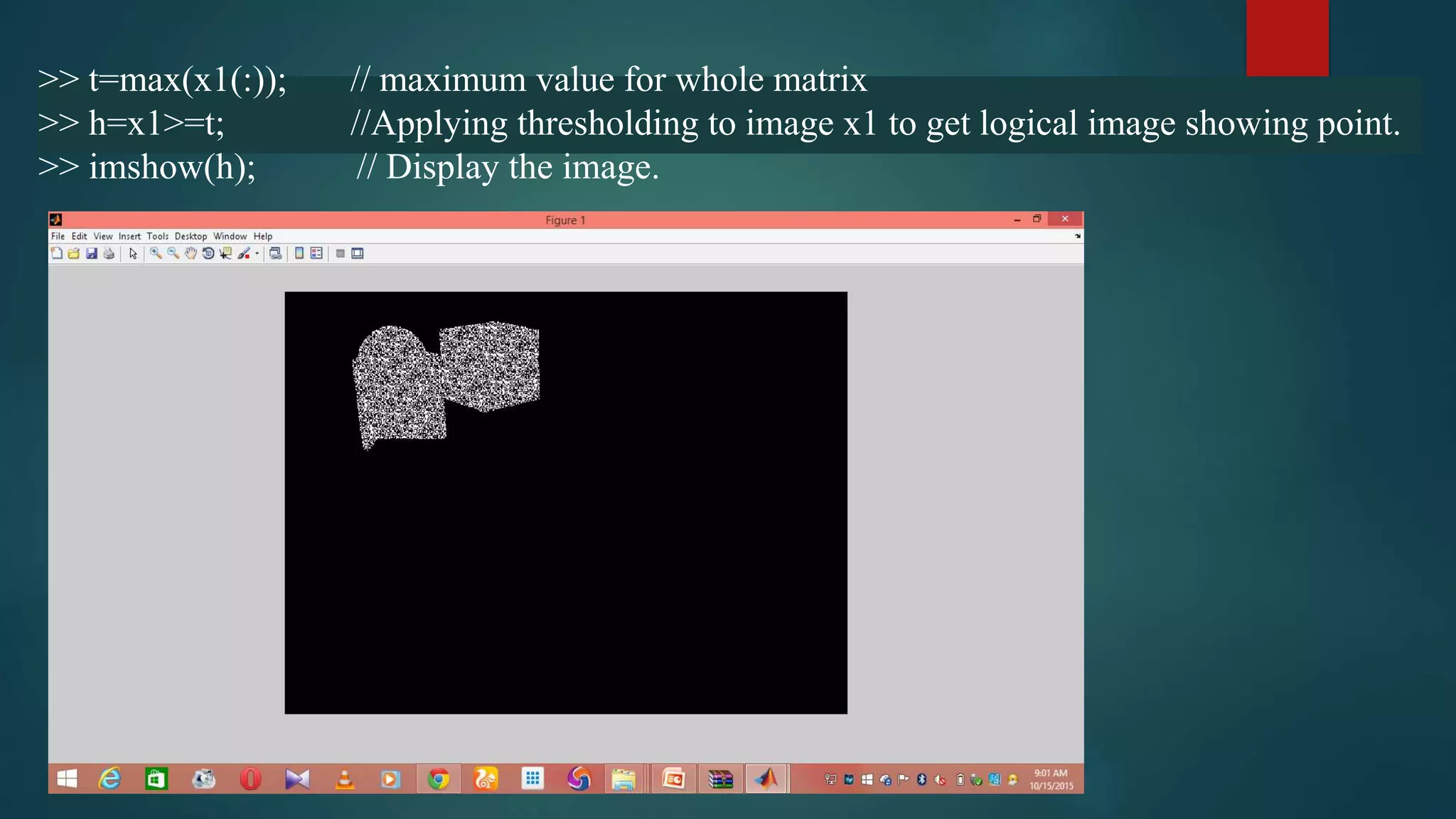
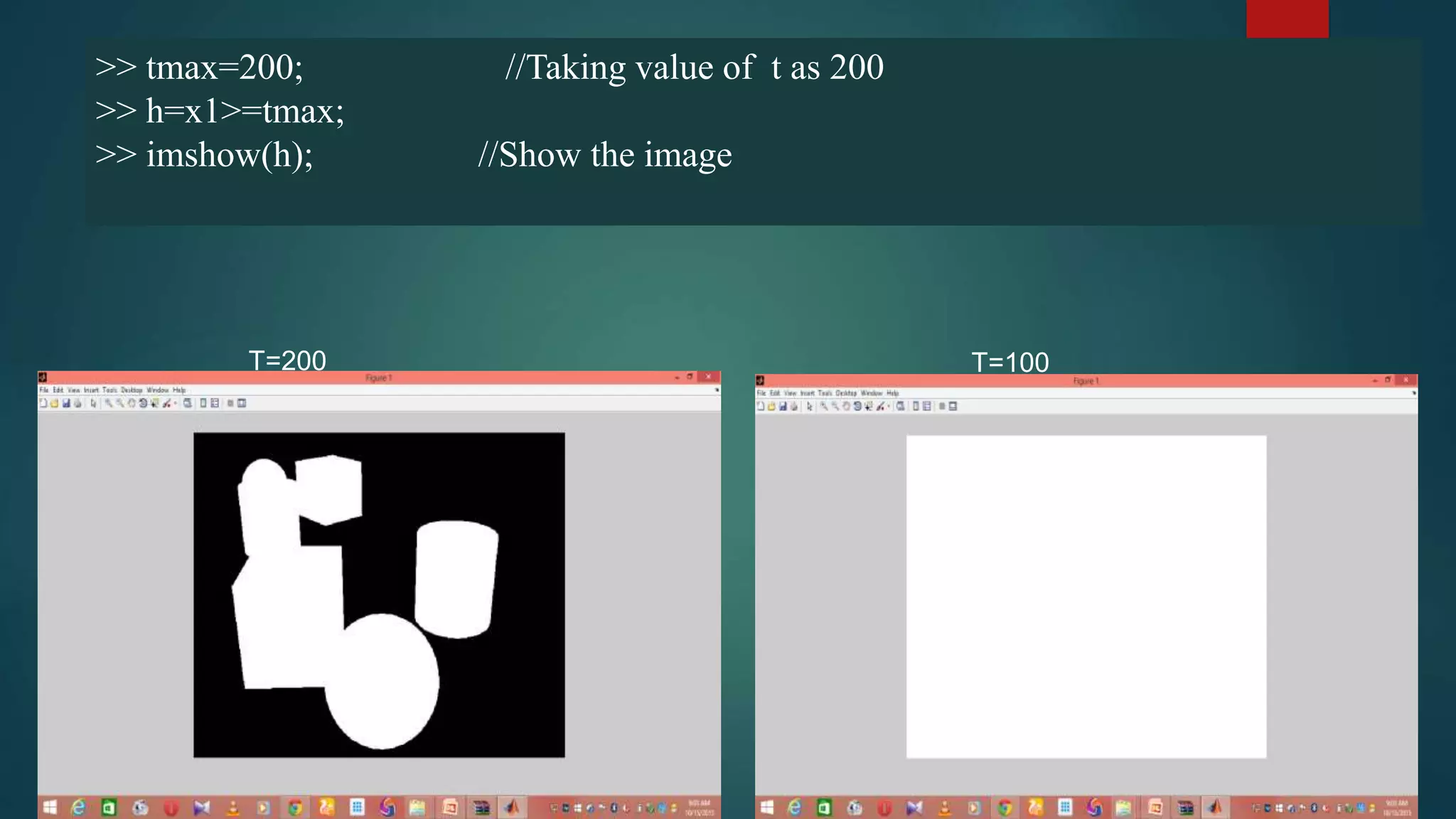
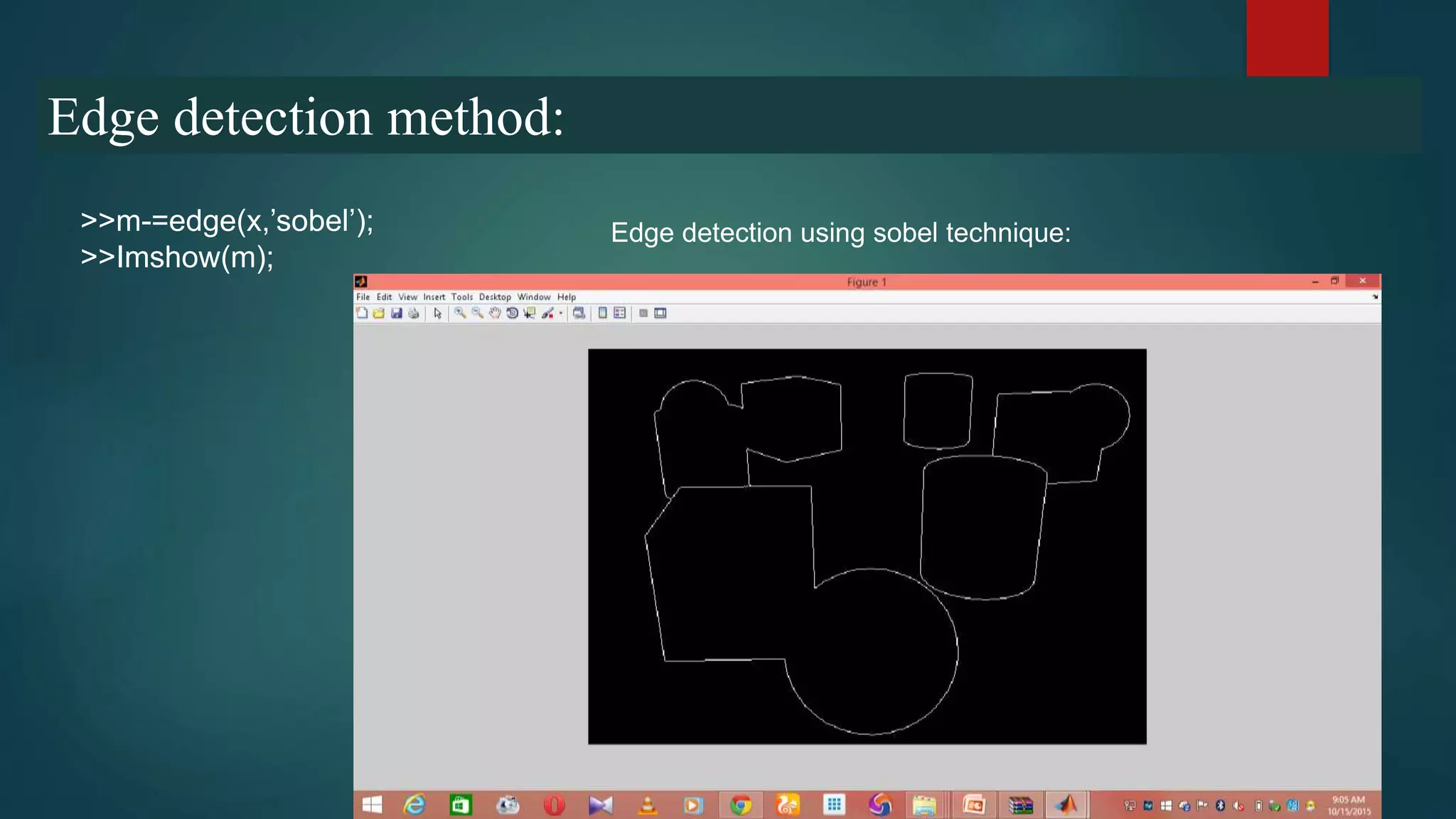
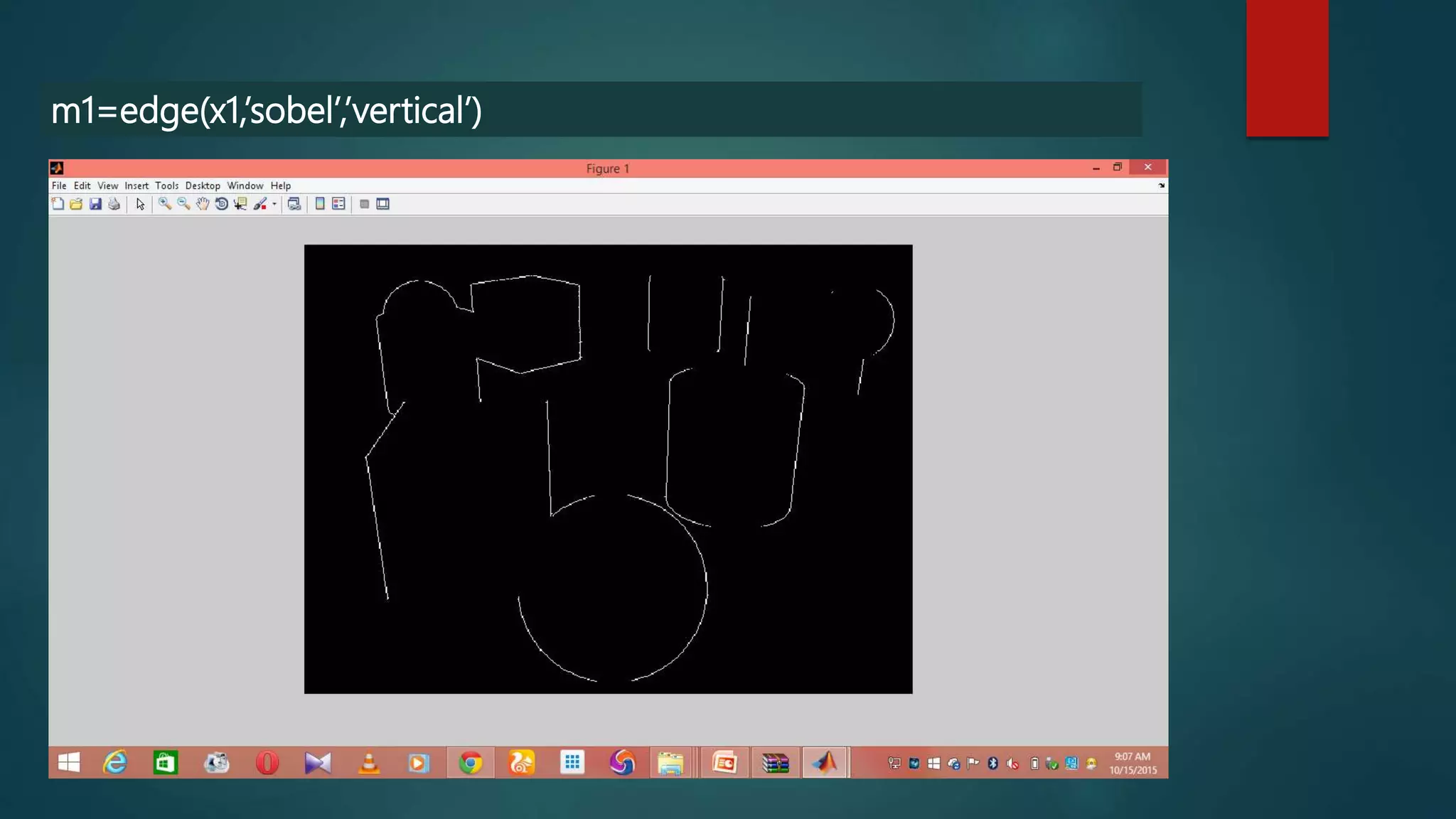
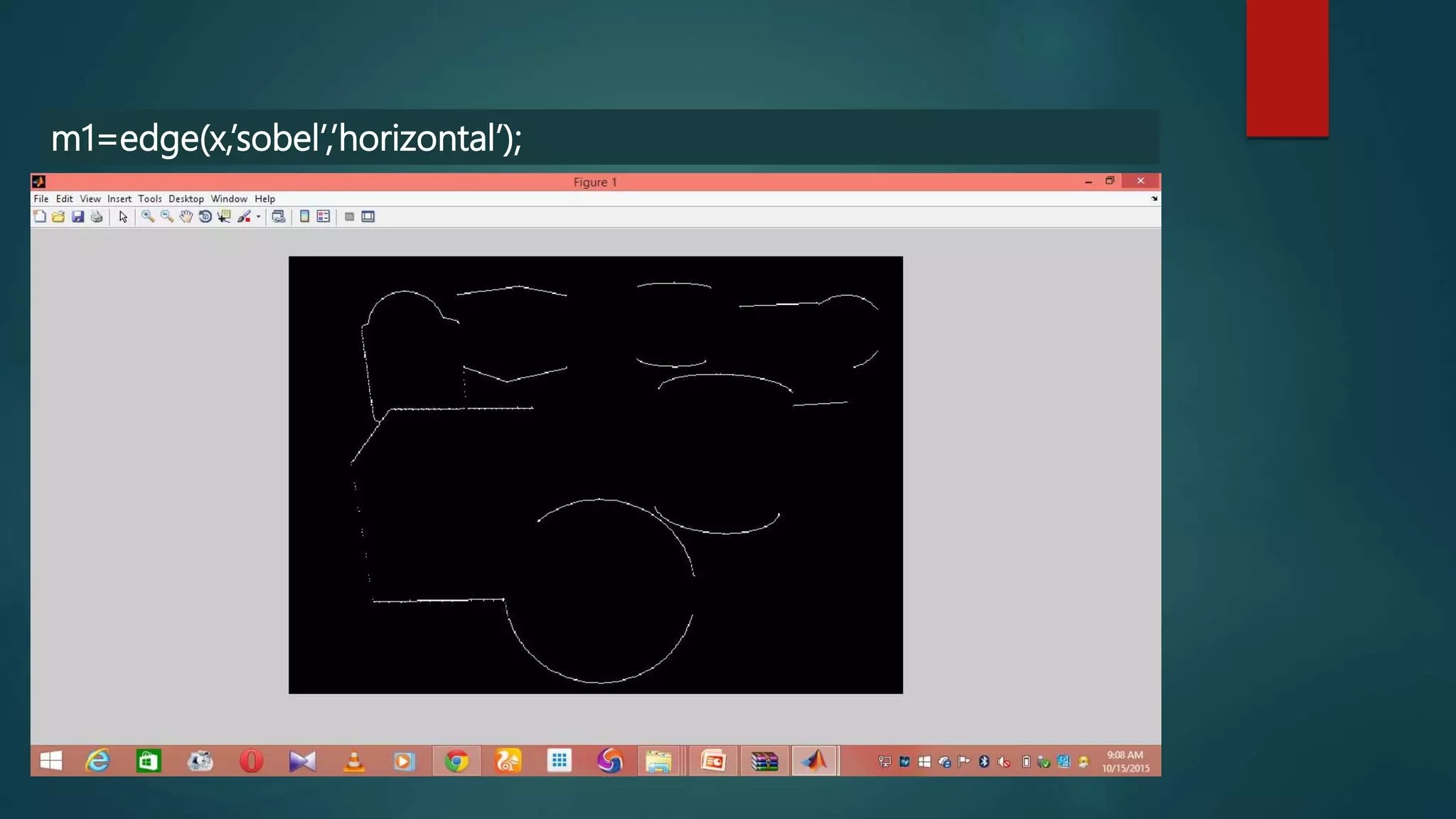
This document summarizes techniques for image segmentation based on global thresholding and gradient-based edge detection. It discusses image segmentation, approaches like thresholding and edge detection in MATLAB. Thresholding is demonstrated on sample images to extract objects at different threshold values. Edge detection is also shown using Sobel filters. Issues like segmenting similar objects and boundary detection in the presence of noise are mentioned.