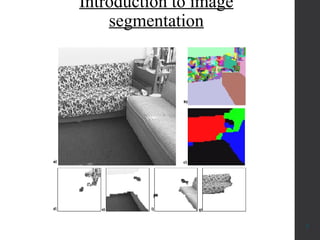
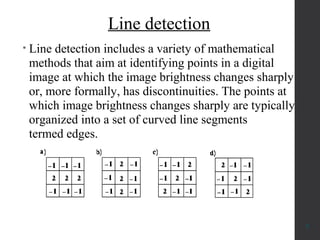
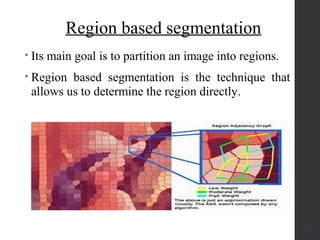
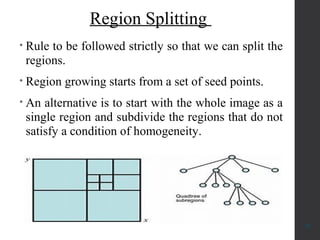
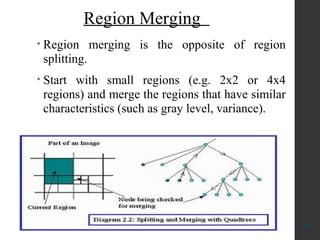
The document provides an overview of image segmentation, which is the process of partitioning an image into meaningful regions based on characteristics such as color, texture, or depth. It outlines various methods including edge detection, region-based segmentation, and algorithms used for detecting objects, particularly in applications like medical imaging and fruit disease detection. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of segmentation in retaining crucial data while minimizing irrelevant information.