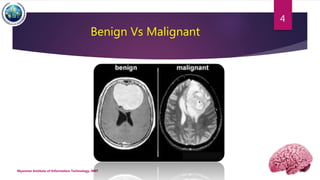
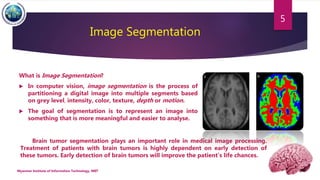
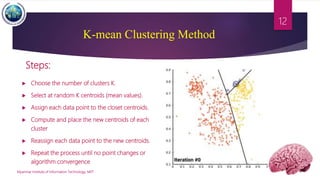
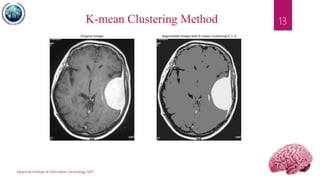
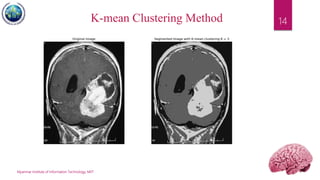
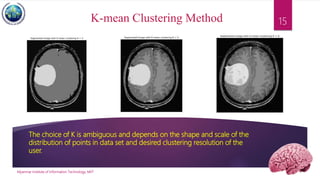
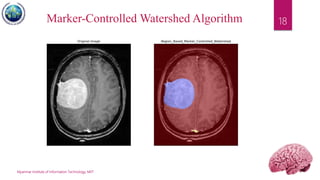
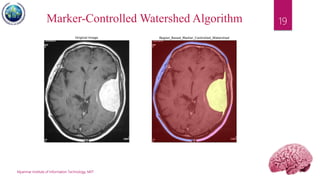
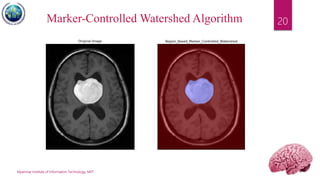
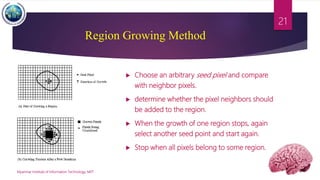
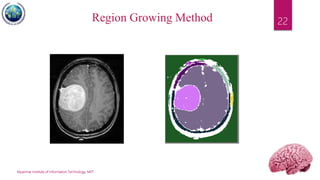
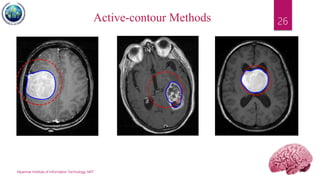
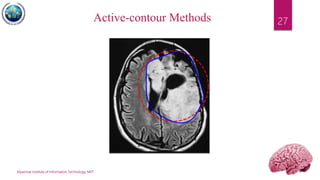
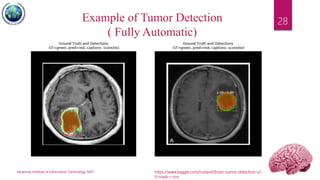
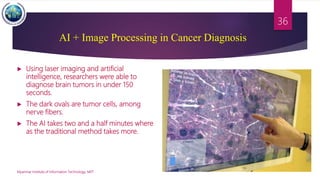
This document discusses applications of image segmentation in brain tumor detection. It begins by defining brain tumors and different types. It then discusses various image segmentation methods that can be used for brain tumor segmentation, including k-means clustering, region-based watershed algorithm, region growing, and active contour methods. It demonstrates how these methods can be implemented in Python for segmenting tumors from MRI images. The document also discusses computer-aided diagnosis systems and the roles of artificial intelligence and machine learning in medical image analysis and cancer diagnosis using image processing.