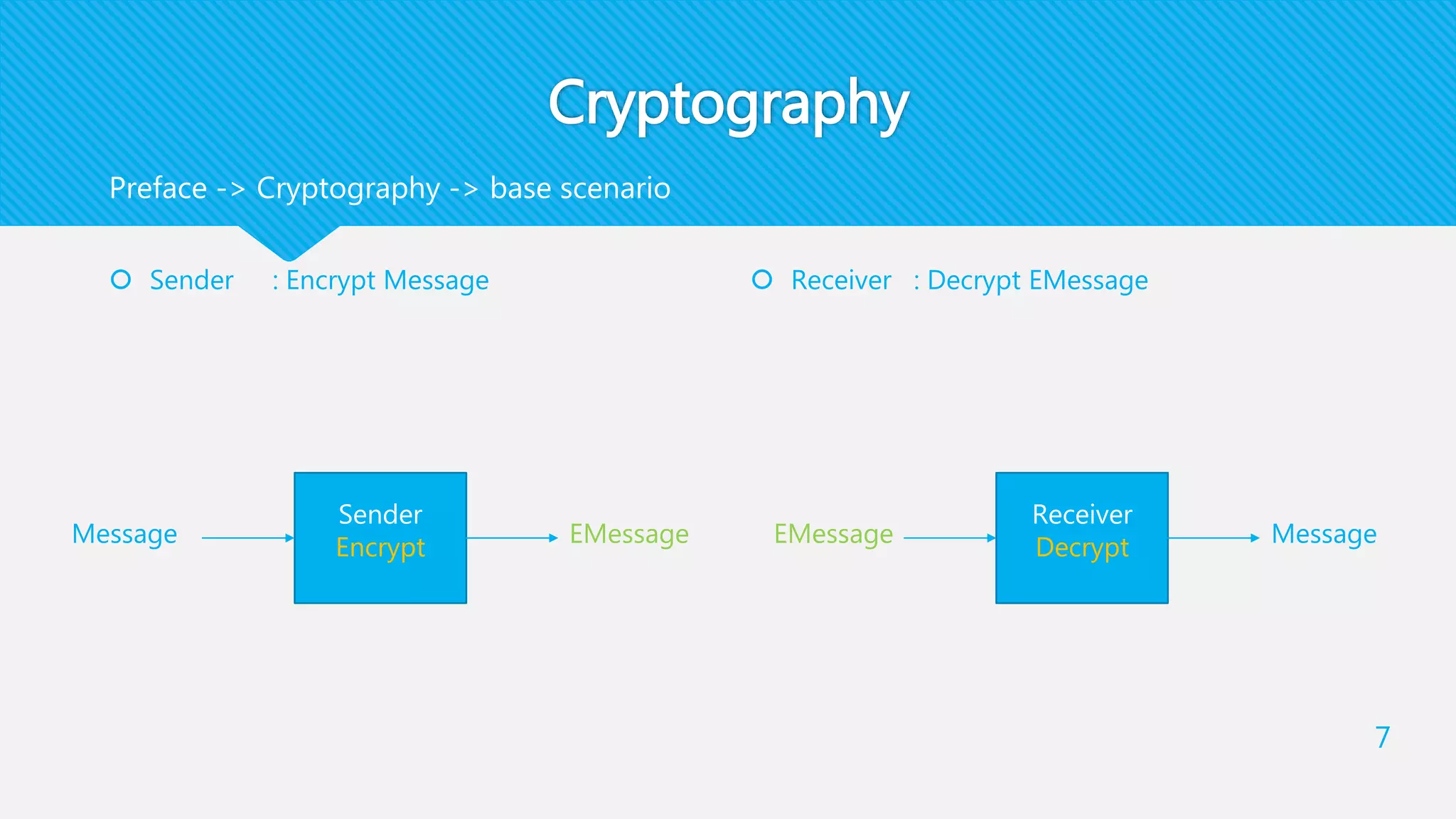
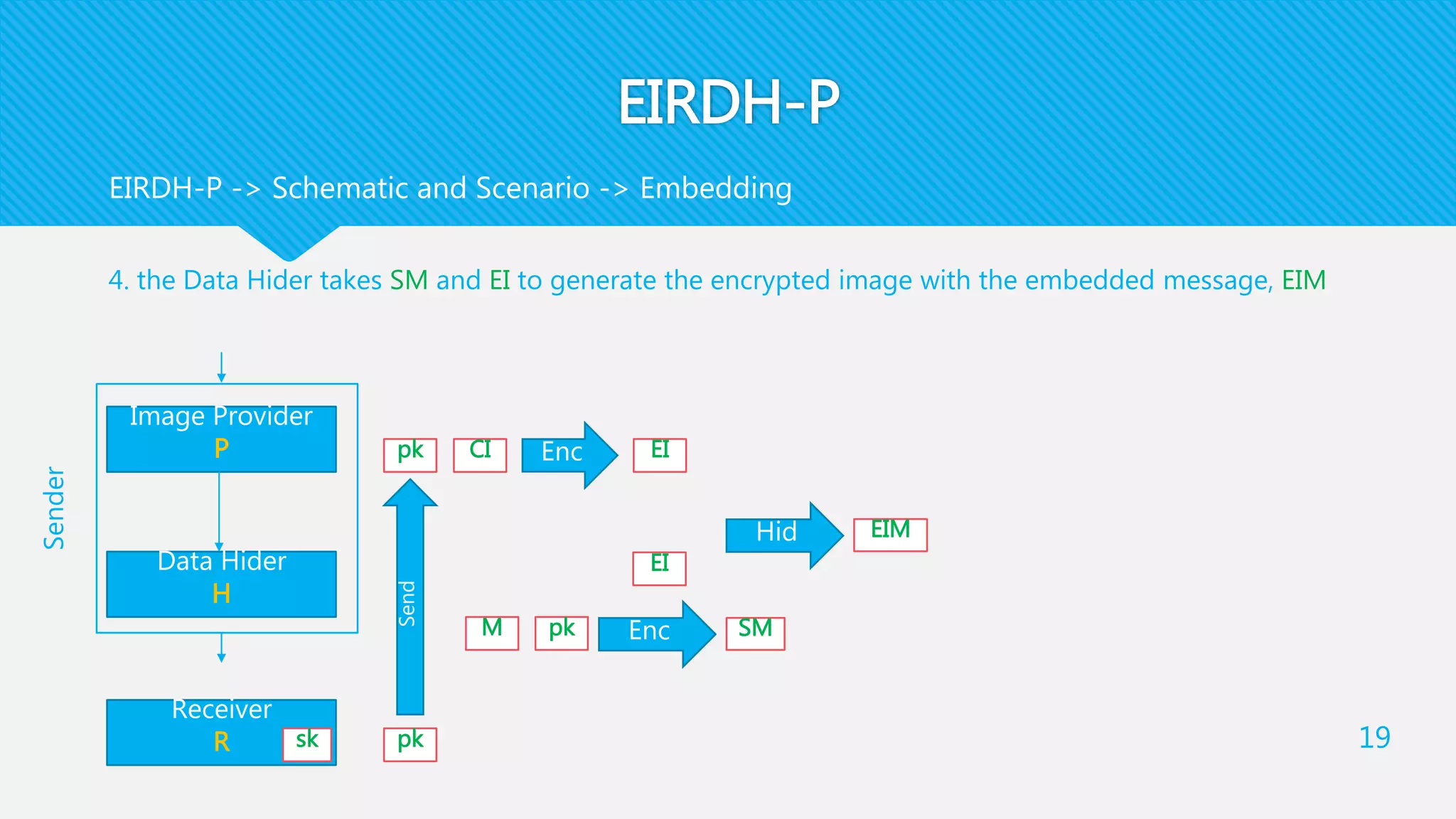
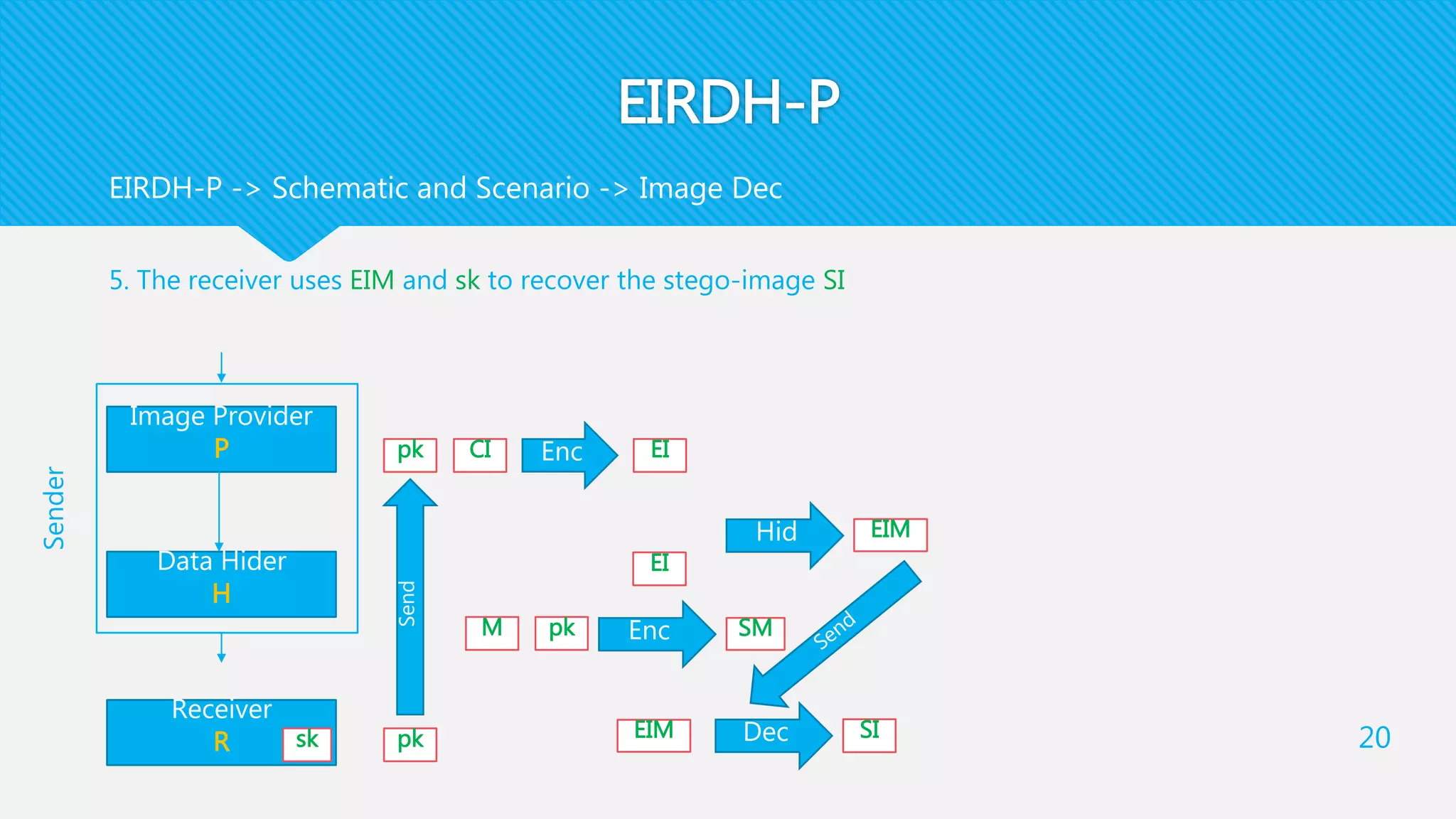
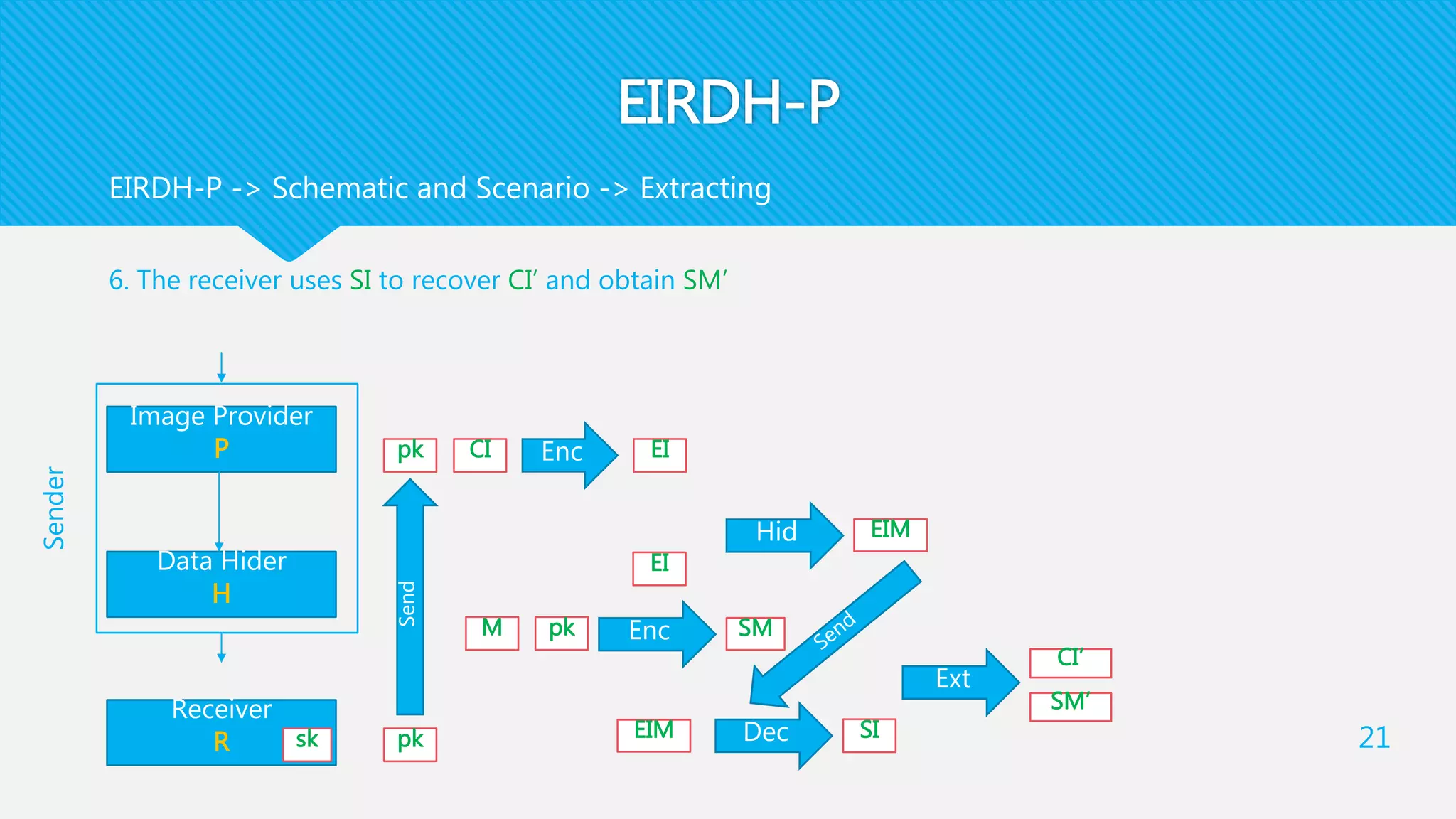
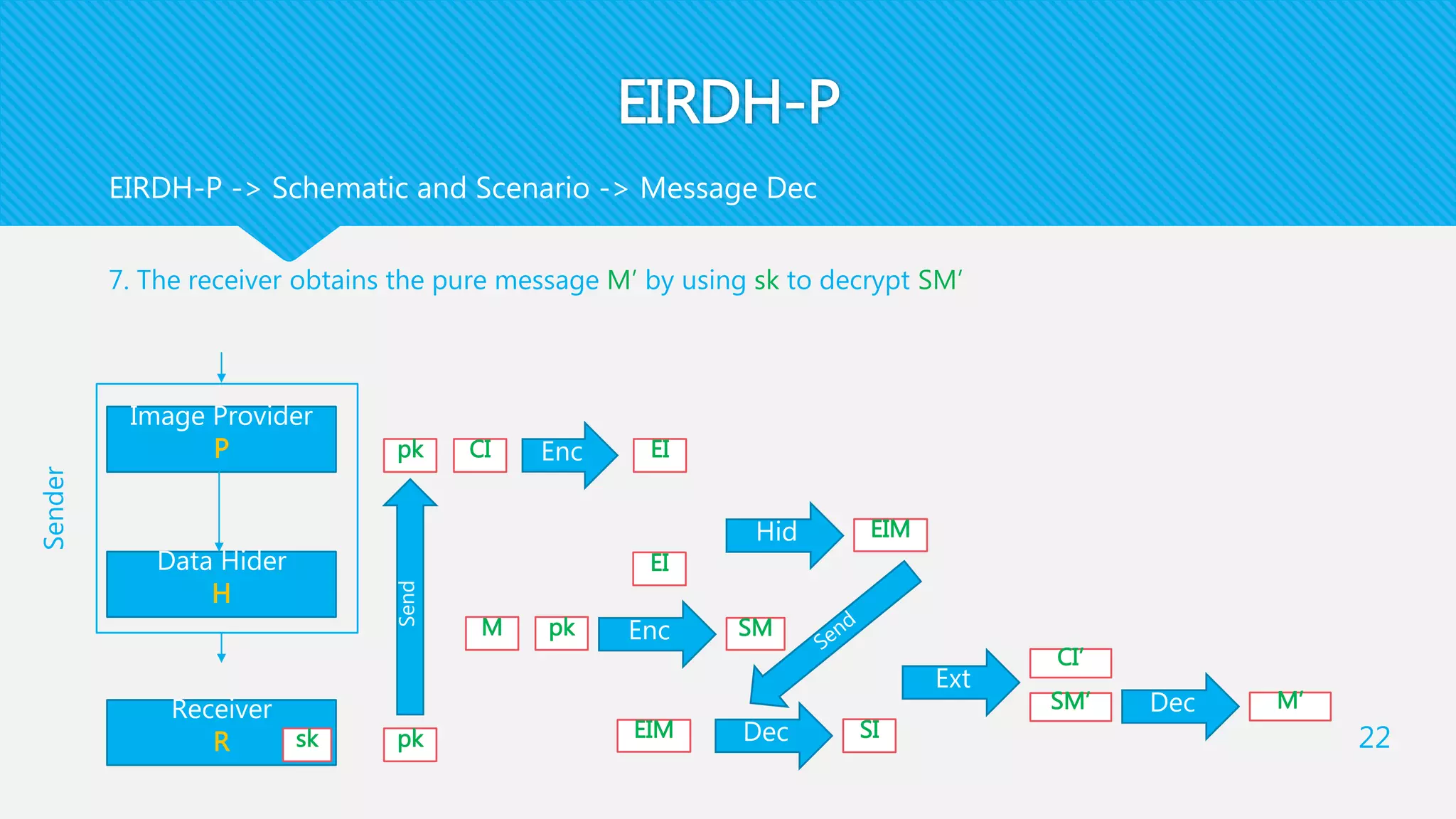
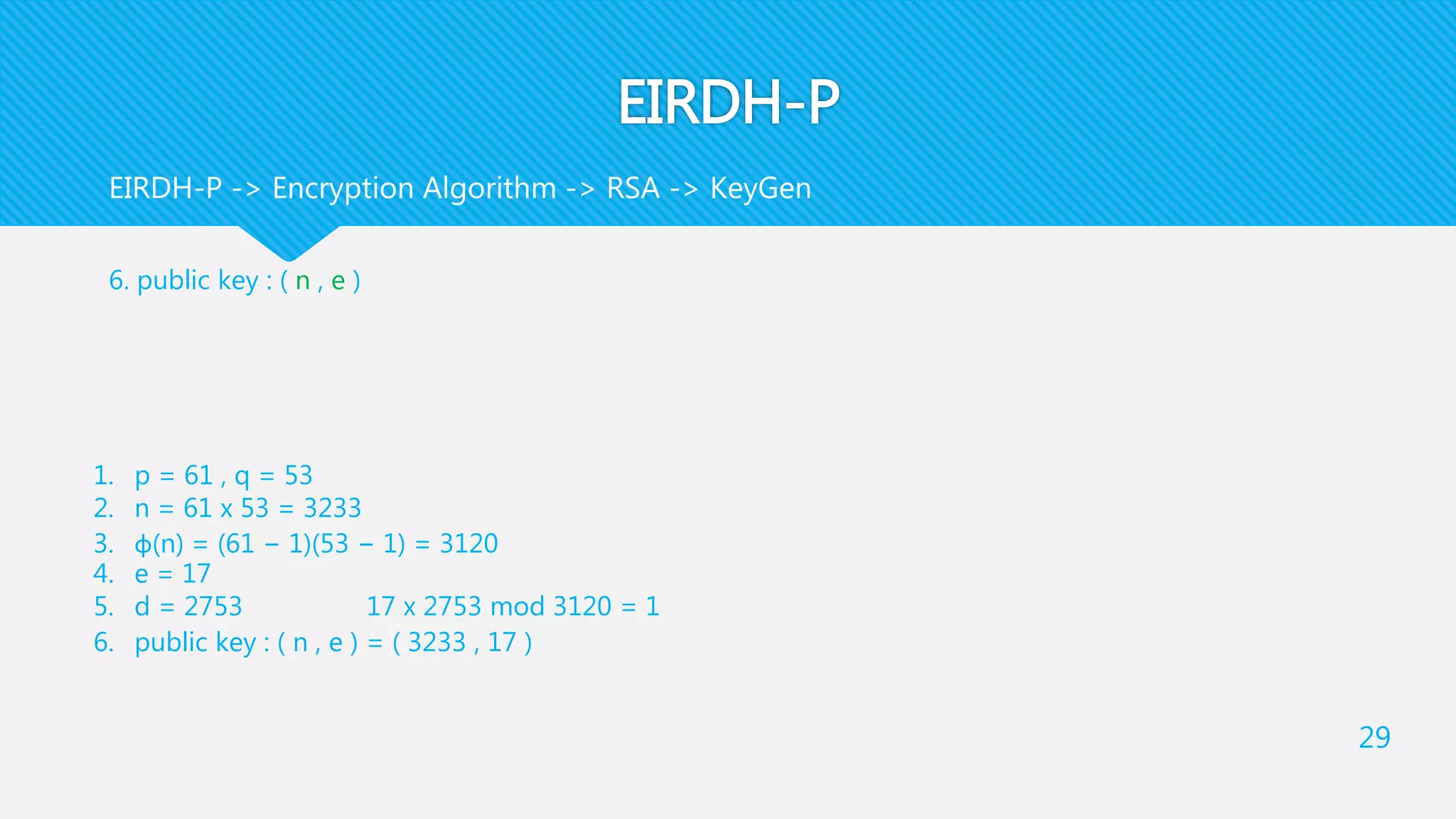
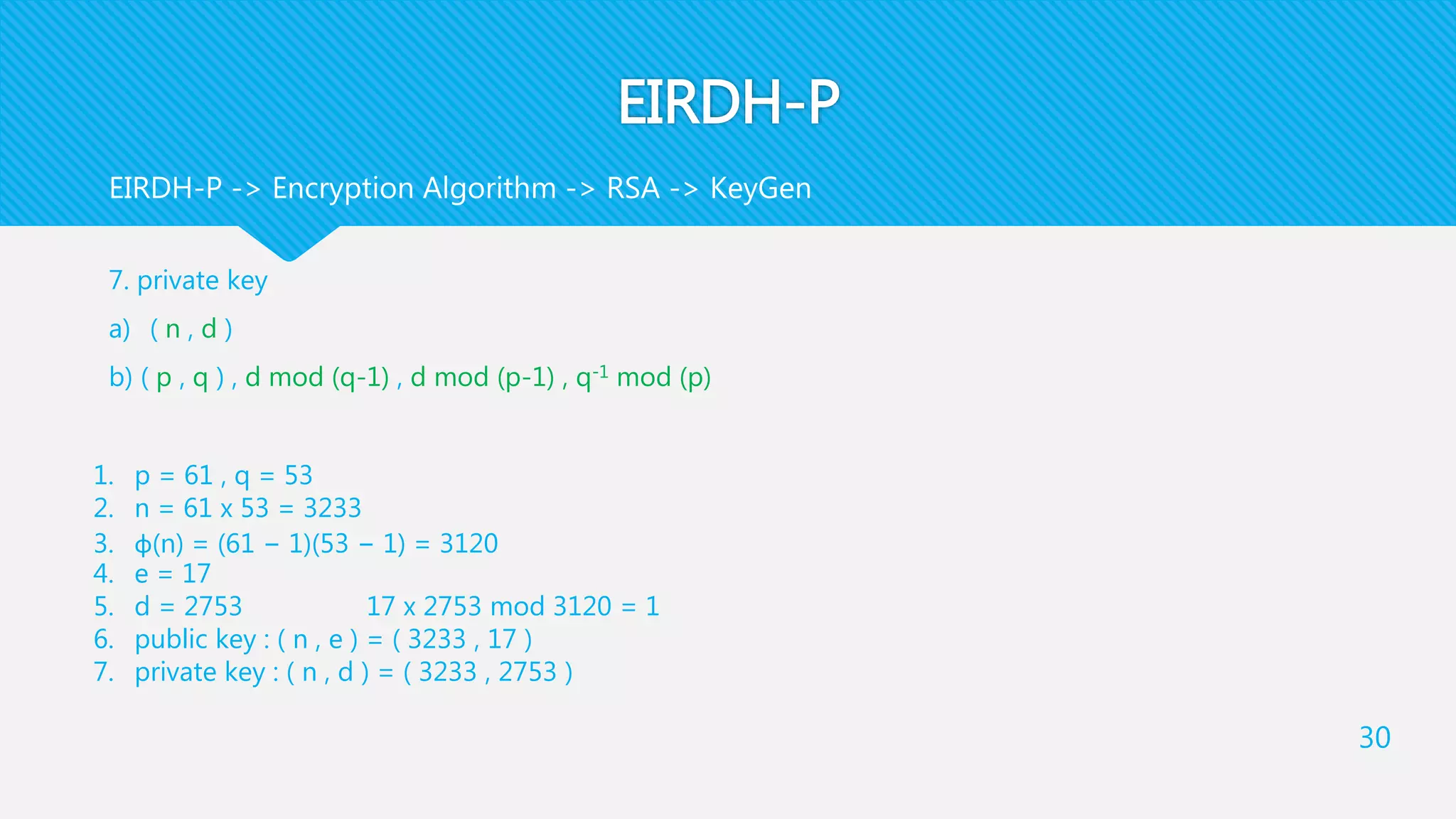
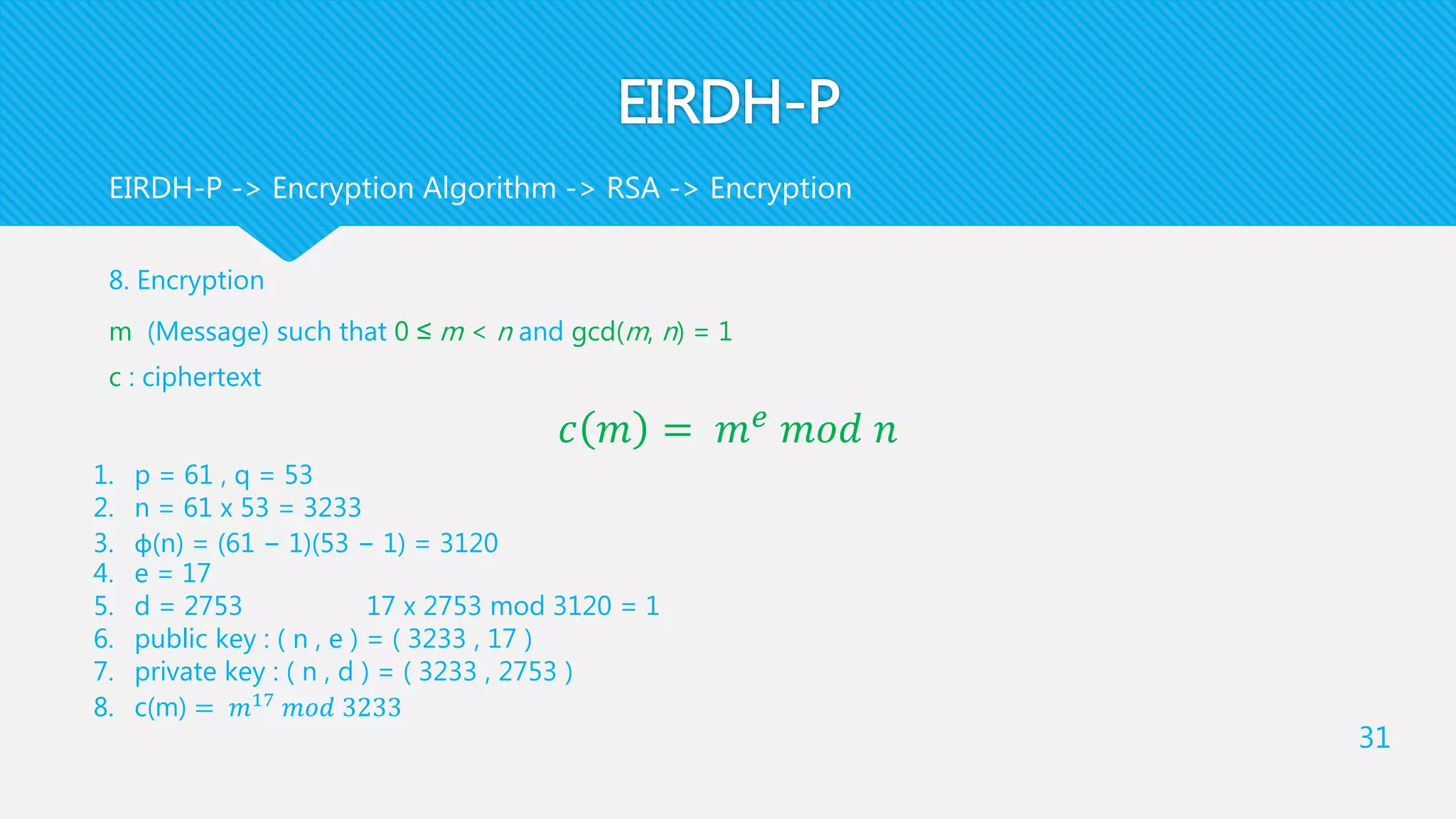
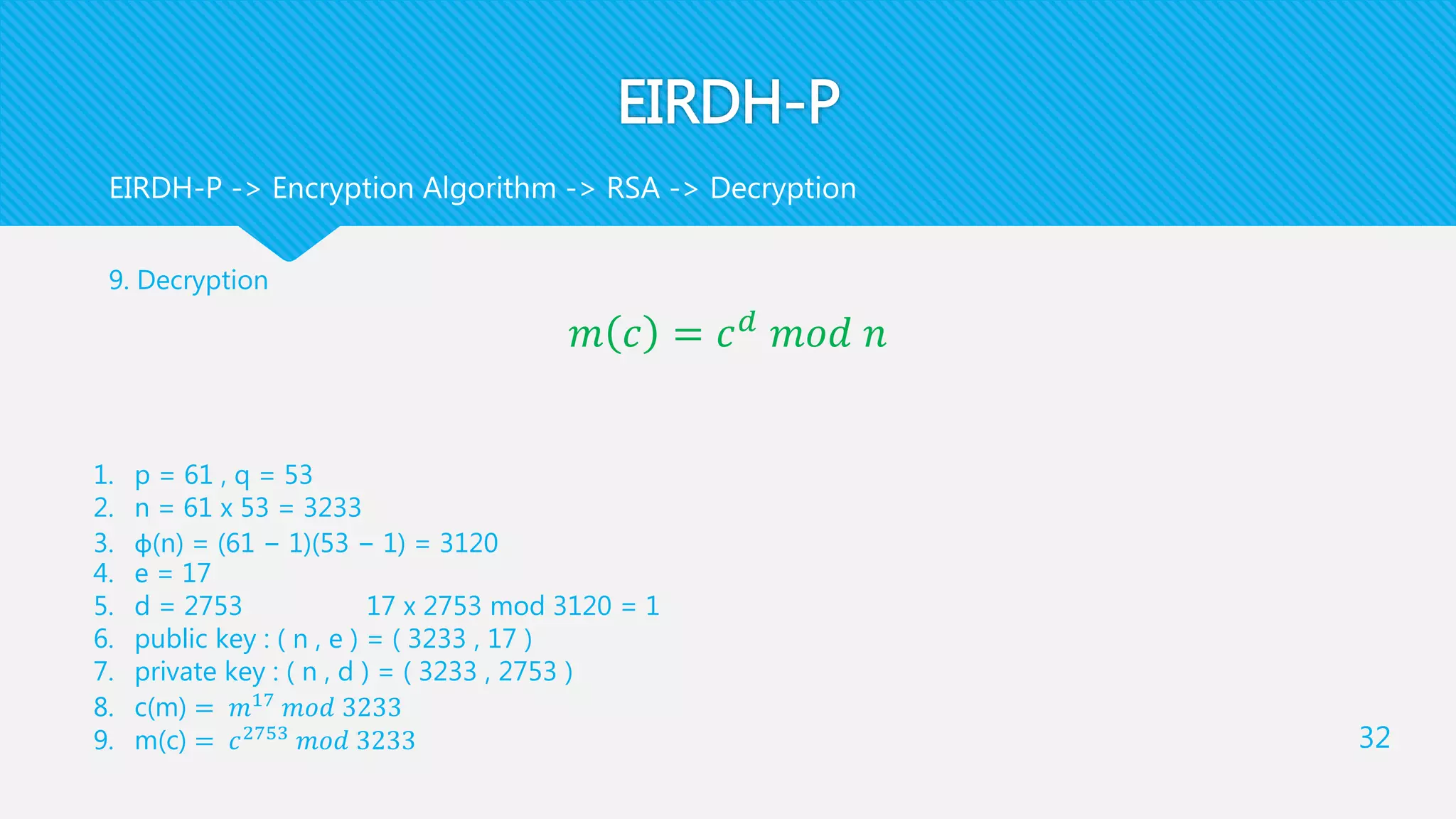
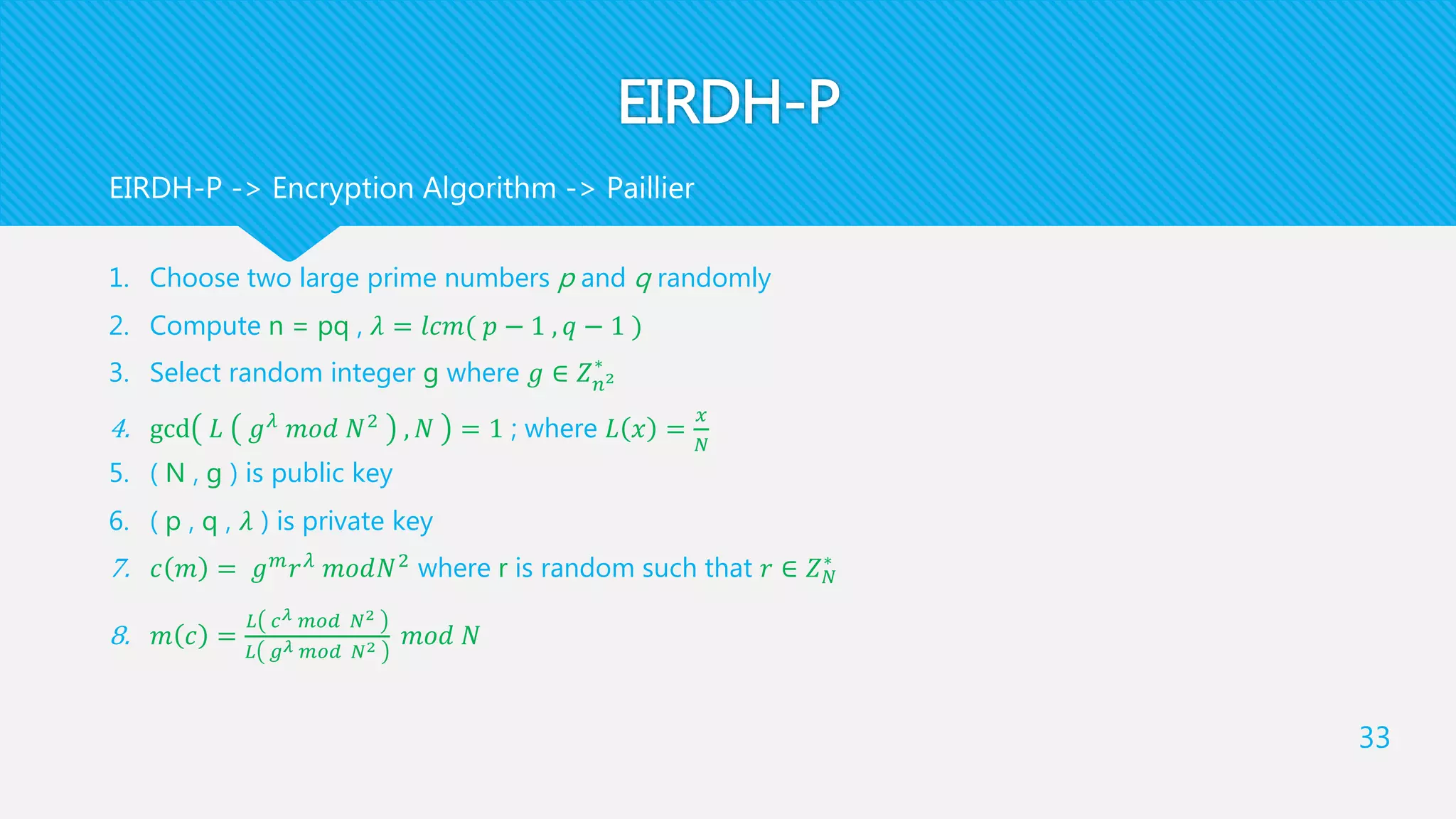
1) EIRDH-P combines public key cryptography and steganography by encrypting images and embedding secret messages within the encrypted images.
2) It involves an Image Provider who encrypts a cover image using public key encryption. A Data Hider then embeds a secret message within the encrypted image.
3) The receiver decrypts the stego-image to extract the secret message and recover the original cover image using their private key.









![new EIRDH-P
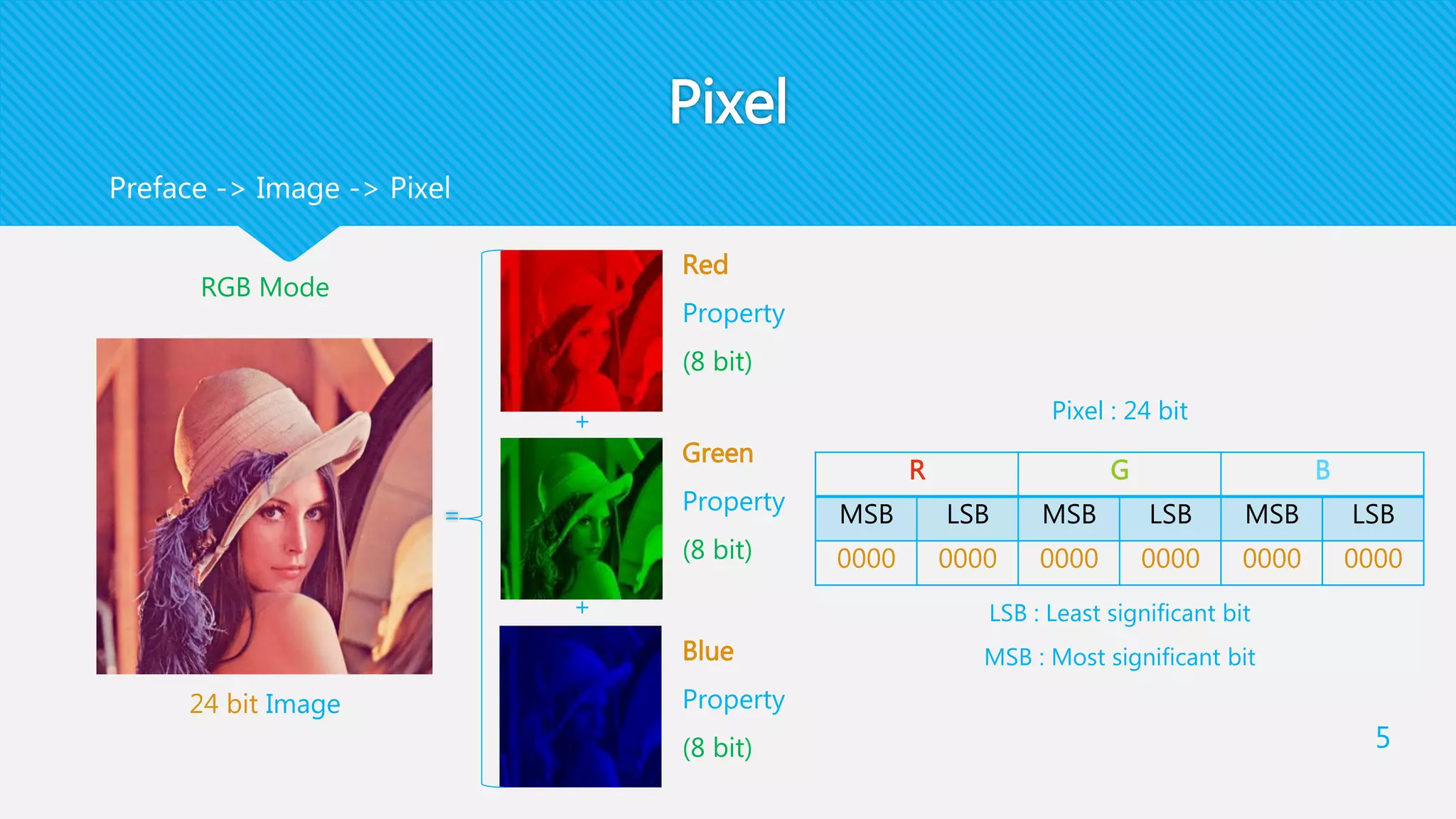
each pixel is divided into two parts : an even integer and a bit, where the summation of them is
equal to the pixel value
any pixel = x + y + bit
(x , y) is an even integer , x > y
[[m]] = c(m) = ciphertext of m
[[m1]] [[m2]] = [[ m1 + m2 ]]
34
new EIRDH-P](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdfd0337-3211-465c-babc-f37ac55373f9-151222181937/75/Image-Cryptography-and-Steganography-34-2048.jpg)
![new EIRDH-P
2. Image Provider pre-processes (x,y) to compute 𝑙 =
𝑥+𝑦
2
and 𝑑 = 𝑥 − 𝑦 , and then computes
𝑥′
= 𝑙 + 𝑑 and 𝑦′
= 𝑙 − 𝑑
Note that d can be positive or negative
He generates [ 𝑥′
] and [ 𝑦′
] by using pk to encrypt 𝑥′
, 𝑦′
Here [ 𝑥′
] and [ 𝑦′
] are the encrypted pixel pair in the encrypted image
This step will produce EI
36
new EIRDH-P -> Algorithm -> Image Enc
yx
Cover Image
Pre Process y'x' Encrypt [[y‘]][[x‘]]
Enc Image
𝑥′ = 𝑙 + 𝑑
𝑦′
= 𝑙 − 𝑑](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdfd0337-3211-465c-babc-f37ac55373f9-151222181937/75/Image-Cryptography-and-Steganography-36-2048.jpg)

![new EIRDH-P
4. For a bit b of SM , Data Hider generates [𝑏] and computes 𝑥′′
= 𝑏 [ 𝑥′ ] and 𝑦′′
= [ 𝑦′
]
Note that [𝑏] is only inserted into the first encrypted pixel
Finally, he generates 𝑥′′
and 𝑦′′
as a pixel pair of EIM. This step will output EIM
38
new EIRDH-P -> Algorithm -> Embedding
[[y‘]][[x‘]][[y”]][[x”]] Embed
b = 1 , 𝑥′′
= [ 𝑥′ ] 1 , 𝑦′′
= 𝑦′
b = 0 , 𝑥′′
= [ 𝑥′ ] , 𝑦′′
= 𝑦′](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdfd0337-3211-465c-babc-f37ac55373f9-151222181937/75/Image-Cryptography-and-Steganography-38-2048.jpg)
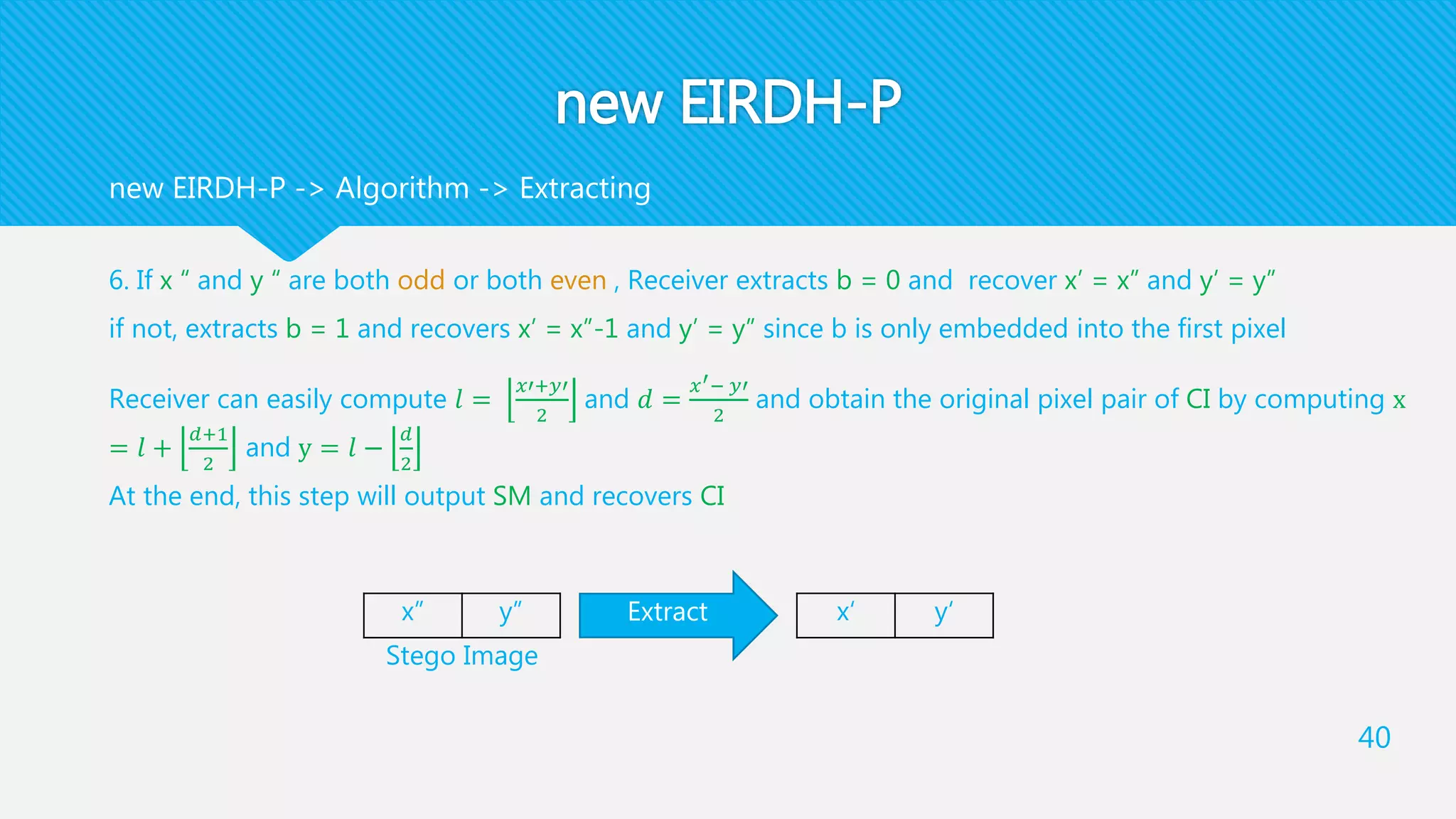
![new EIRDH-P
5. Receiver uses 𝑥 ′′
and 𝑦 ′′
and sk to recover x ″ , y ″ as a pixel pair of the stego-image SI
This step will finally output SI
39
new EIRDH-P -> Algorithm -> Image Dec
[[y”]][[x"]] Dec y “x “
Stego Image](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdfd0337-3211-465c-babc-f37ac55373f9-151222181937/75/Image-Cryptography-and-Steganography-39-2048.jpg)
![new EIRDH-P
42
new EIRDH-P -> Schematic
Cover Image
Pre Process Encrypt
Enc Image
𝑥′
= 𝑙 + 𝑑
𝑦′
= 𝑙 − 𝑑
[[y‘]][[x‘]][[y”]][[x”]] Embed
If bit = 1 , 𝑥′′
= [ 𝑥′ ] 1 , 𝑦′′
= 𝑦′
If bit = 0 , 𝑥′′
= [ 𝑥′ ] , 𝑦′′
= 𝑦′
[[y”]][[x"]]
Dec
y “x “
Stego Image
Extract y‘x‘ Recover
𝑙 =
𝑥′+𝑦′
2
, 𝑑 =
𝑥′− 𝑦′
2
x = 𝑙 +
𝑑+1
2
, y = 𝑙 −
𝑑
2
P
H
R](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cdfd0337-3211-465c-babc-f37ac55373f9-151222181937/75/Image-Cryptography-and-Steganography-42-2048.jpg)