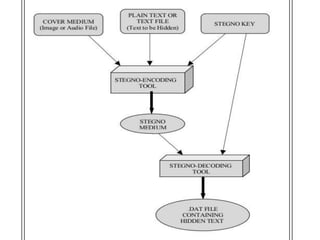
This document provides an overview of steganography and its modules for a PowerPoint presentation. Steganography is the art of hiding communication by concealing messages within other information. It uses various techniques to hide information in digital images or audio files. The presentation covers the encryption and decryption modules used for steganography. Encryption hides data in a host file using an algorithm while decryption extracts the data using the reverse algorithm. The modules create an application for encrypting and decrypting data files within media files to perform steganography.