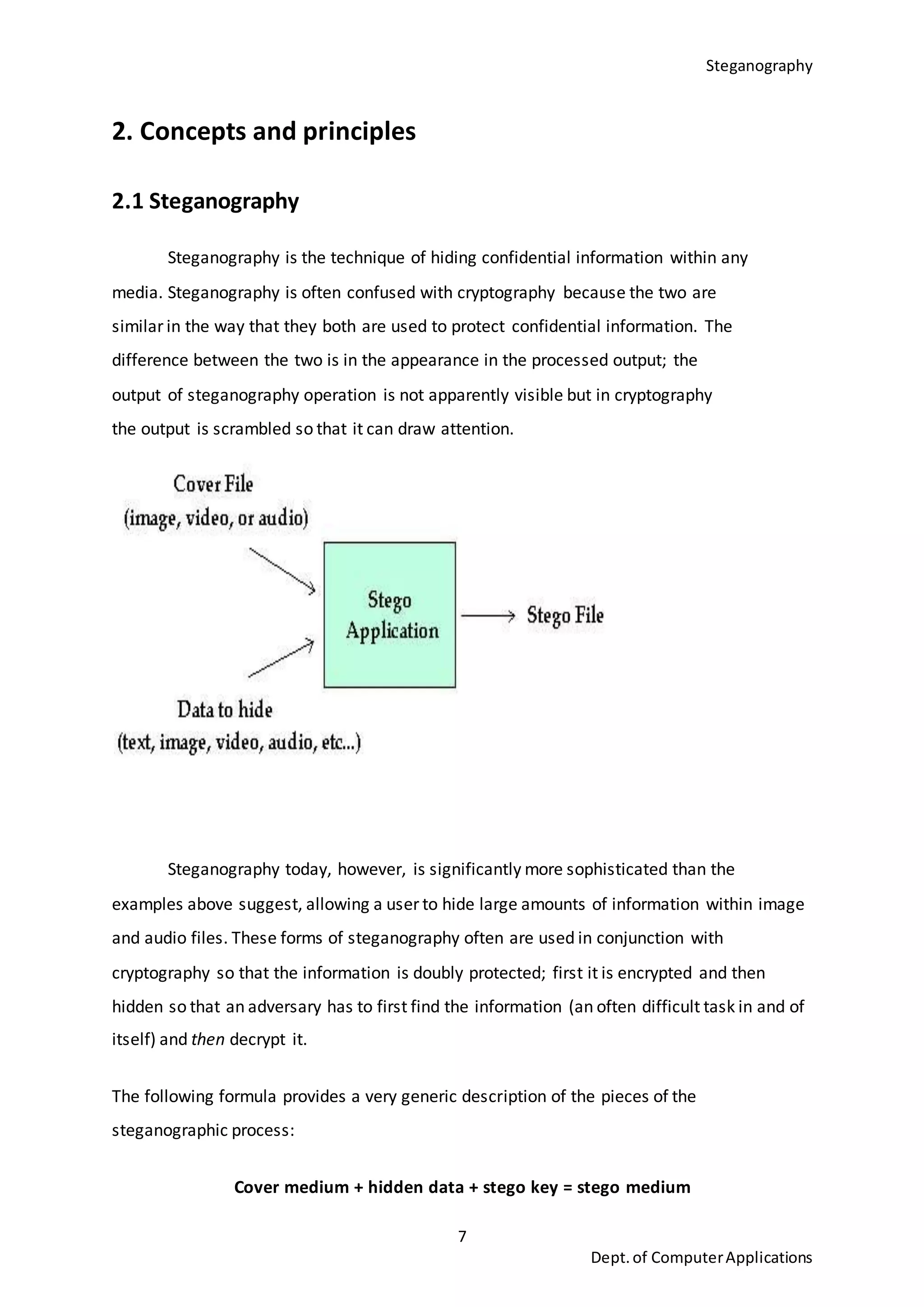
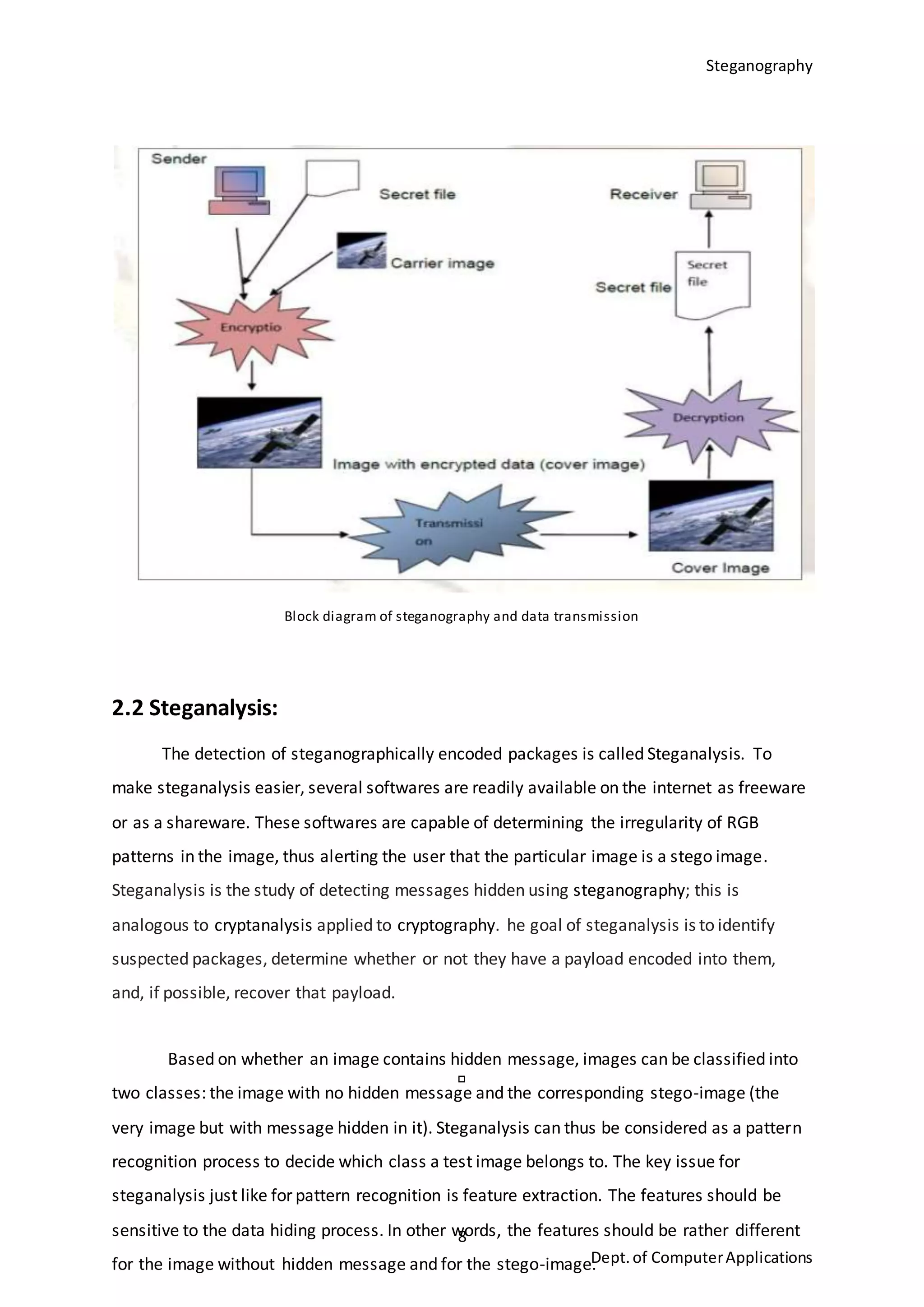
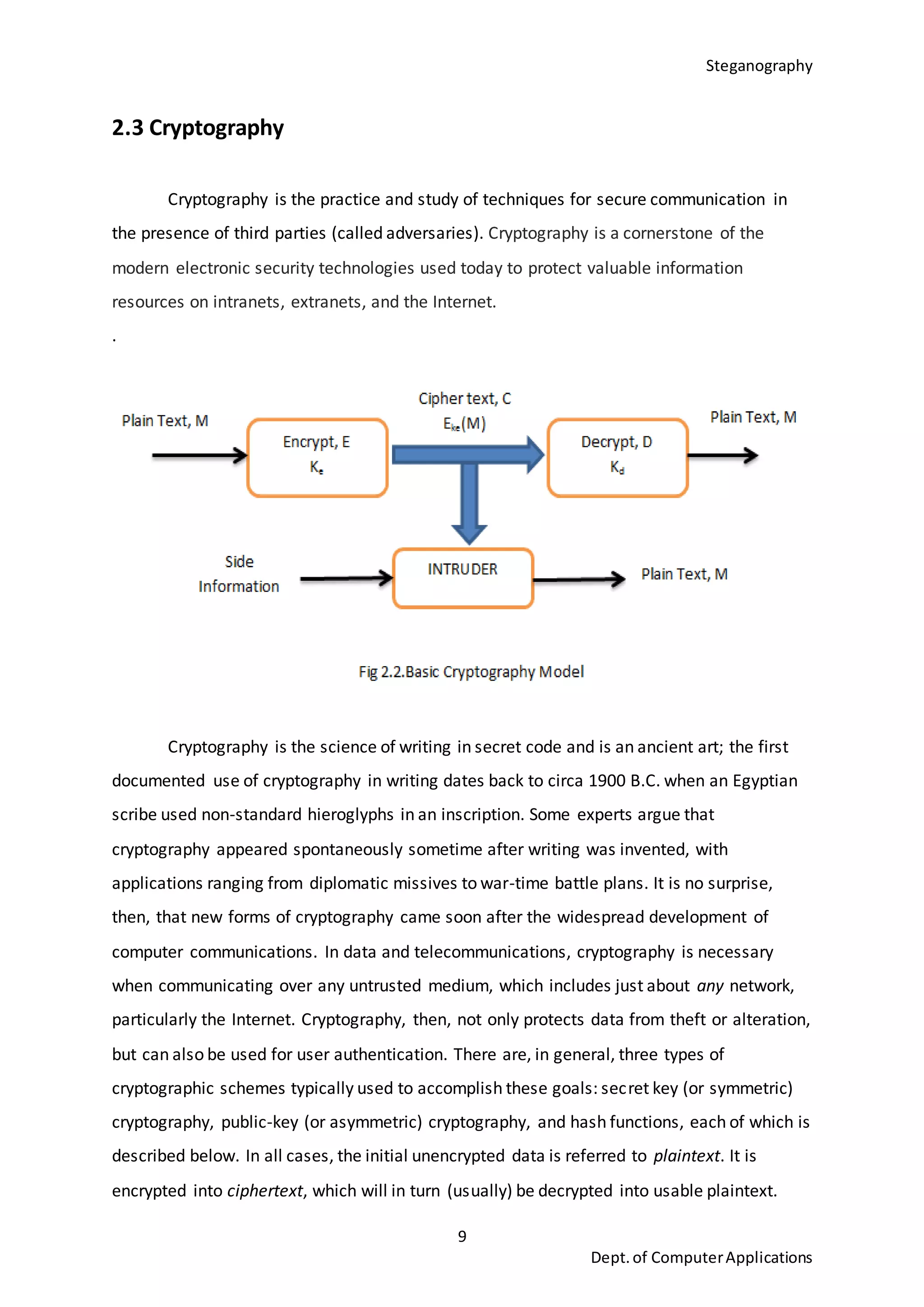
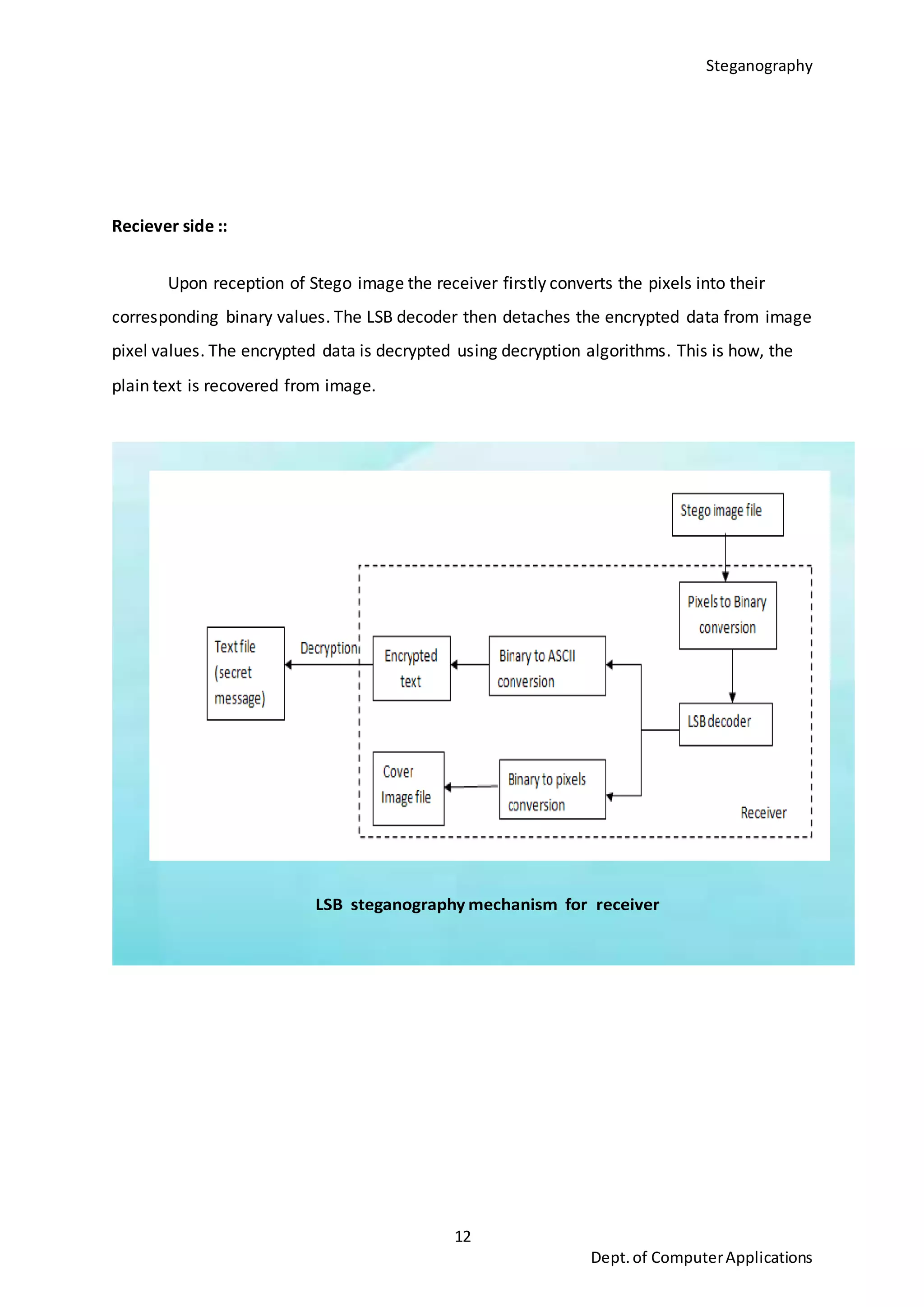
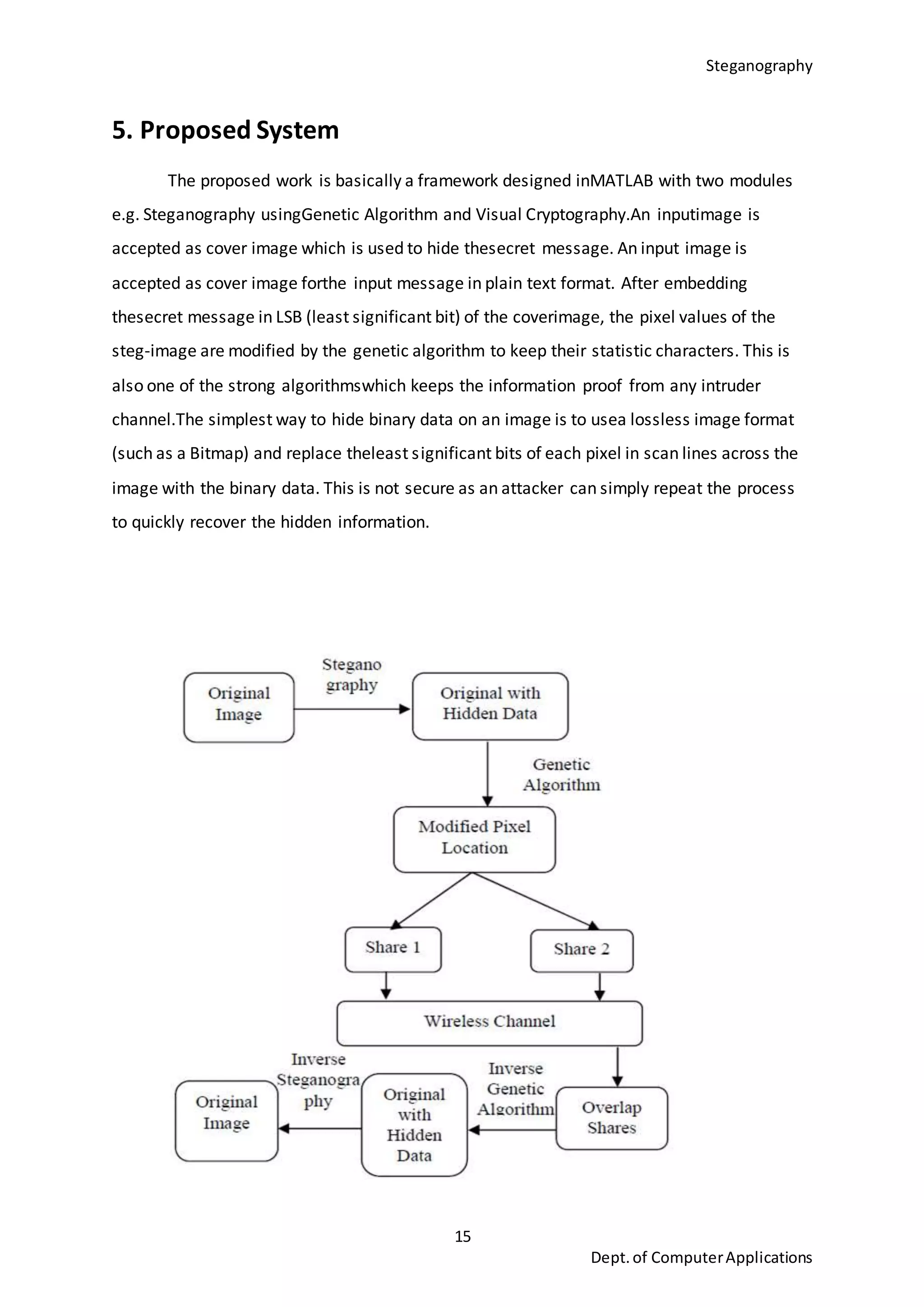
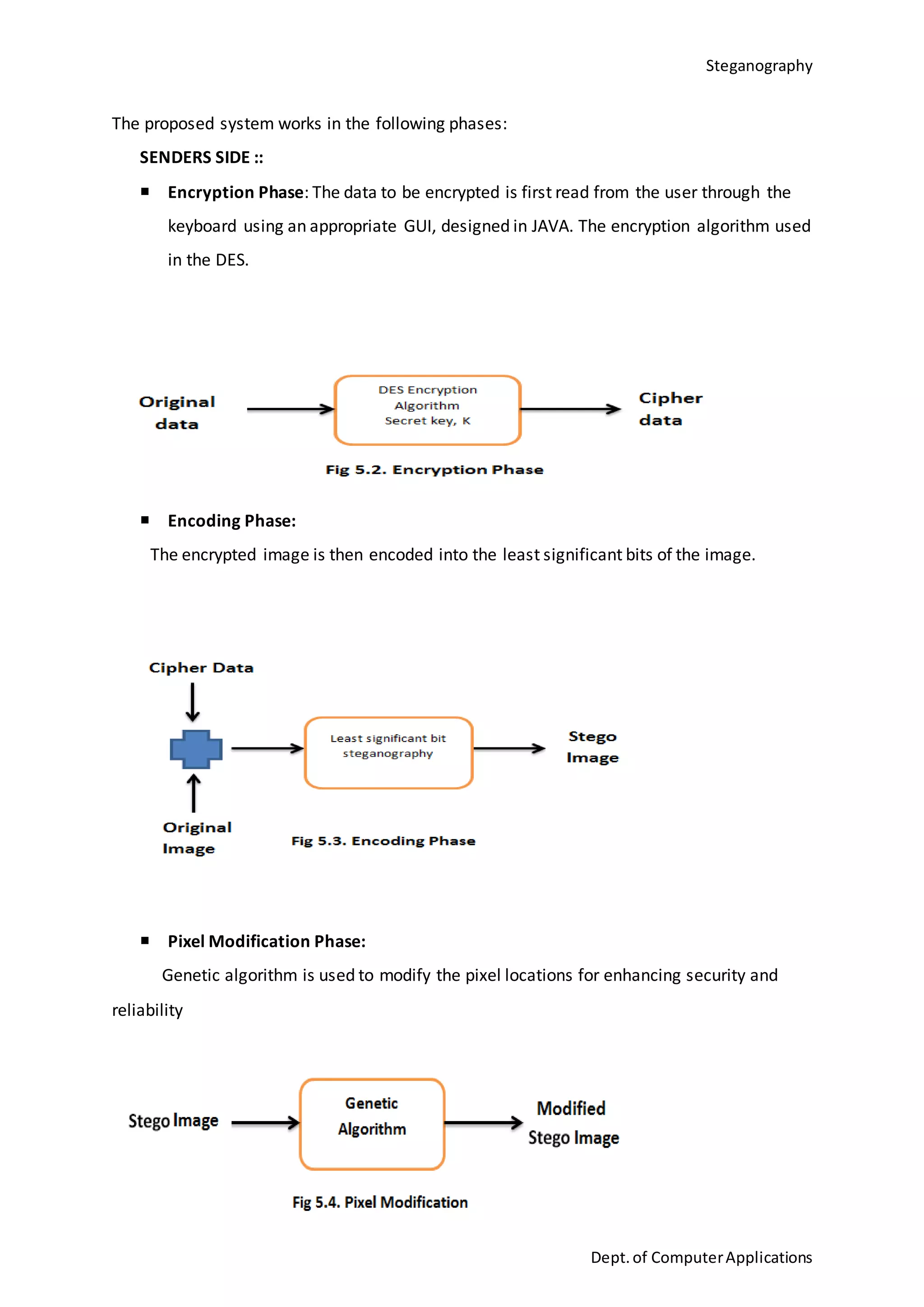
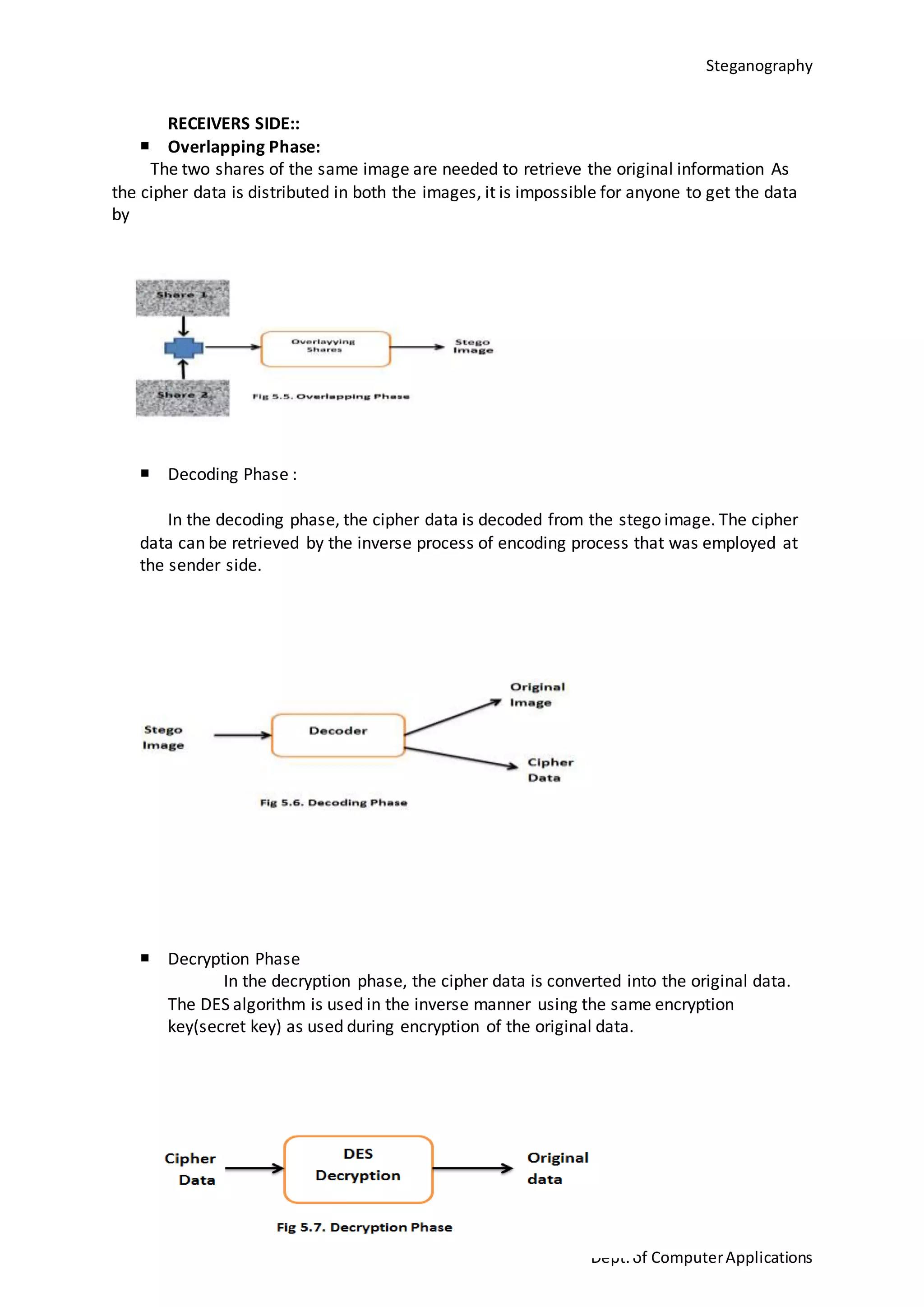
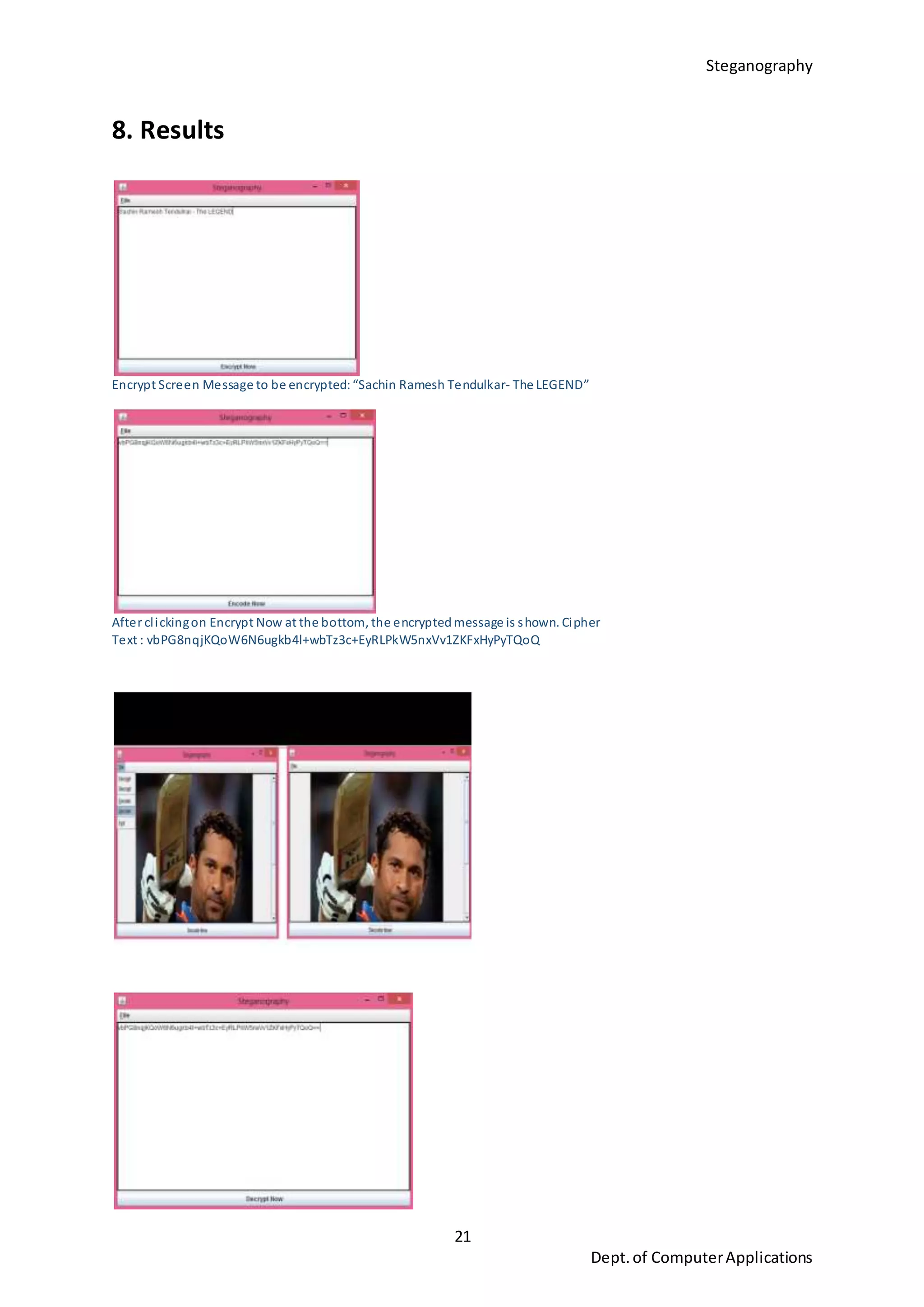
This document is a seminar report submitted by Aparna N K to the University of Kerala in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a Master of Computer Applications degree. The report discusses steganography using a genetic algorithm along with visual cryptography for wireless network applications. It provides background on steganography, cryptography, genetic algorithms, the LSB steganography algorithm, and describes a proposed system that uses LSB embedding combined with genetic algorithm pixel modification and visual cryptography to hide secret messages in images for secure transmission. The performance of the proposed system is analyzed based on metrics like mean squared error and peak signal-to-noise ratio.