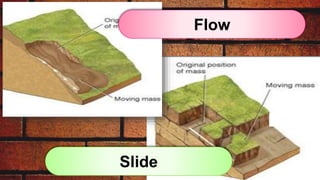
The document discusses various geologic processes of Earth including weathering, erosion, and mass wasting. It defines different types of weathering such as physical and chemical weathering. It also defines different types of mass wasting processes like falls, slides, avalanches, and flows. The document provides examples of each type of process and factors that contribute to them. It describes an activity where students identify types of rock weathering outside and factors affecting it. It also discusses designing a model to simulate rapid and slow erosion.