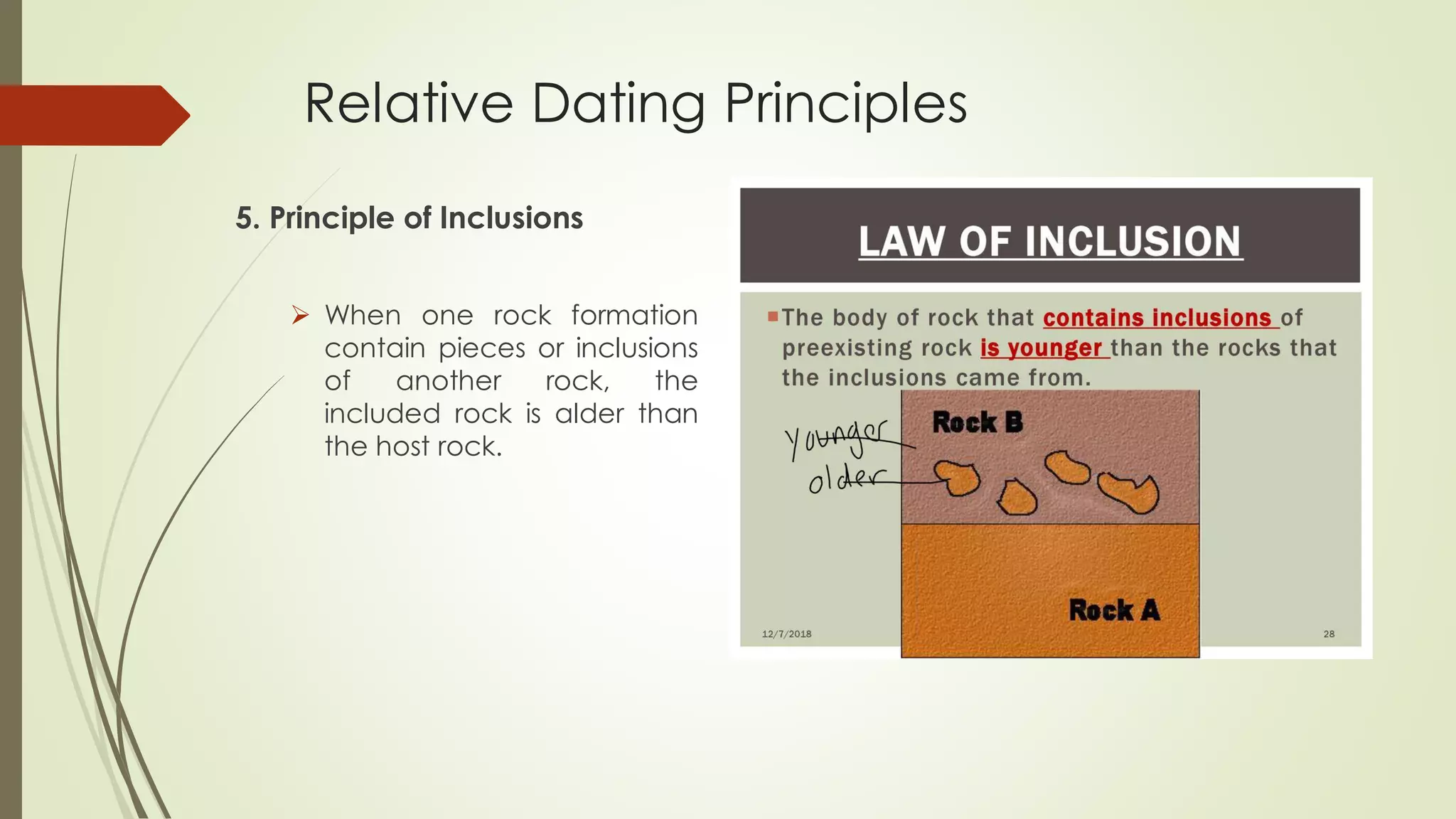
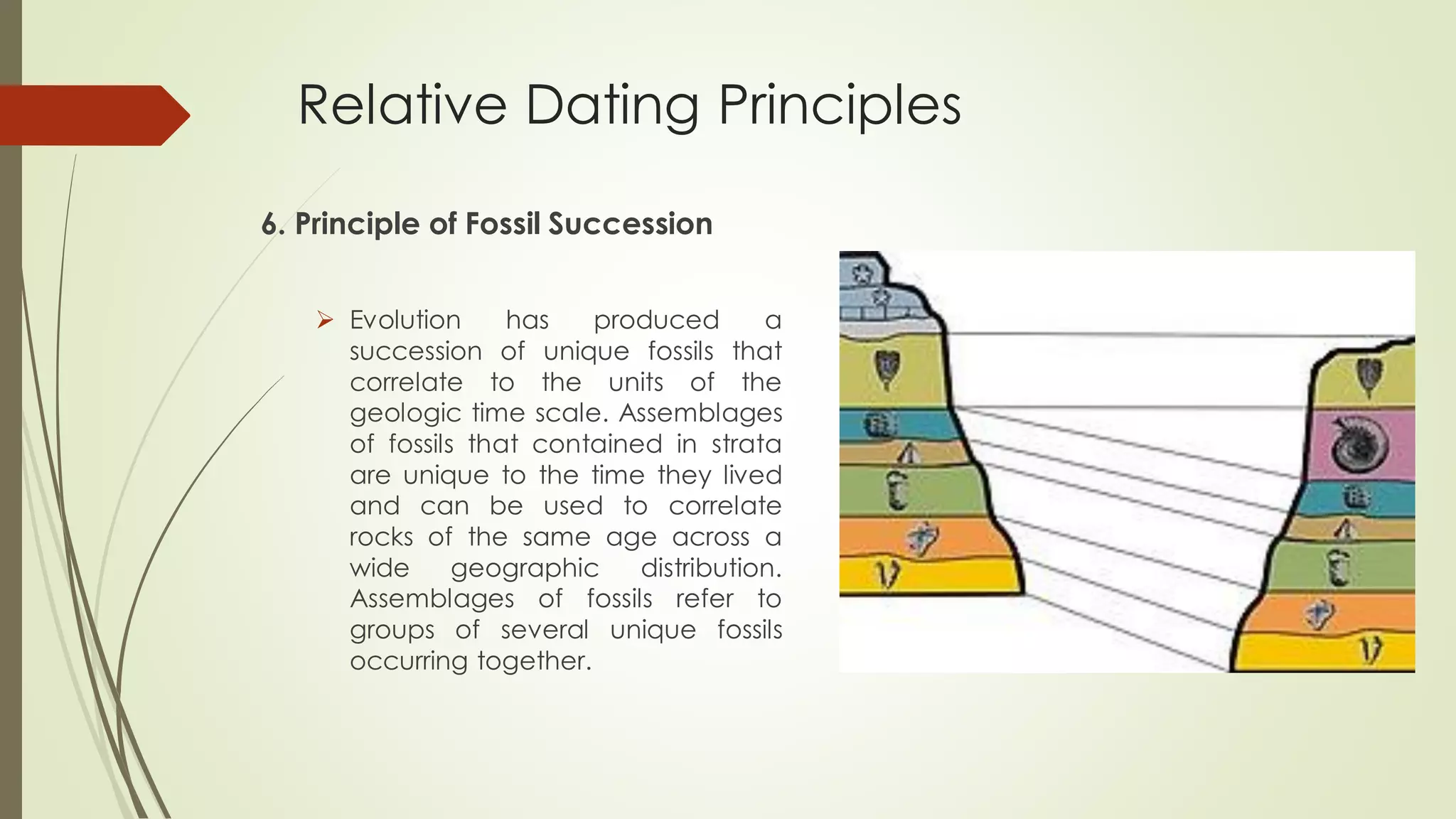
Relative dating is used to arrange geological events and rocks in a sequence without providing actual dates. It determines if one rock or event is older or younger than another based on principles like:
1) The principle of superposition states that in an undisturbed sequence, layers below are older than those above.
2) Sedimentary rocks are originally deposited horizontally according to the principle of original horizontality.
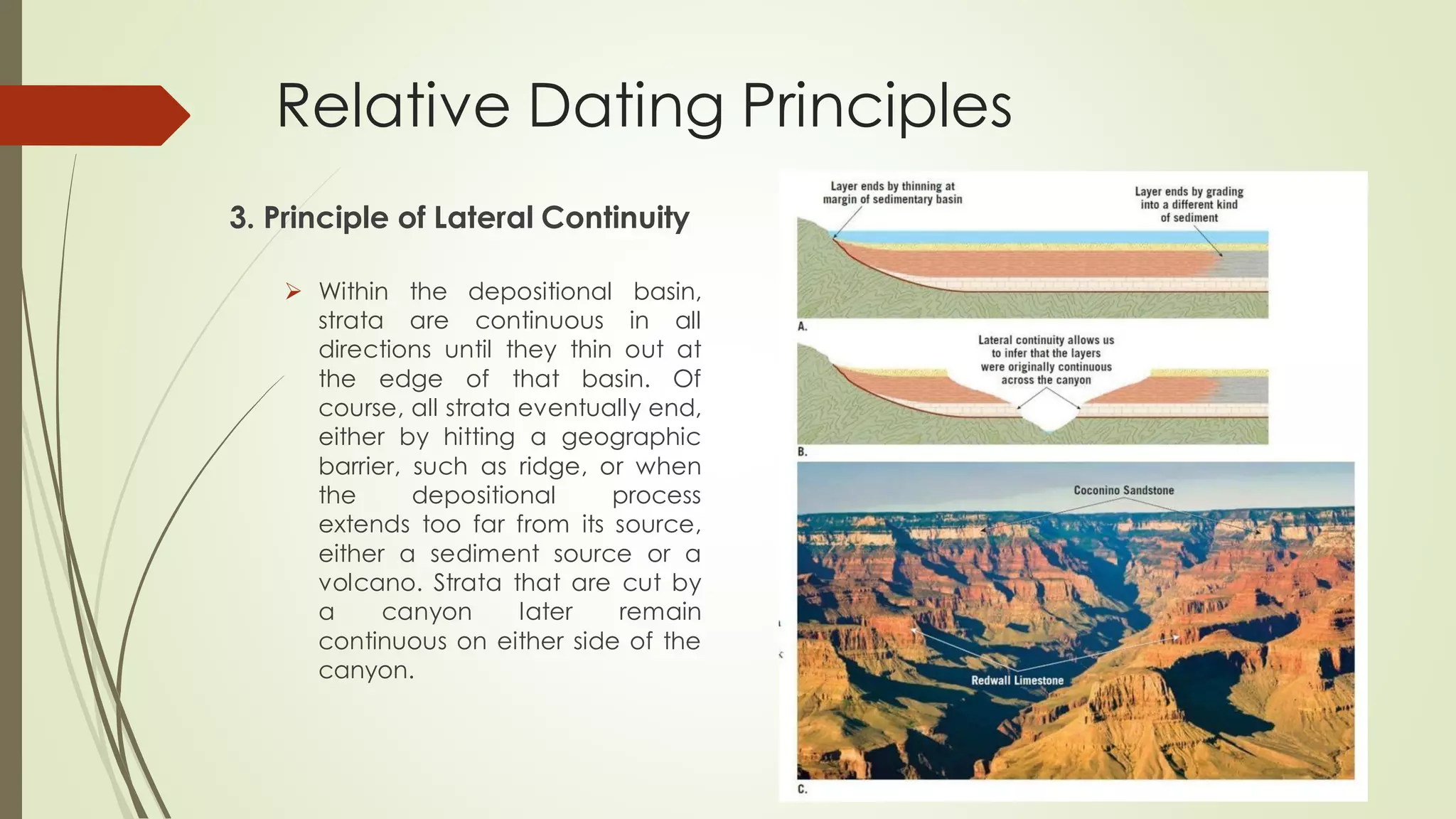
3) Within a basin, rock layers continue laterally until the edge under the principle of lateral continuity.
4) Features like faults that cut across rocks must be younger than the rocks based on the principle of cross-cutting relationships.