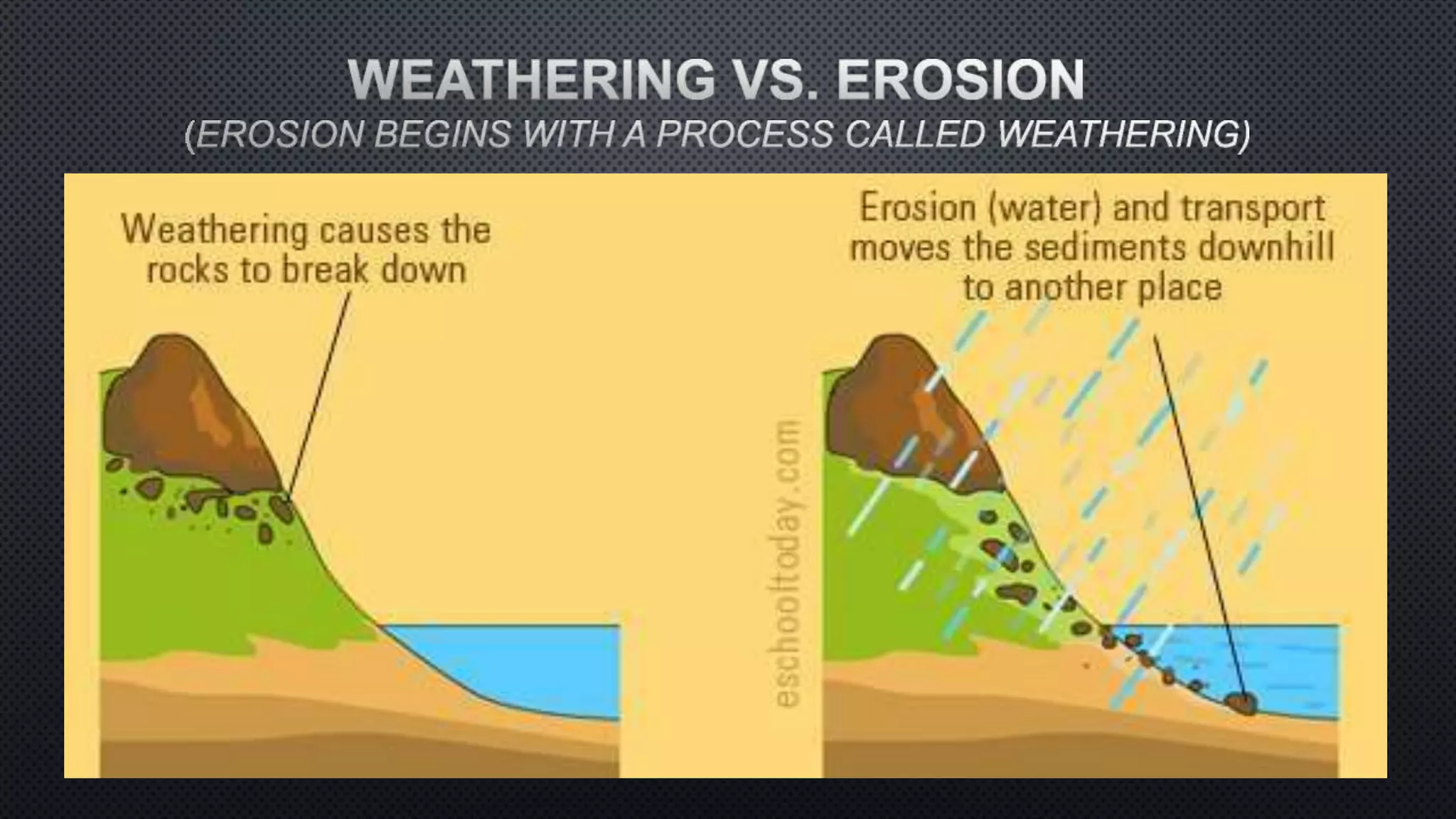
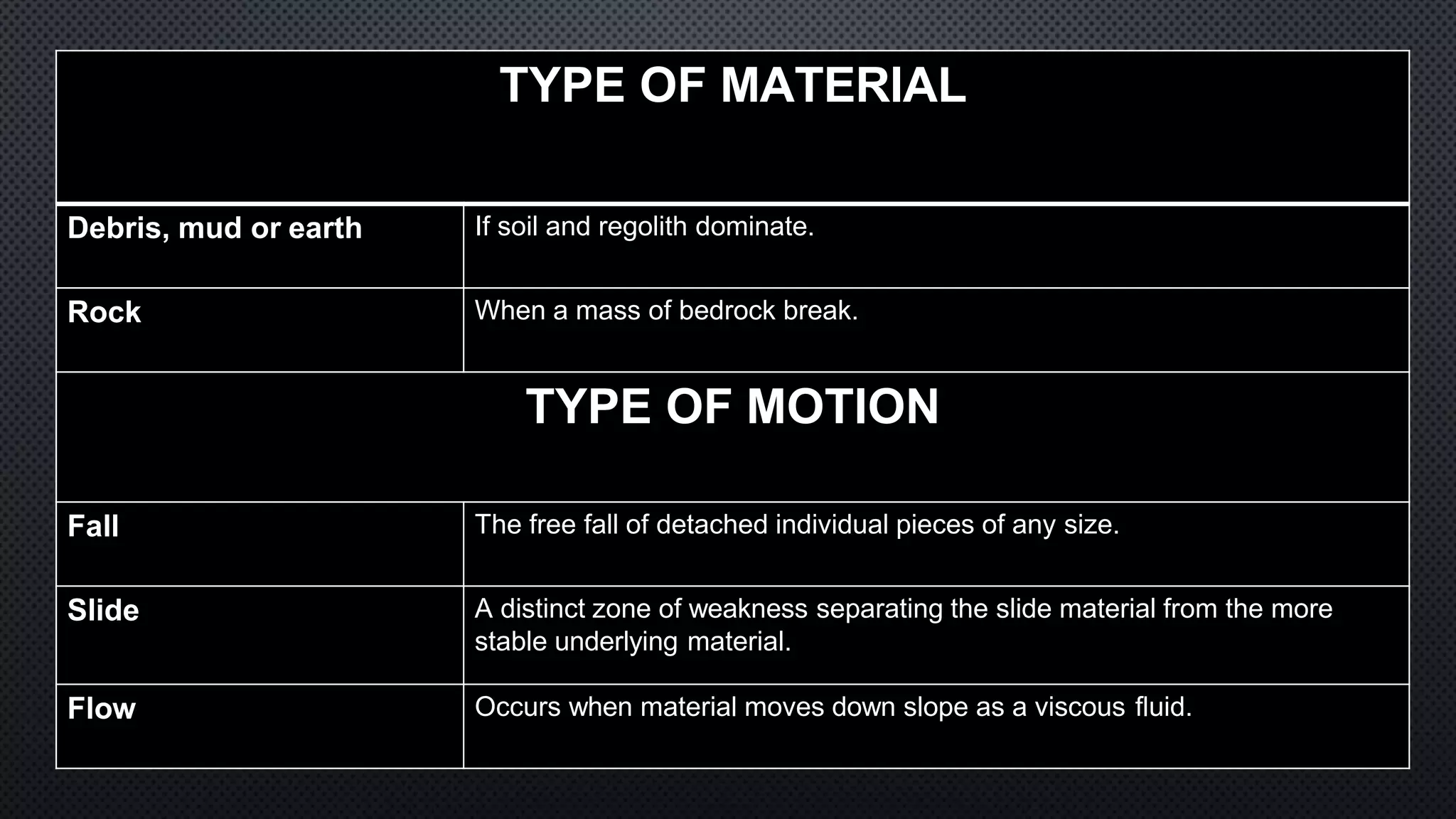
Exogenic processes are processes that take place at or near the Earth's surface that cause the surface to wear away through physical and chemical weathering. Some physical weathering processes include ice wedging, release of pressure, growth of plants, animals burrowing, and abrasion by wind and water. Chemical weathering breaks down rock through processes like reaction with water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, acids, and living organisms. Erosion by various agents like water, wind, ice and gravity further transports weathered materials and shapes the landscape over time.