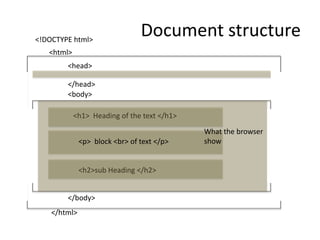
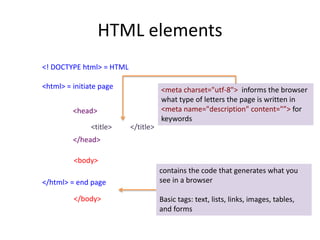
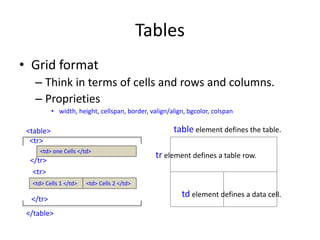
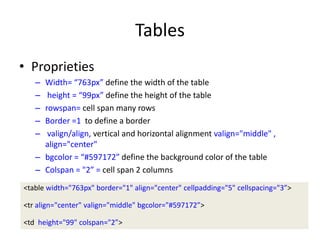
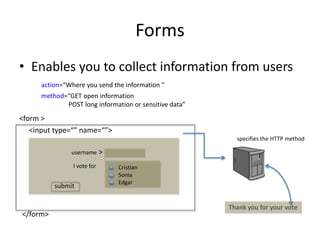
This document provides an overview of HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) including basic concepts, elements, and structure. It discusses HTML as a markup language interpreted by web browsers to define the structure of web pages and present content. The key elements covered include text formatting, lists, hyperlinks, images, tables, and forms. It also discusses HTML5 additions and differences between HTML and XHTML.