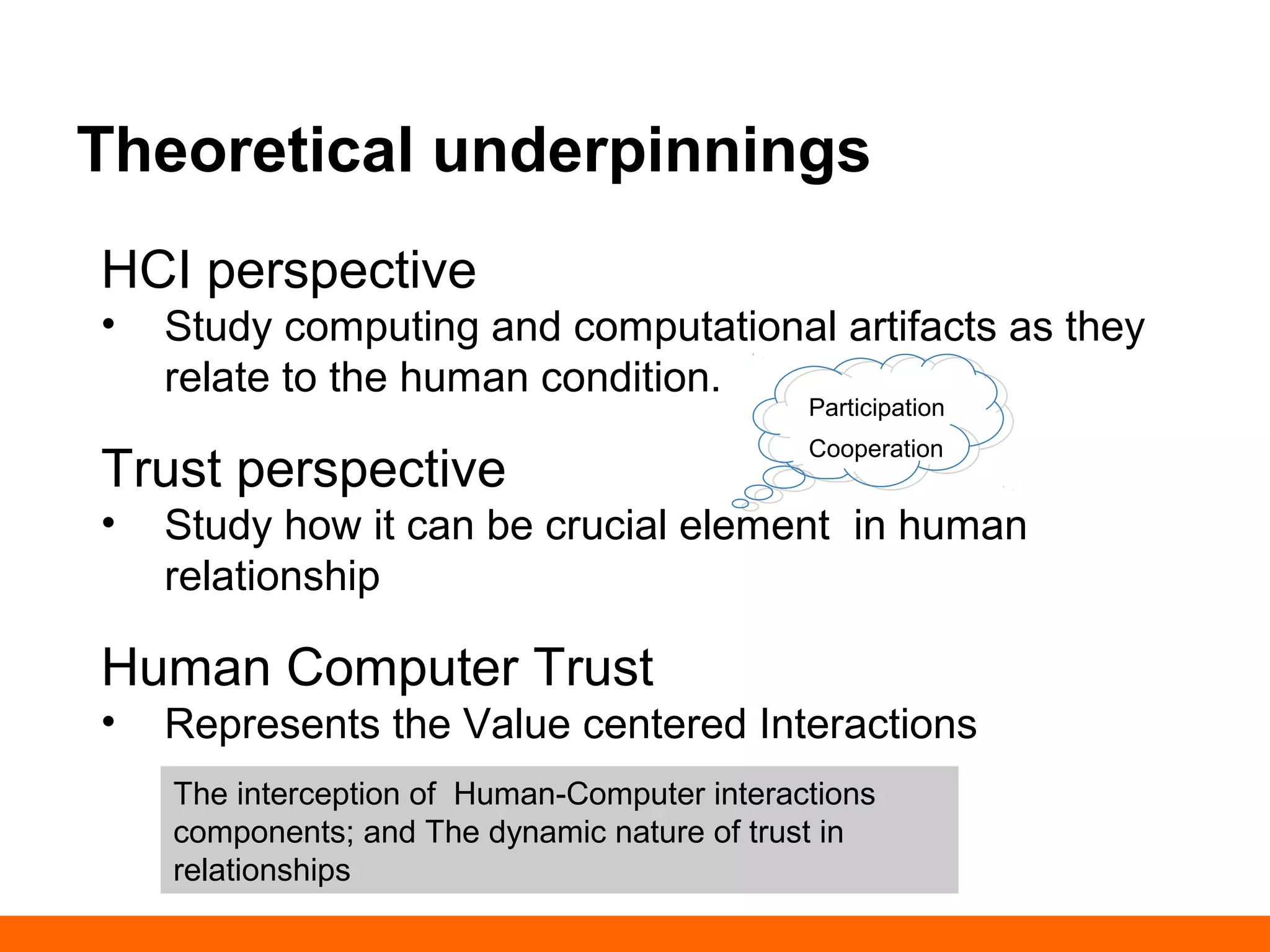
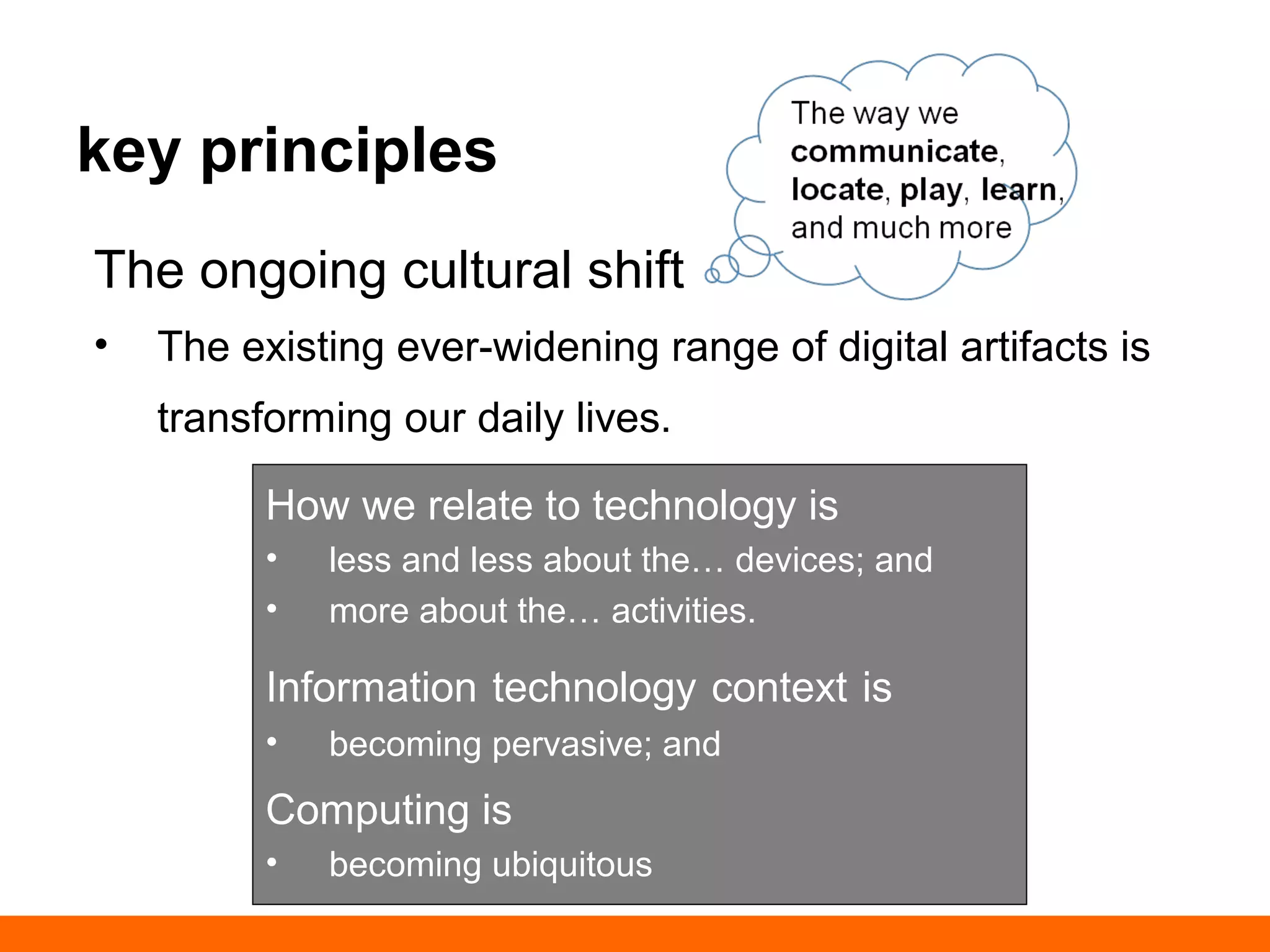
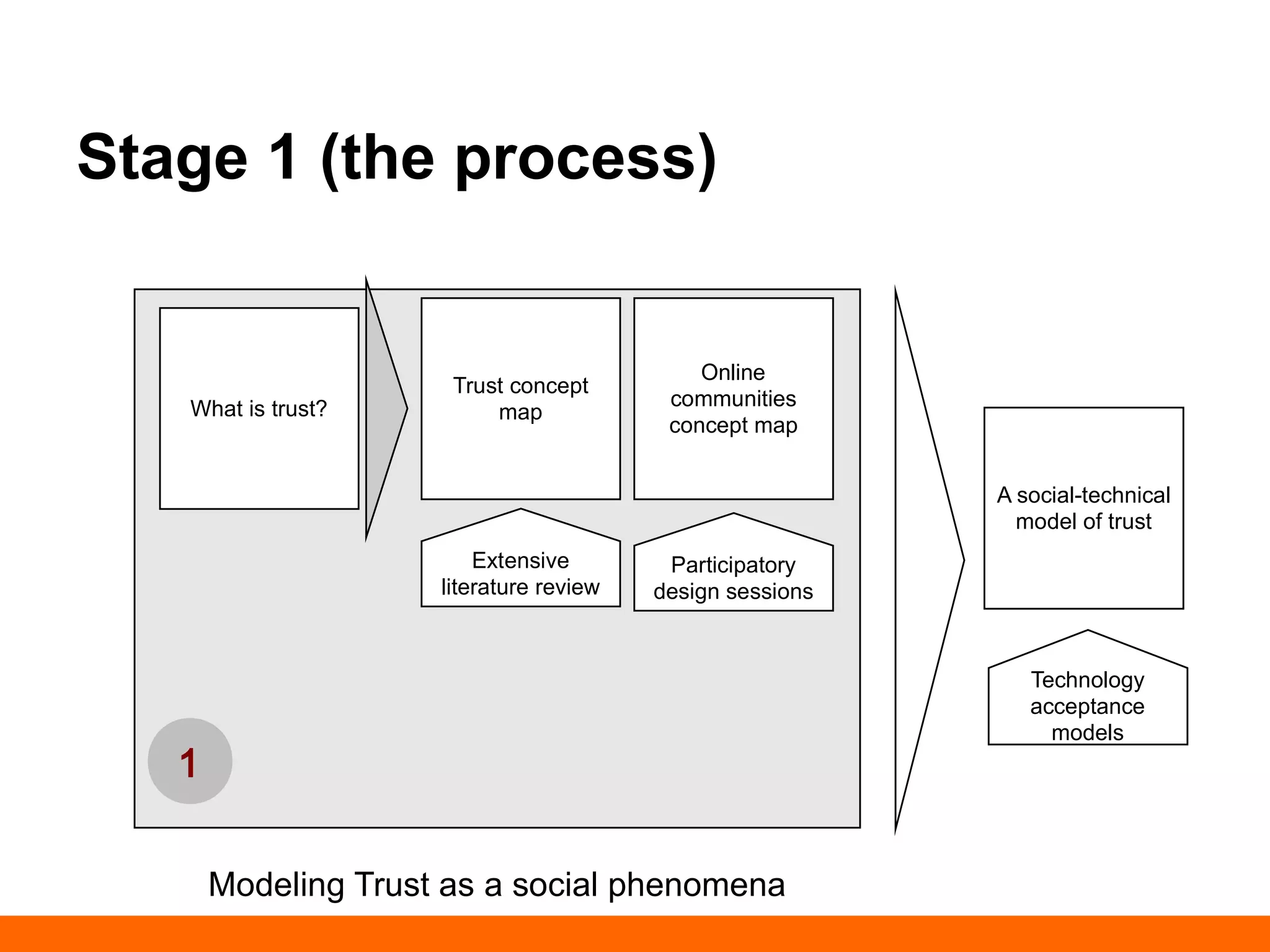
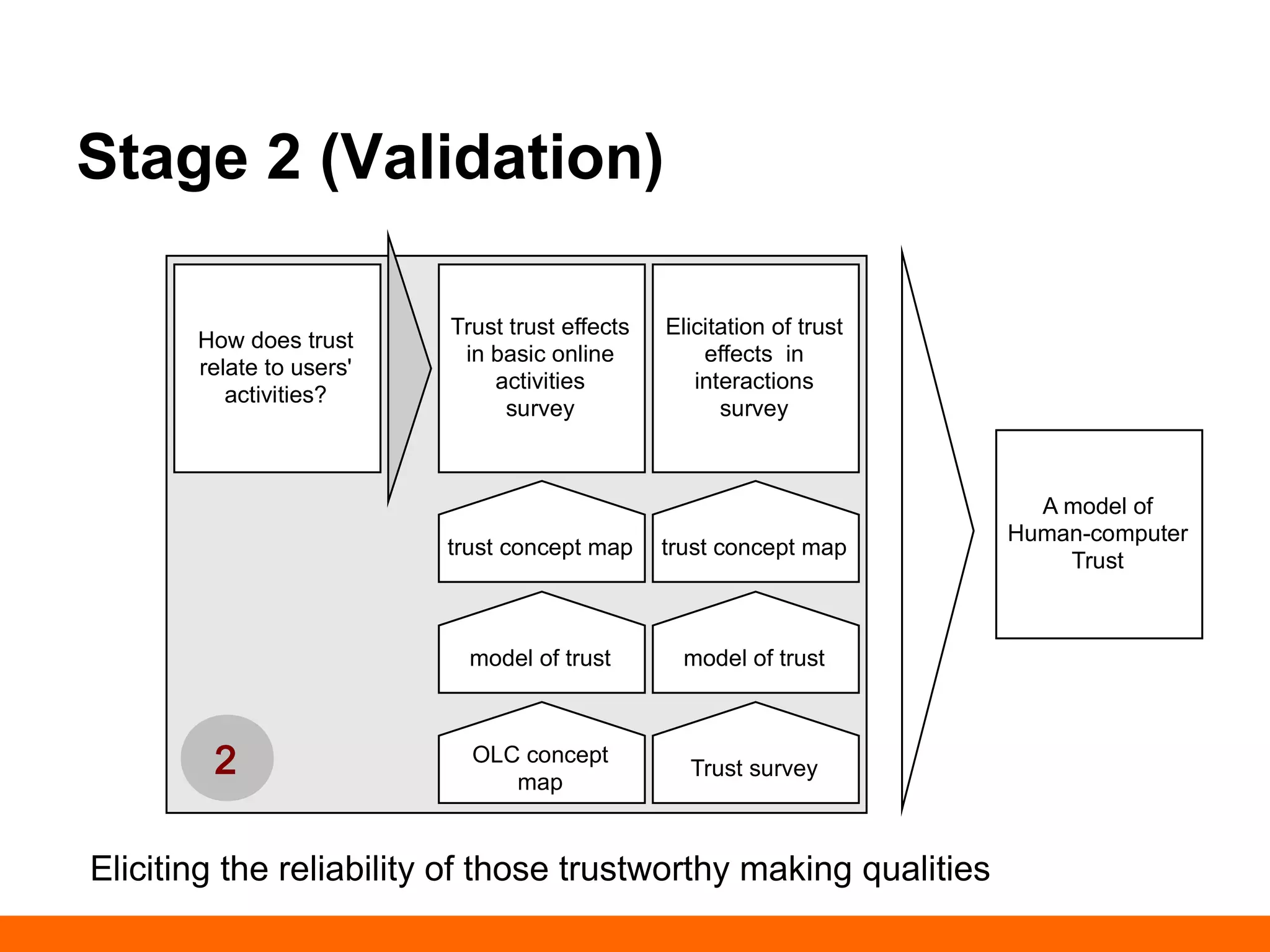
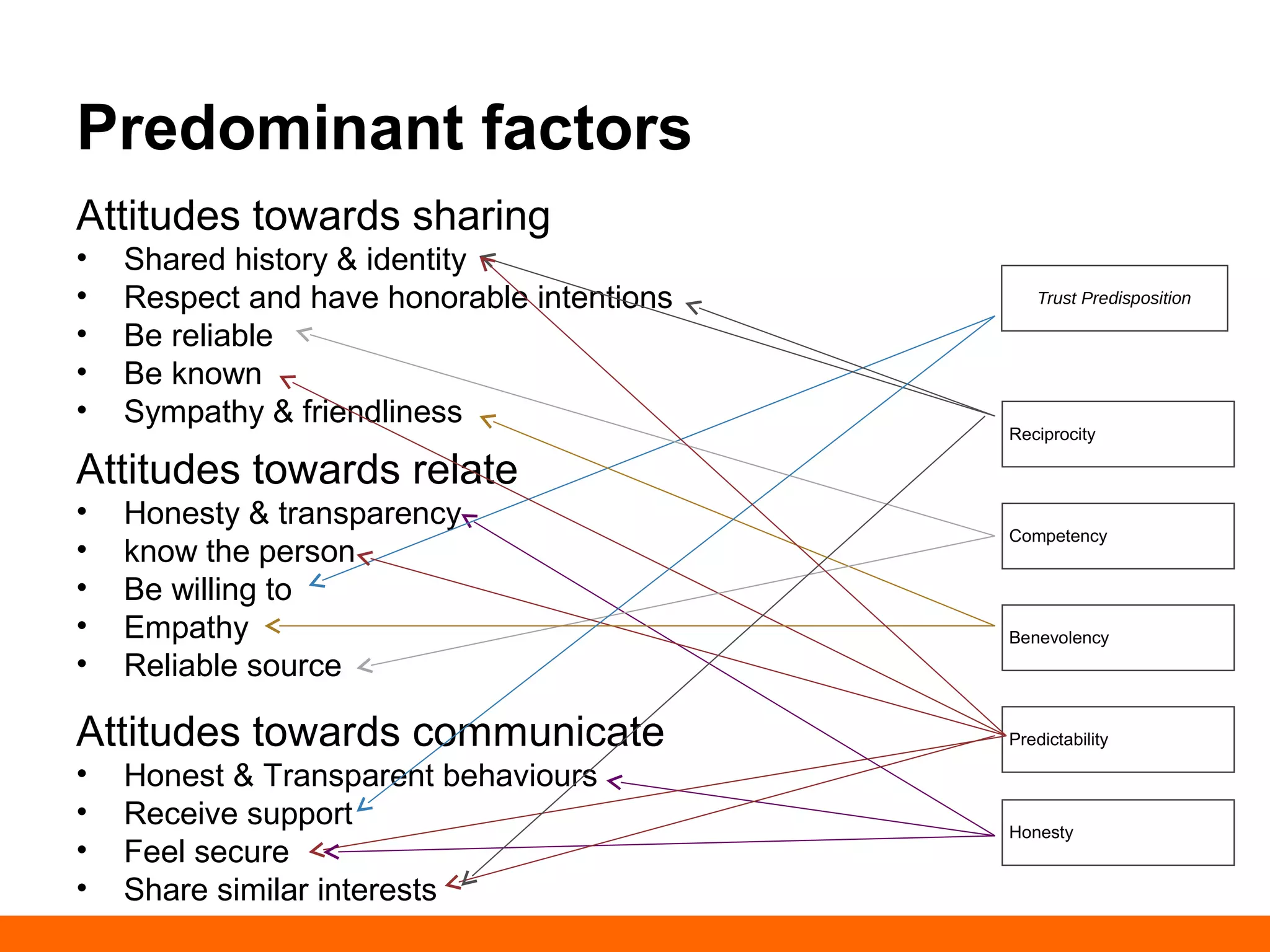
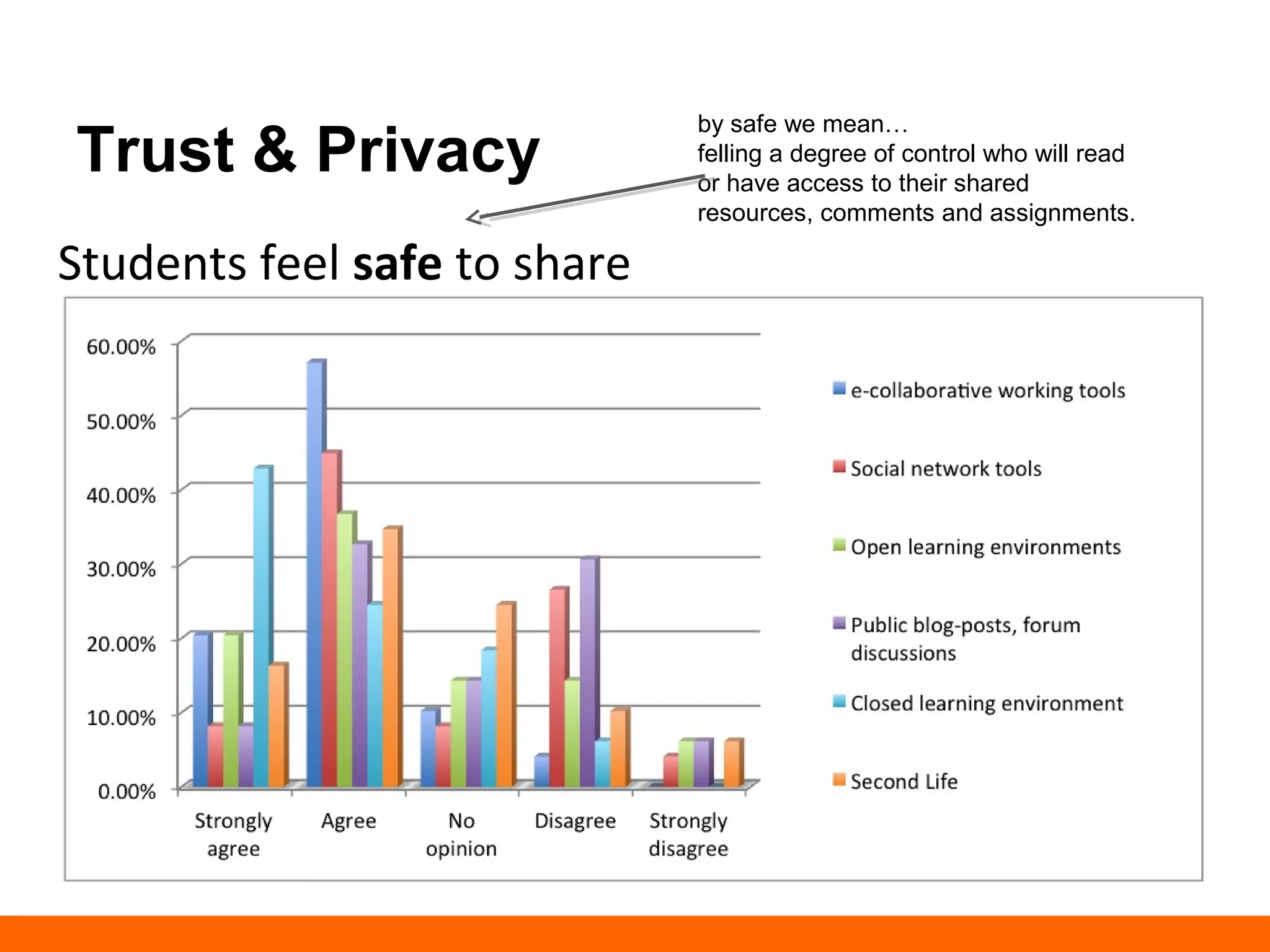
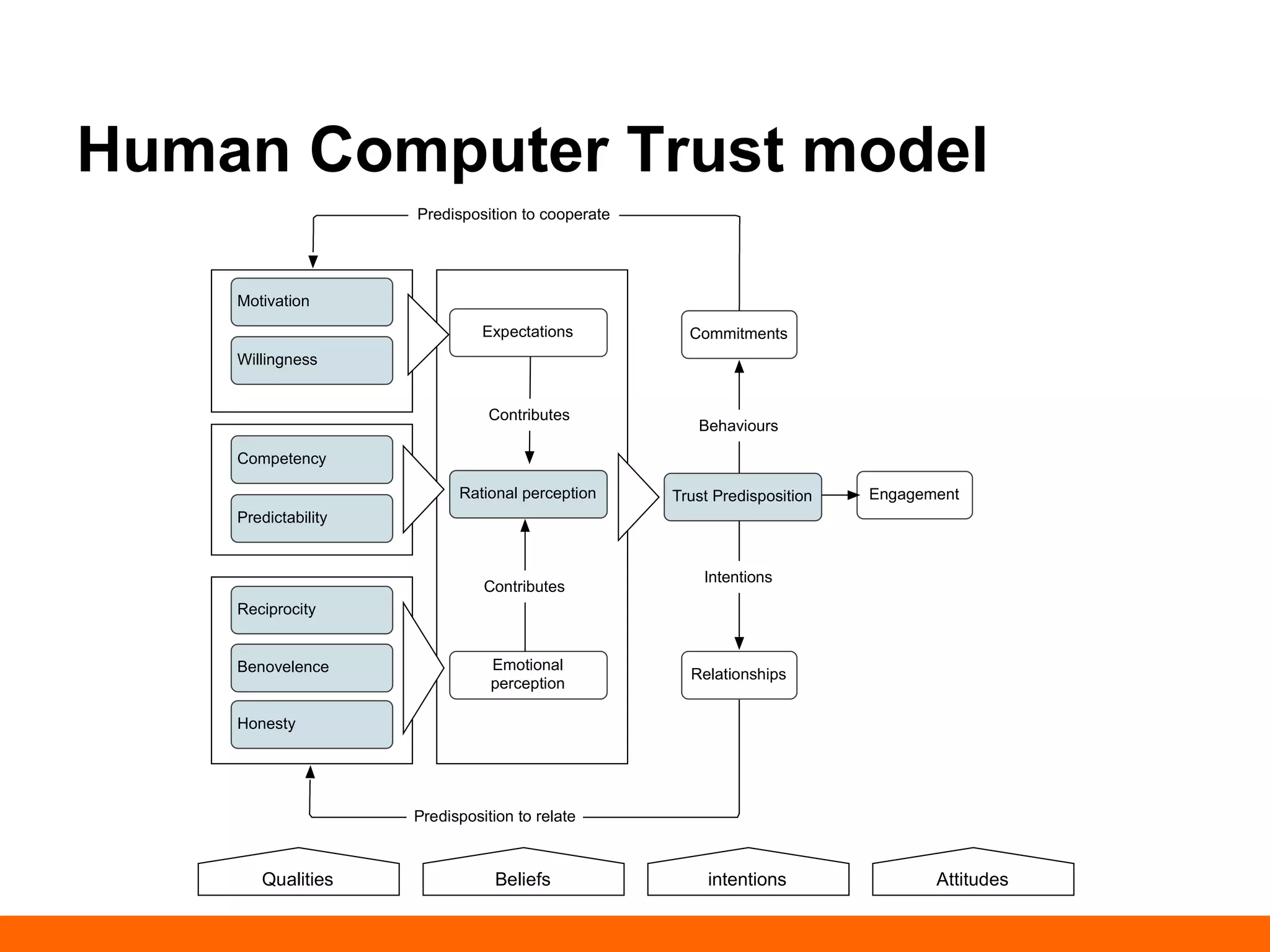
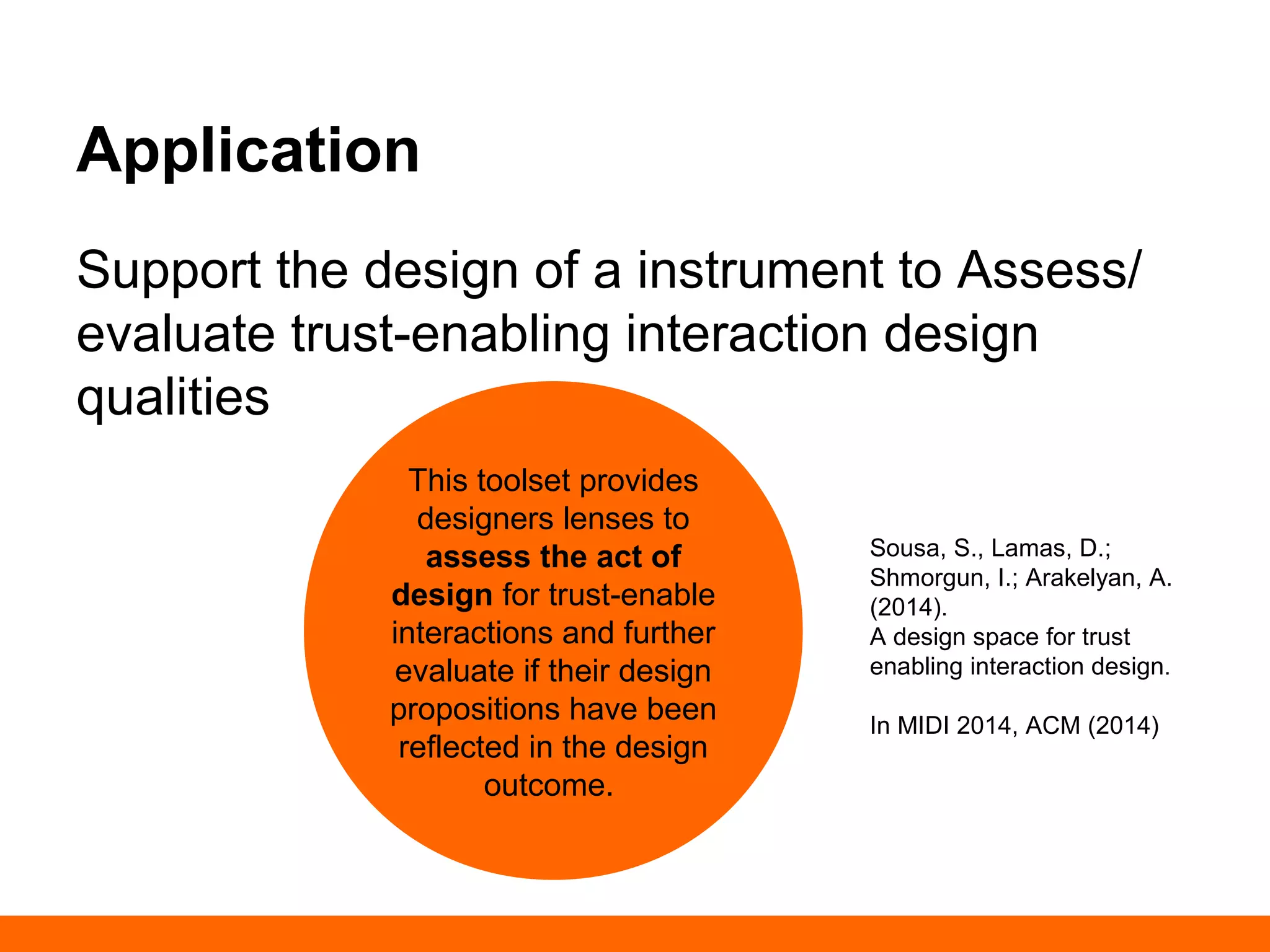
This document discusses human-computer trust from both an HCI and trust perspective. It examines trust as a crucial element in human relationships and represents value-centered interactions between humans and computers. The research aims to identify the social values and qualities that underlie people's trust beliefs and how those trustworthy qualities are represented with technology becoming more ubiquitous. Through literature reviews and participatory design sessions, the research models trust as a social phenomenon and validates how trust relates to users' activities. It identifies factors like honesty, reliability, and predictability that influence users' attitudes around sharing, relating, and communicating. The results are used to develop a model of human-computer trust and a design space toolset to assess and evaluate trust-en