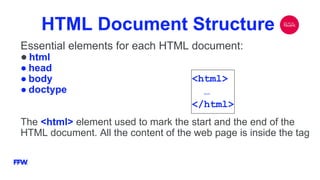
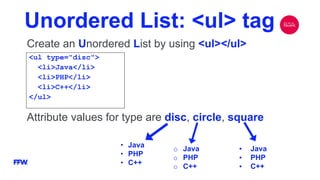
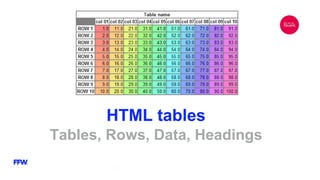
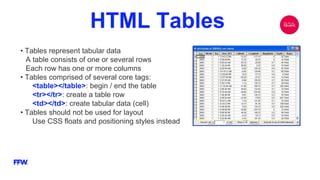
The document is a comprehensive overview of HTML, its history, structure, and common elements used in web development. It details the creation of HTML documents, key tags, attributes, and elements, as well as best practices for writing valid HTML. Additionally, it explains the role of W3C in maintaining standards and includes examples of different HTML components like forms, tables, and lists.