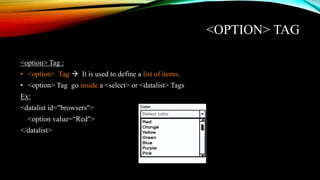
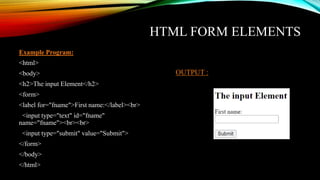
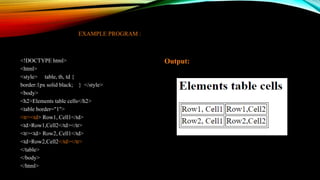
The document provides an overview of HTML (Hyper Text Markup Language) including its structure, essential tags, elements, and forms used in web development. It covers topics such as input fields, lists, links, tables, and the evolution of HTML5, highlighting new features and comparisons with HTML4. Additionally, it contains example code demonstrating various HTML components and their usage.