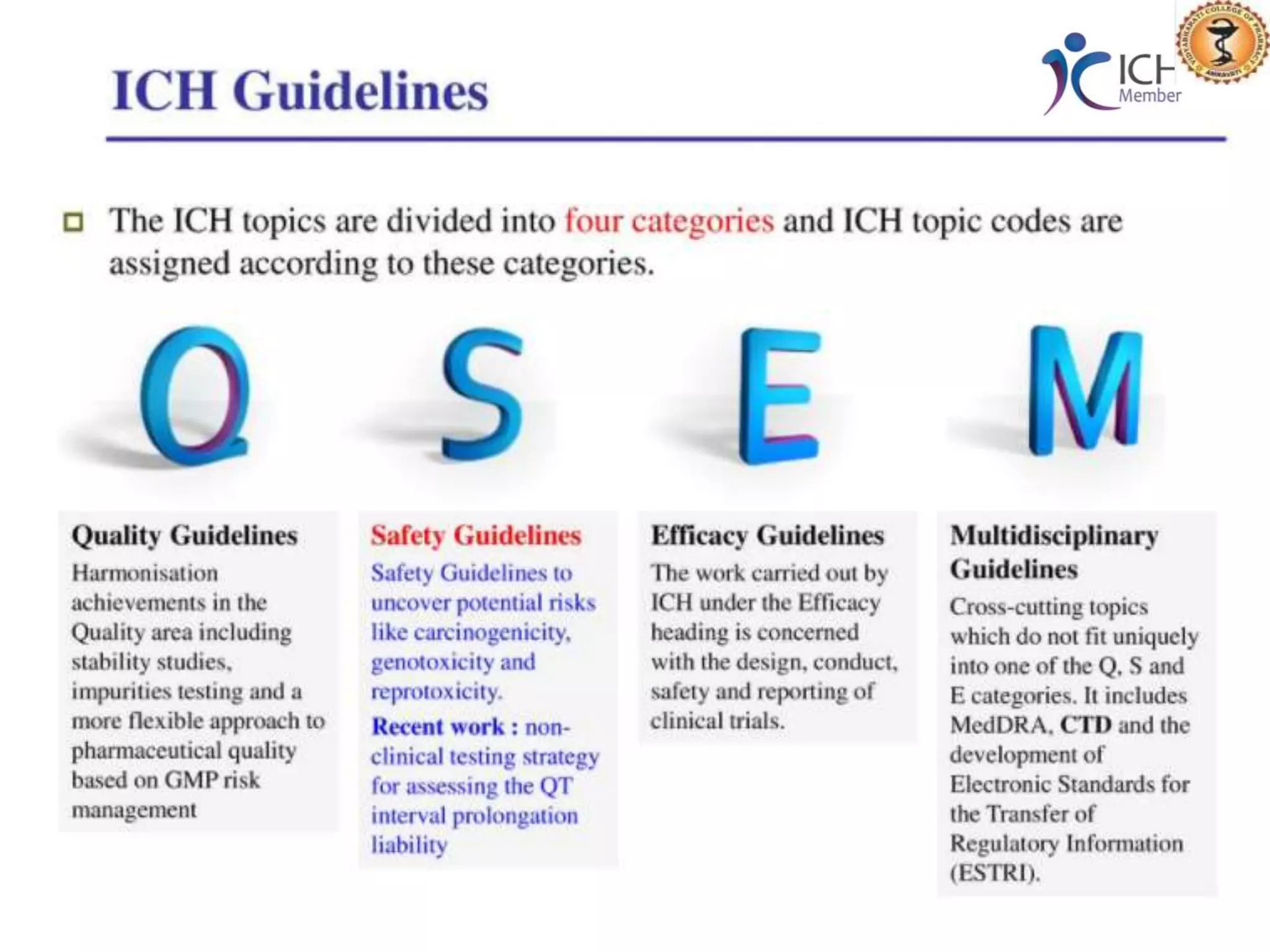
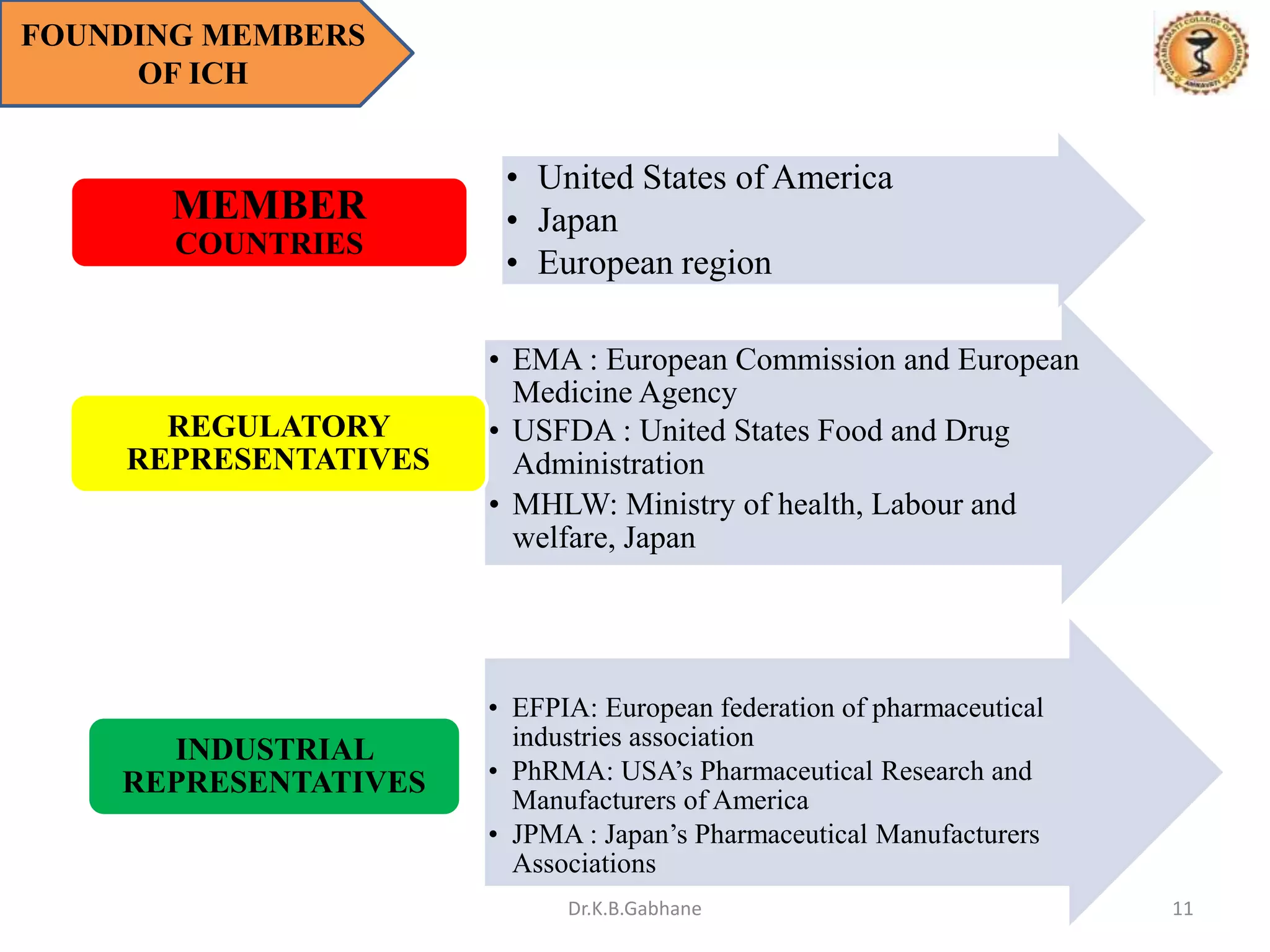
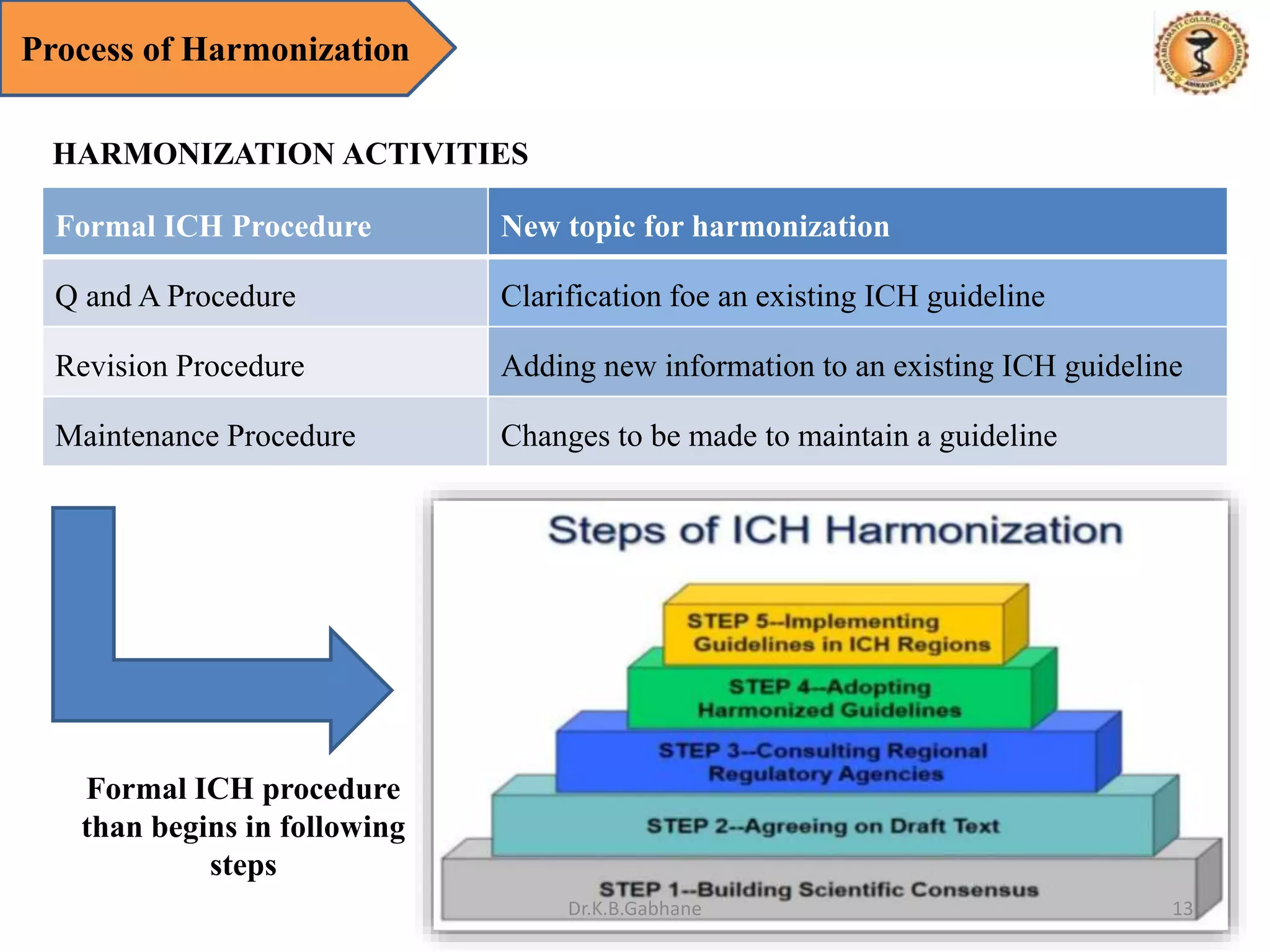
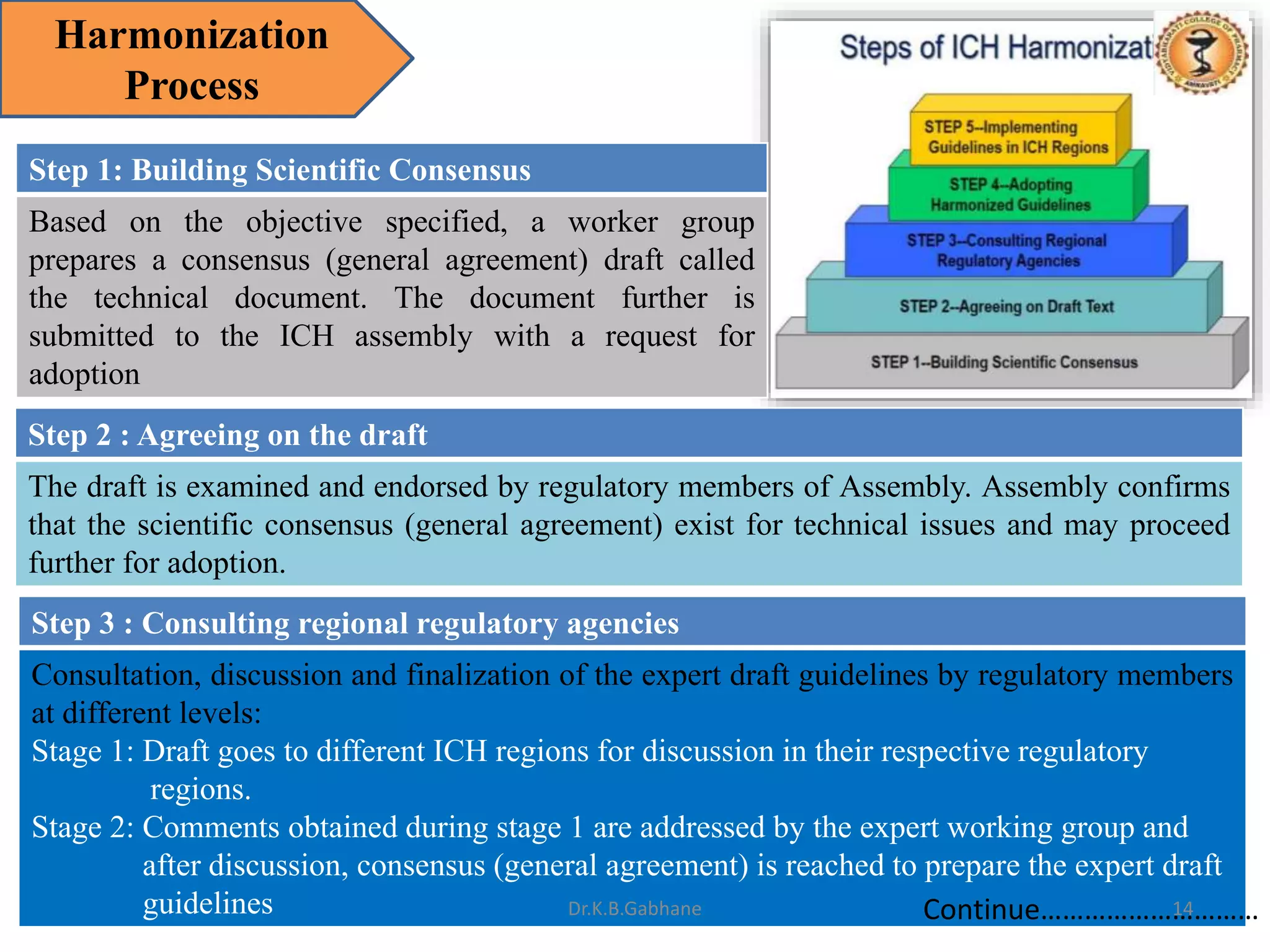
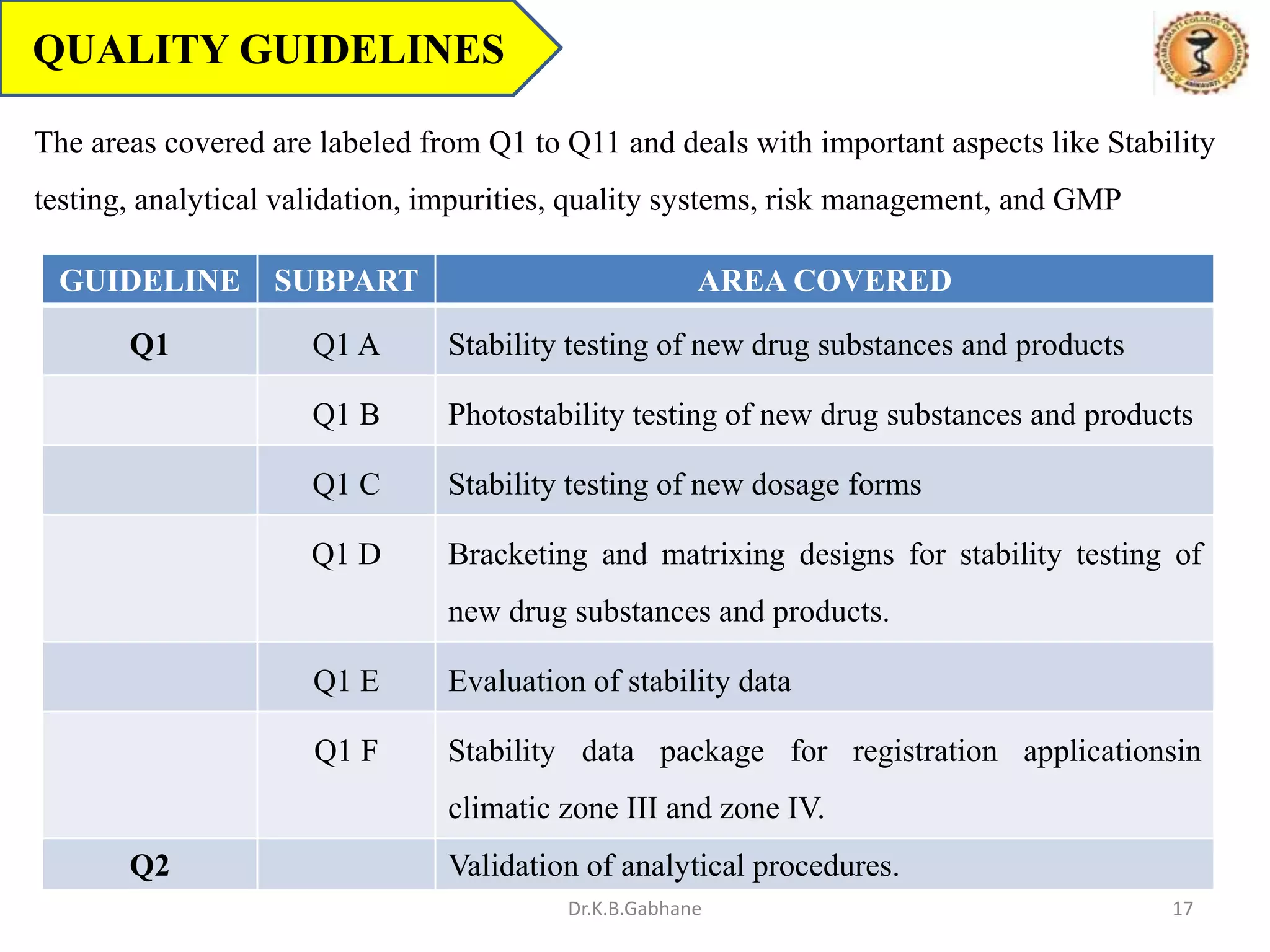
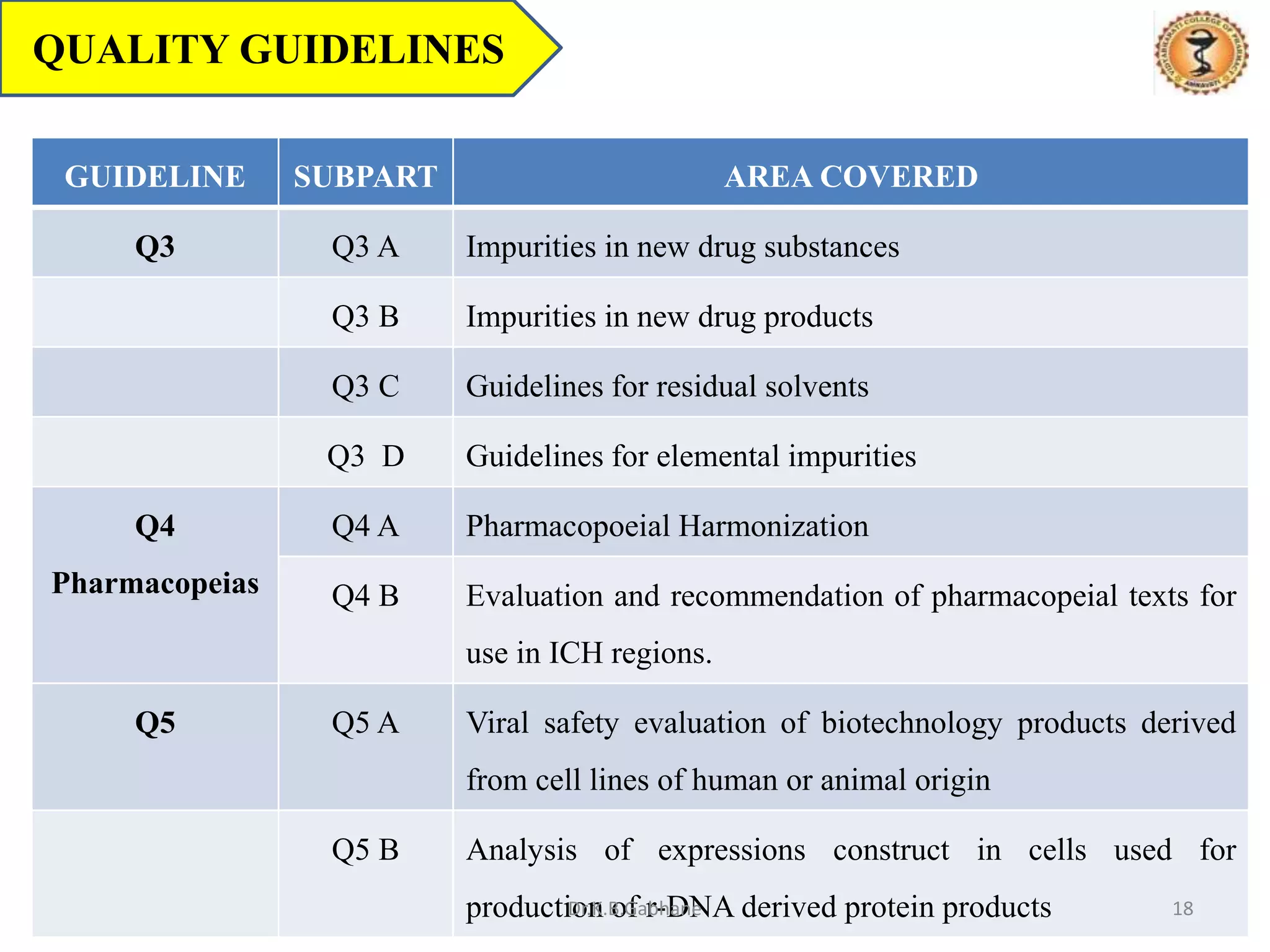
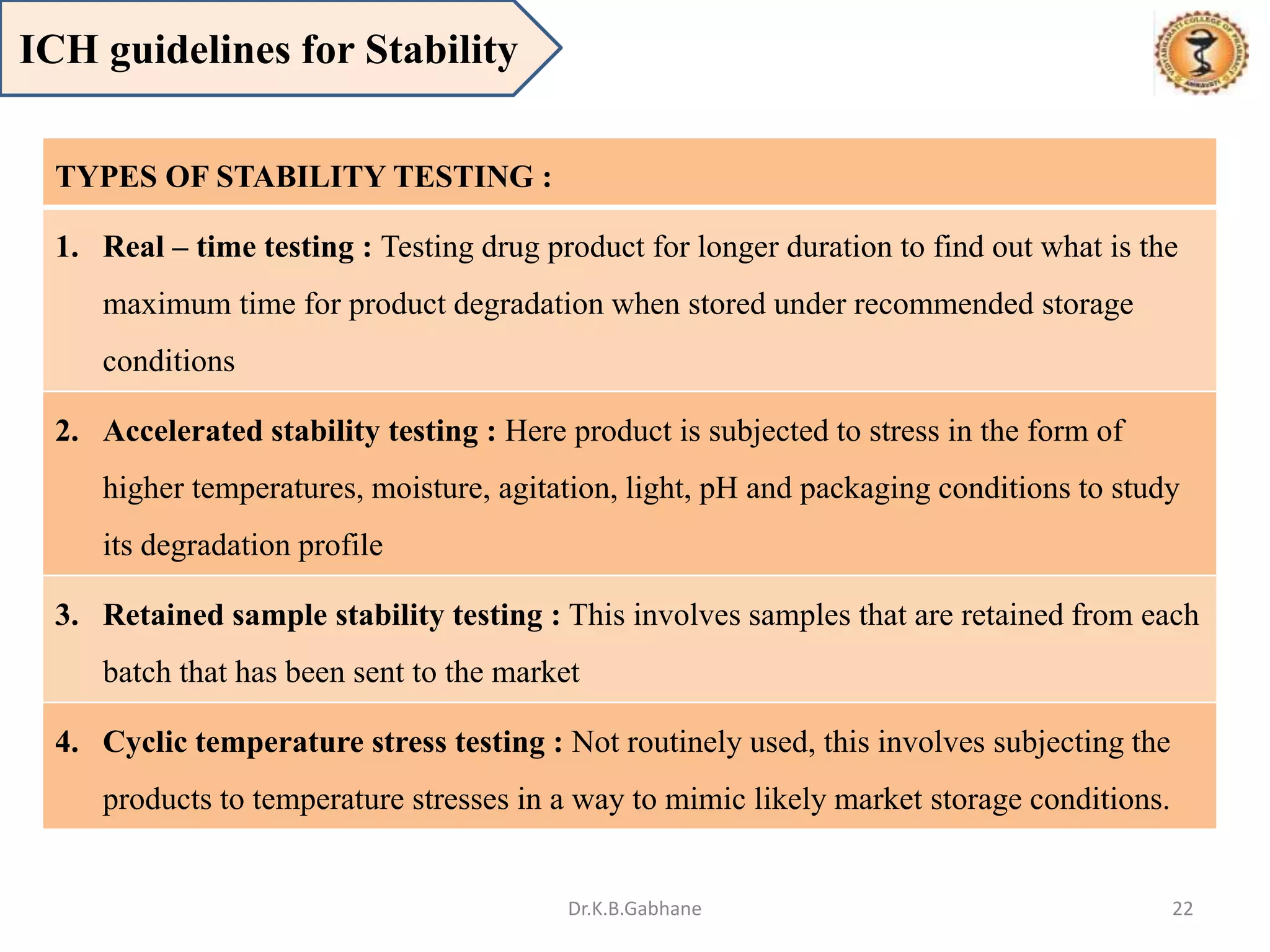
The document outlines the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) guidelines, focusing on the harmonization of technical requirements for drug registration to enhance safety, efficacy, and quality while minimizing redundancy in clinical trials. It details the objectives, organizational structure, and process of harmonization, covering aspects such as stability testing, quality guidelines, and risk management. The guidelines aim to streamline the registration process across regions like the USA, Japan, and the EU, ensuring that once a drug is registered in one region, additional testing in others is not necessary.