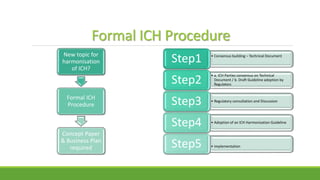
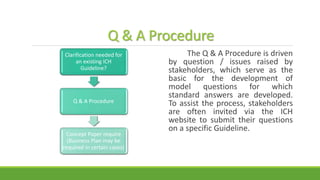
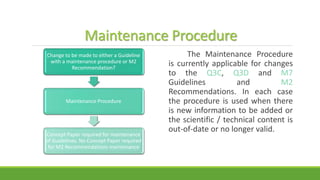
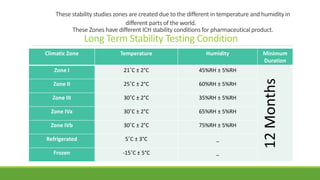
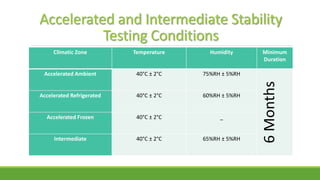
The document summarizes information from the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) website. ICH is an international body that brings together regulatory authorities and the pharmaceutical industry to discuss guidelines for drug development and regulation. The document outlines ICH's history, mission, members and observers, processes for harmonizing guidelines, and categories of guidelines related to quality, safety, efficacy, and multidisciplinary topics. It provides details on ICH guidelines for stability testing, analytical validation, impurities, and other quality-related topics.