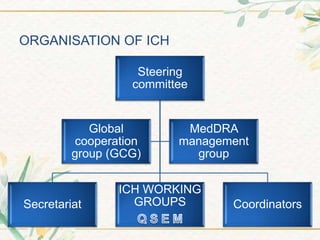
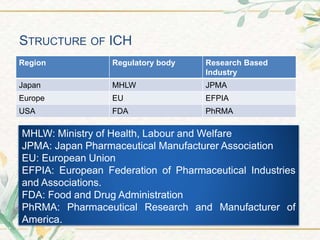
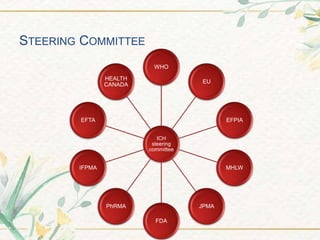
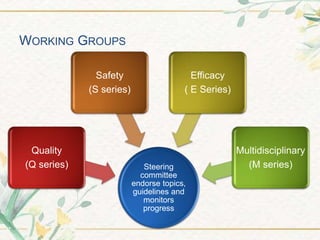
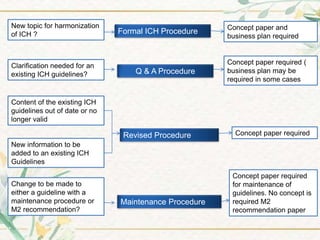
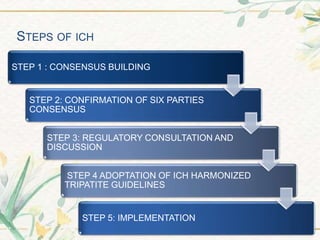
The document discusses the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) guidelines. It provides definitions for ICH as a joint initiative between regulators and industry in the EU, Japan, and US to harmonize technical requirements for pharmaceutical registration. The objectives of ICH are outlined as increasing harmonization to ensure safe, effective, and high quality medicines are developed efficiently. The organizational structure and processes of ICH are described, including its steering committee, working groups, and 5 step guideline development process. An overview is provided of the various ICH guidelines categories including quality, safety, efficacy, and multidisciplinary guidelines. Specific stability testing guidelines are also briefly discussed.