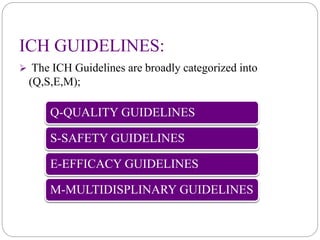
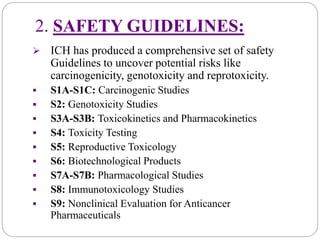
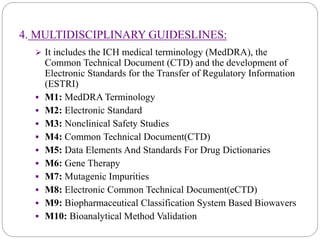
The document discusses the International Council for Harmonization of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) guidelines. It provides an introduction to ICH, the need for harmonization, the origin and evolution of ICH, its objectives and members. It then describes the process of ICH harmonization and provides examples of ICH guidelines related to quality, safety, efficacy, and multidisciplinary topics. The quality guidelines address stability testing, impurities thresholds, and good manufacturing practices.