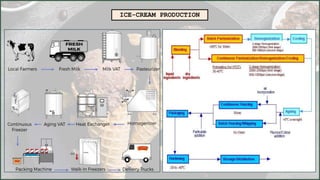
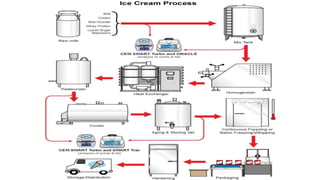
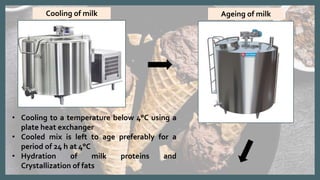
This document summarizes the process of ice cream production. It begins with raw milk from dairy farms which is pasteurized and homogenized. The milk is then cooled, aged, and has flavors and colors added before undergoing continuous freezing and blast freezing. Finally, the frozen ice cream is packaged in various containers like cups, tubs, or cones before being hardened for consumption or storage.