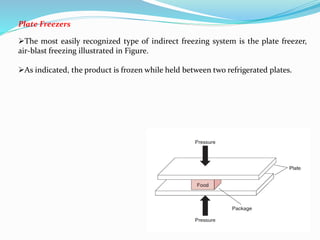
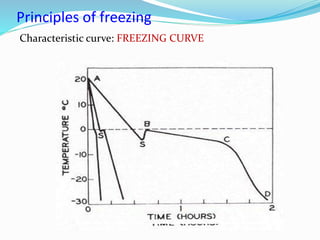
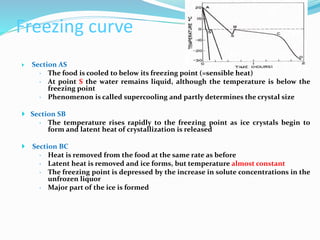
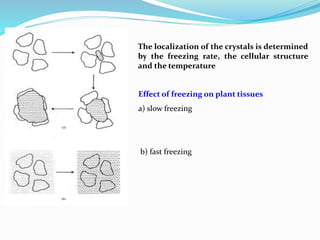
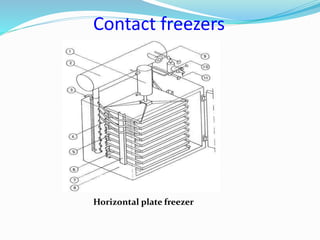
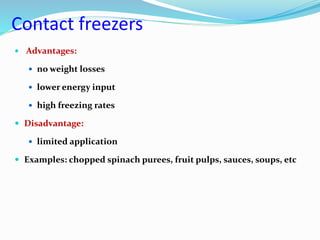
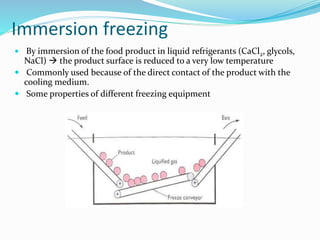
Freezing food involves lowering the temperature so that water inside the food freezes into ice crystals. This process is known as freezing and involves three stages: cooling the food below its freezing point, water changing state to form ice crystals, and further cooling to the freezer temperature for preservation. The rate of freezing impacts crystal size, with fast freezing producing smaller crystals and maintaining food quality better than slow freezing. Proper frozen storage is also important to prevent quality loss from physical, chemical, biochemical, and microbial changes over time. Maintaining temperatures lower than -18°C can help secure food quality and avoid issues like recrystallization according to the time, temperature, tolerance theory of frozen food storage.