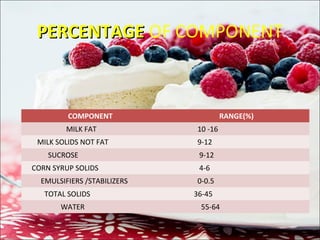
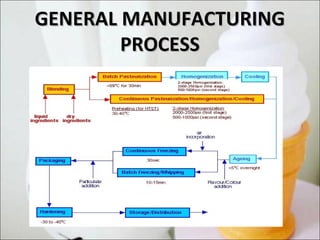
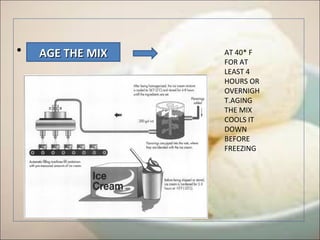
Ice cream manufacturing involves blending ingredients like cream, milk, sugar and emulsifiers. The mix is pasteurized, homogenized and aged before freezing in batch or continuous freezers. Flavors and mix-ins are added during freezing. The frozen ice cream is hardened, packaged and stored at low temperatures. Quality control tests ensure safety by checking for contaminants. Proper handling of ingredients and sterilization of mix-ins helps prevent risks to the finished product.