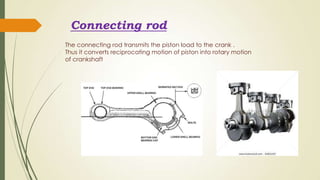
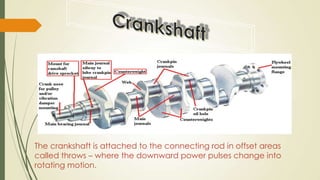
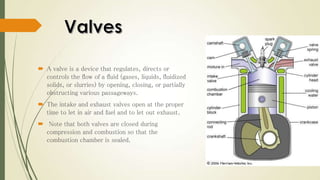
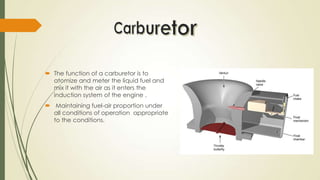
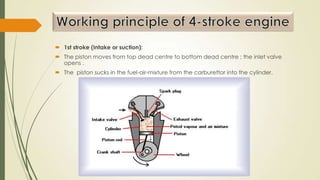
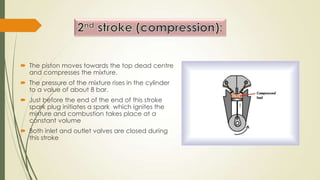
The document discusses heat engines and internal combustion engines. It defines heat engines as engines that convert heat energy from fuel combustion into mechanical work. It describes internal combustion engines as a type of heat engine that can be classified based on their combustion cycle, cylinder arrangement, ignition method, cooling method, and more. The document outlines the common parts of internal combustion engines like the cylinder, piston, valves, and differences between parts of gasoline and diesel engines. It also provides details on 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine cycles.