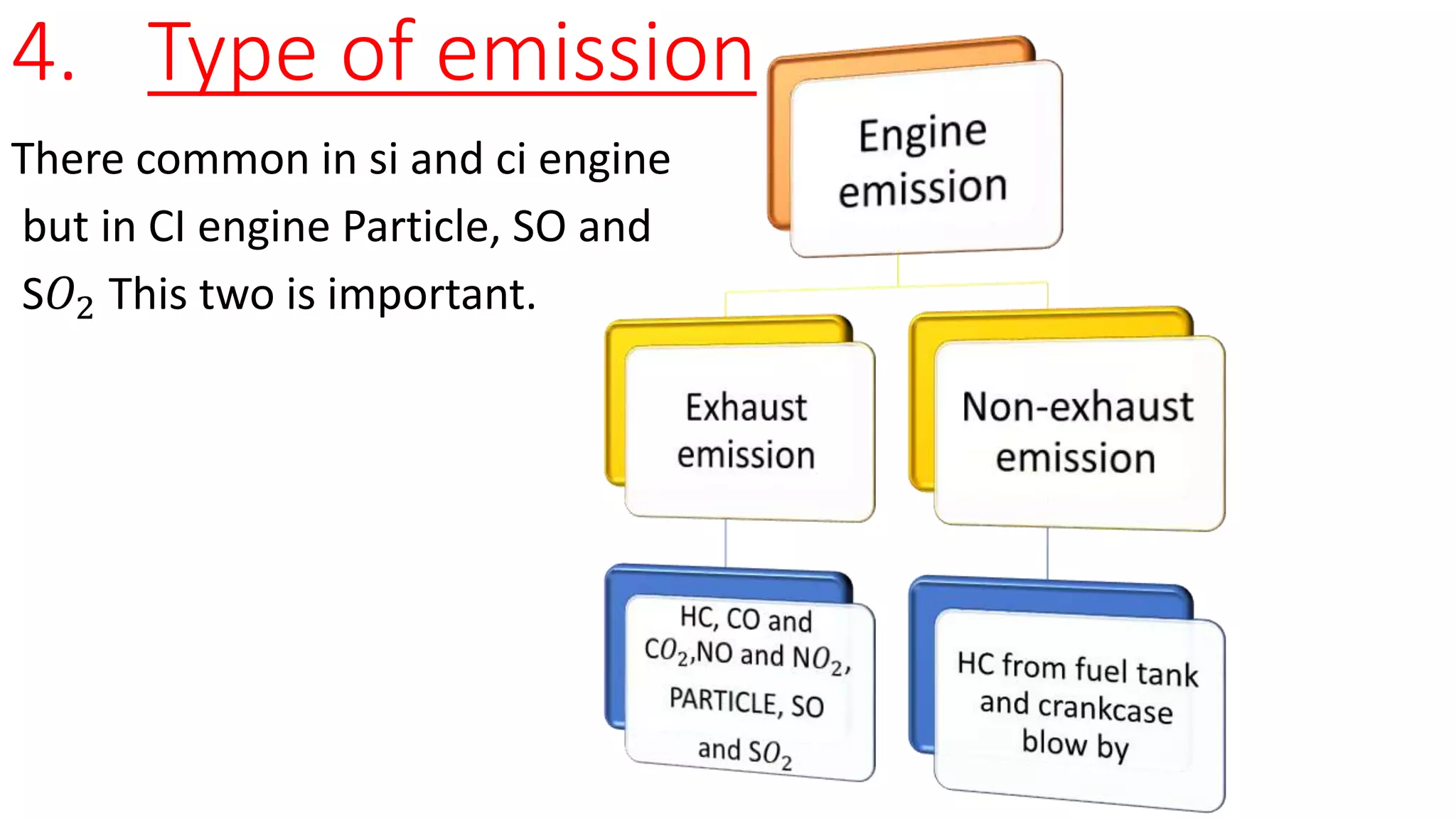
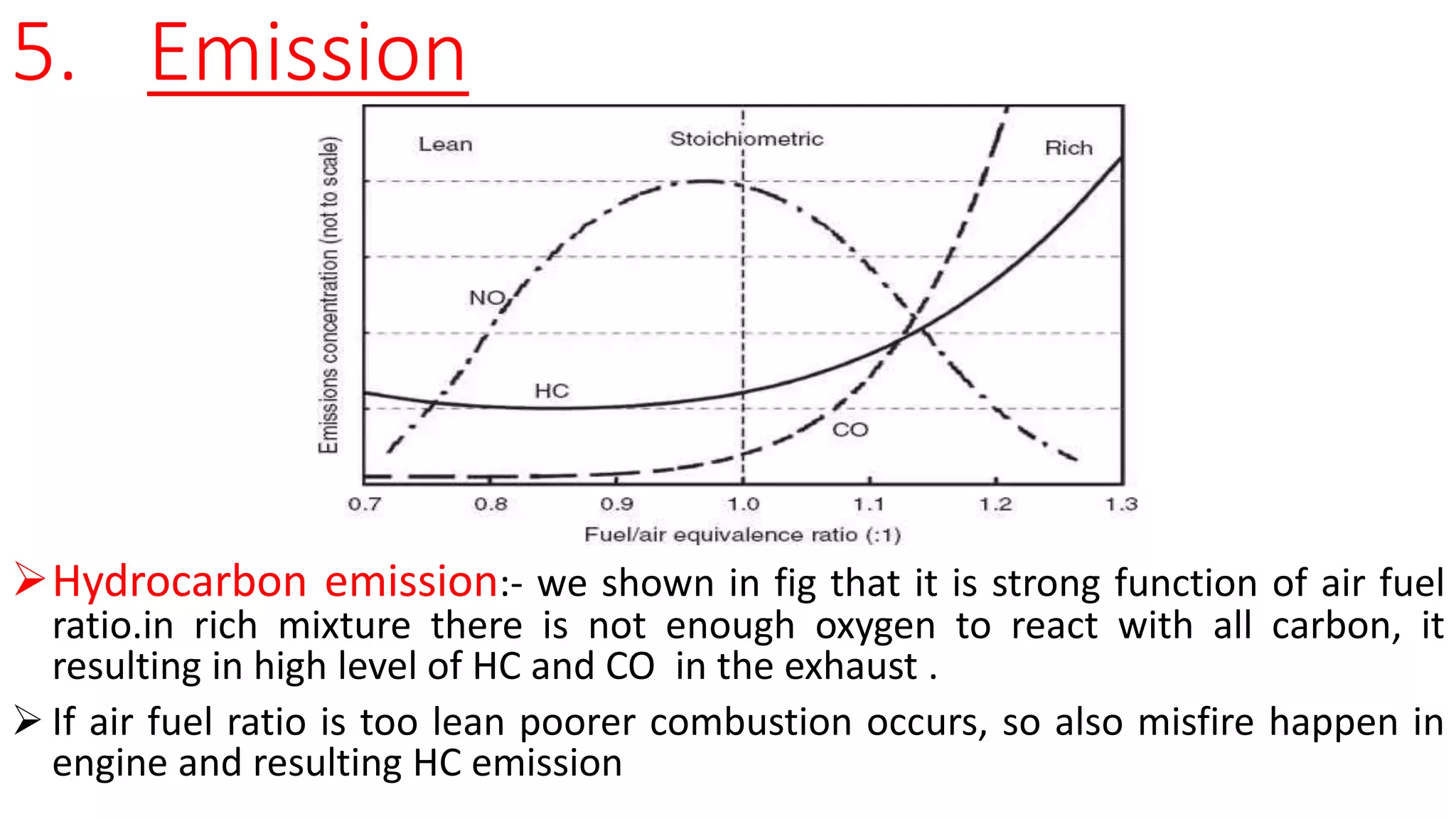
This document provides an overview of engine emissions and emission standards. It discusses the types of emissions from internal combustion engines, including hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and oxides of nitrogen. It also compares Indian Bharat emission standards to European Euro norms, noting differences in testing temperatures and maximum tested speeds. The document outlines the causes of different emissions and how emission standards aim to regulate the amounts of pollutants released.