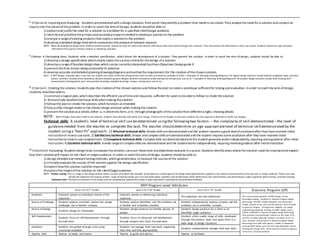
This document outlines criteria and descriptors for evaluating design projects at different levels in the MYP program. It provides descriptors for four criteria (A-D) that are used to evaluate projects at Level 1 (grades 6-8) and Level 2 (grades 6-8) of the MYP design cycle. For each criterion, it describes the skills and achievements expected of students at each level. The criteria include inquiring and analyzing, developing ideas, creating the solution, and evaluating. The document also provides context around the MYP design cycle and approach to group work.