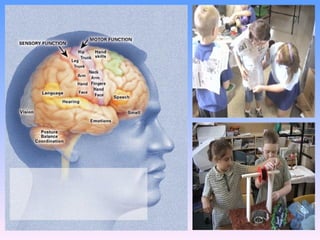
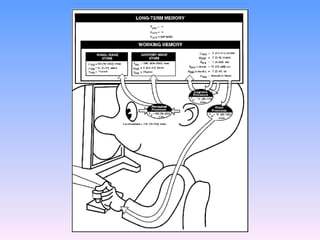
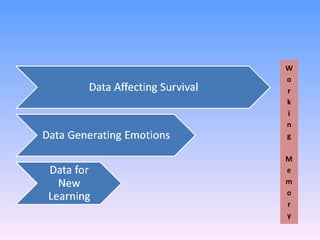
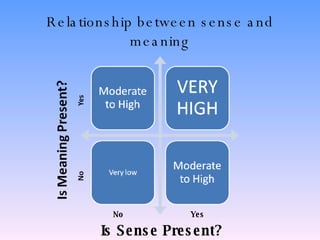
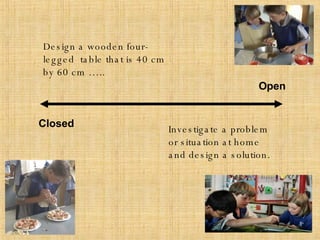
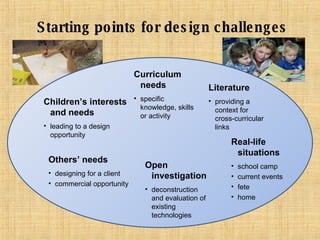
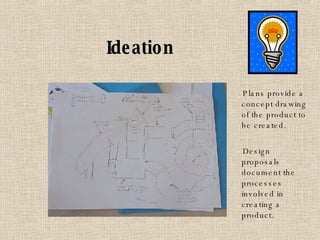
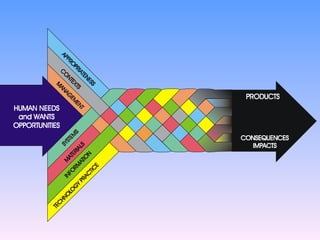
The document discusses key concepts in technology education, including design challenges, the strands of technology, and syllabus structure. It defines open and closed design challenges, noting that open challenges offer more creativity and require students to think more broadly. The four strands of technology - investigation, ideation, production, and evaluation - are introduced. Key concepts within each strand are also defined, such as how investigation involves gathering knowledge and data to meet design challenges.