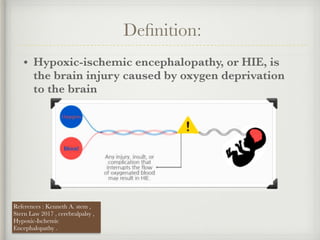
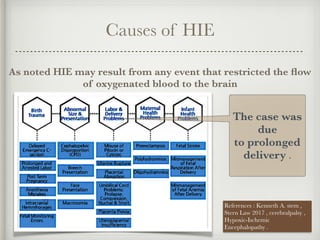
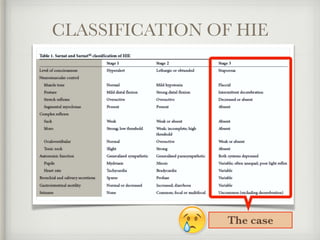
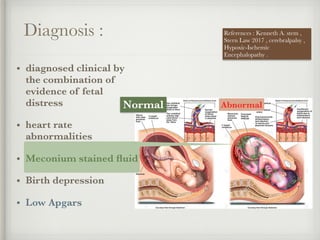
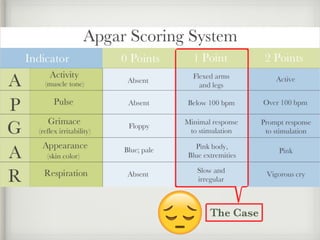
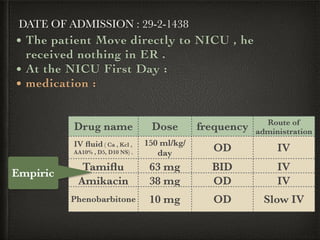
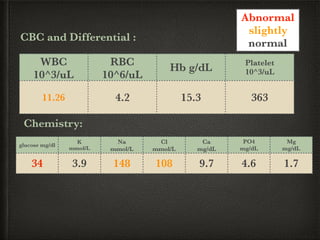
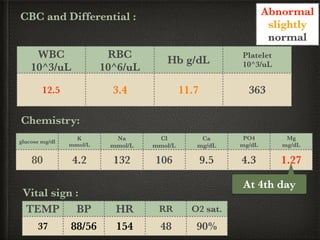
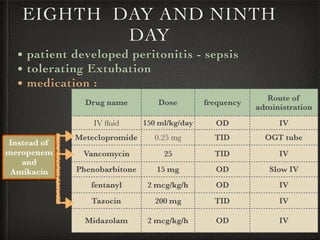
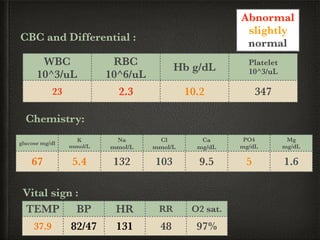
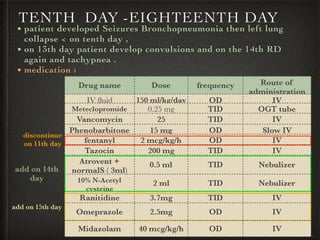
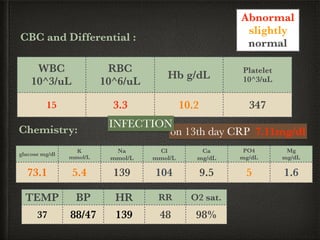
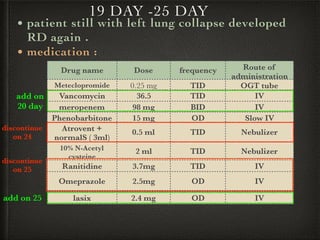
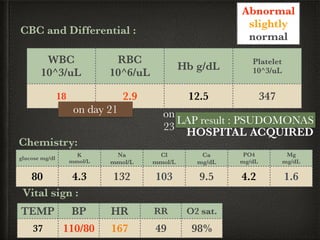
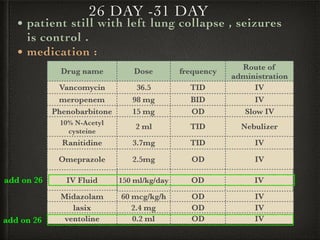
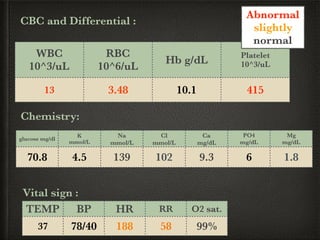
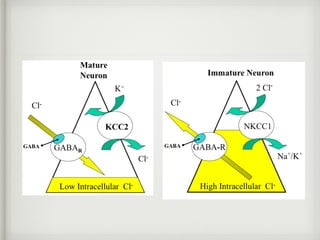
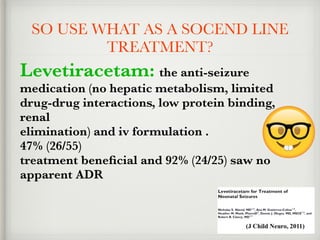
The document presents a case of a 14-day-old male neonate with severe hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) requiring intensive care due to respiratory distress and convulsions. It outlines the definition, causes, prevalence, diagnosis, and treatment options for HIE, along with a detailed medical history and treatment plan for the patient during his NICU stay. The treatment involved mechanical ventilation, various medications, and monitoring for complications, with a focus on addressing seizures and lung infections.