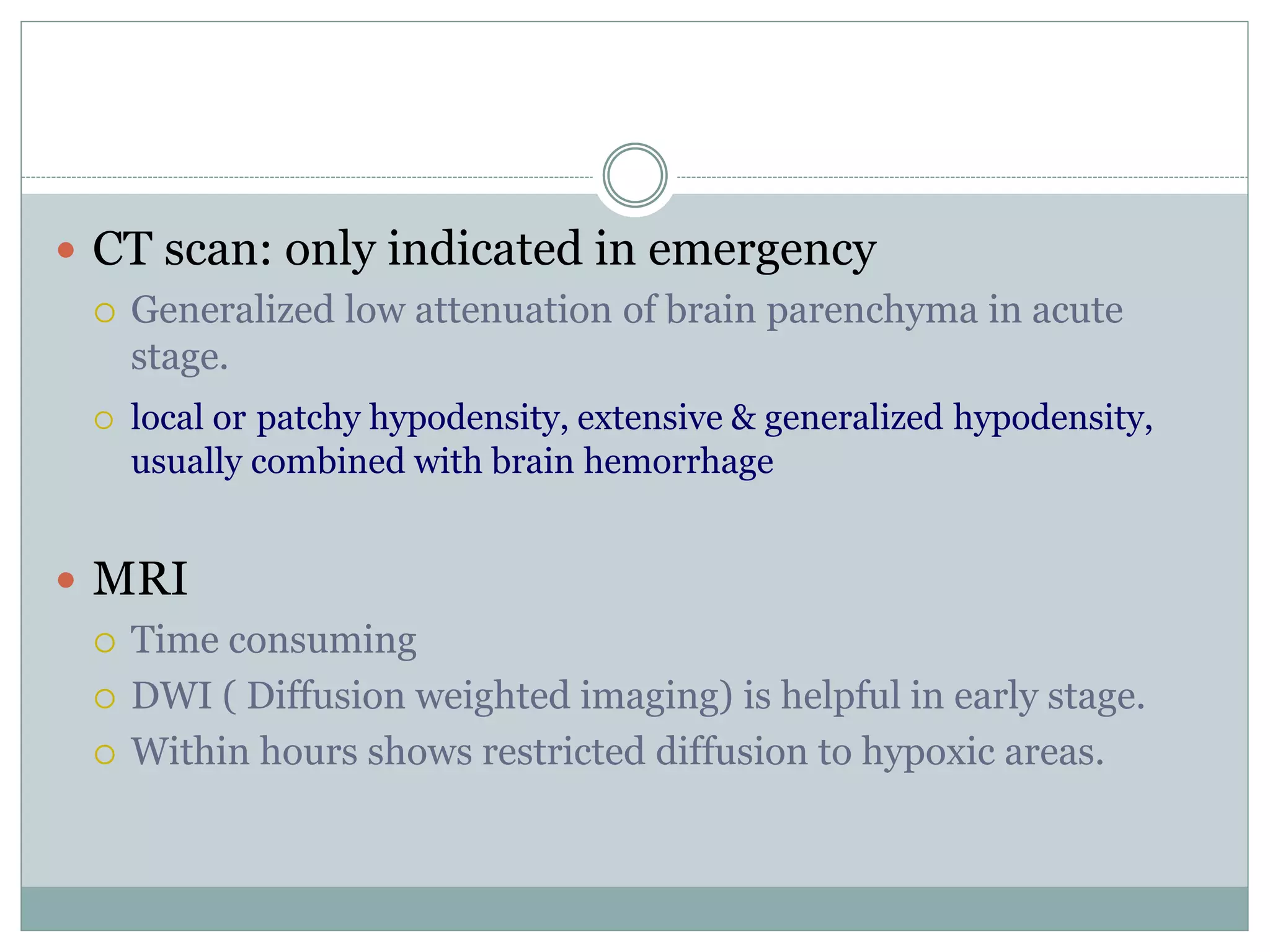
Clinically, more term babies suffered from hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) than premature babies. However, pathologically, more premature babies suffered from HIE than term babies. HIE manifests clinically as symptoms of consciousness changes that can be excitatory like seizures or depressing like coma. Treatment of HIE focuses on monitoring, controlling seizures, maintaining circulation and glucose levels, with therapies like hypothermia and investigates like amplitude integrated EEG shown to improve outcomes. The prognosis depends on the severity of brain damage and treatment, with mild cases often having a full recovery but severe cases having a high risk of mortality or neurological sequele like cerebral palsy.