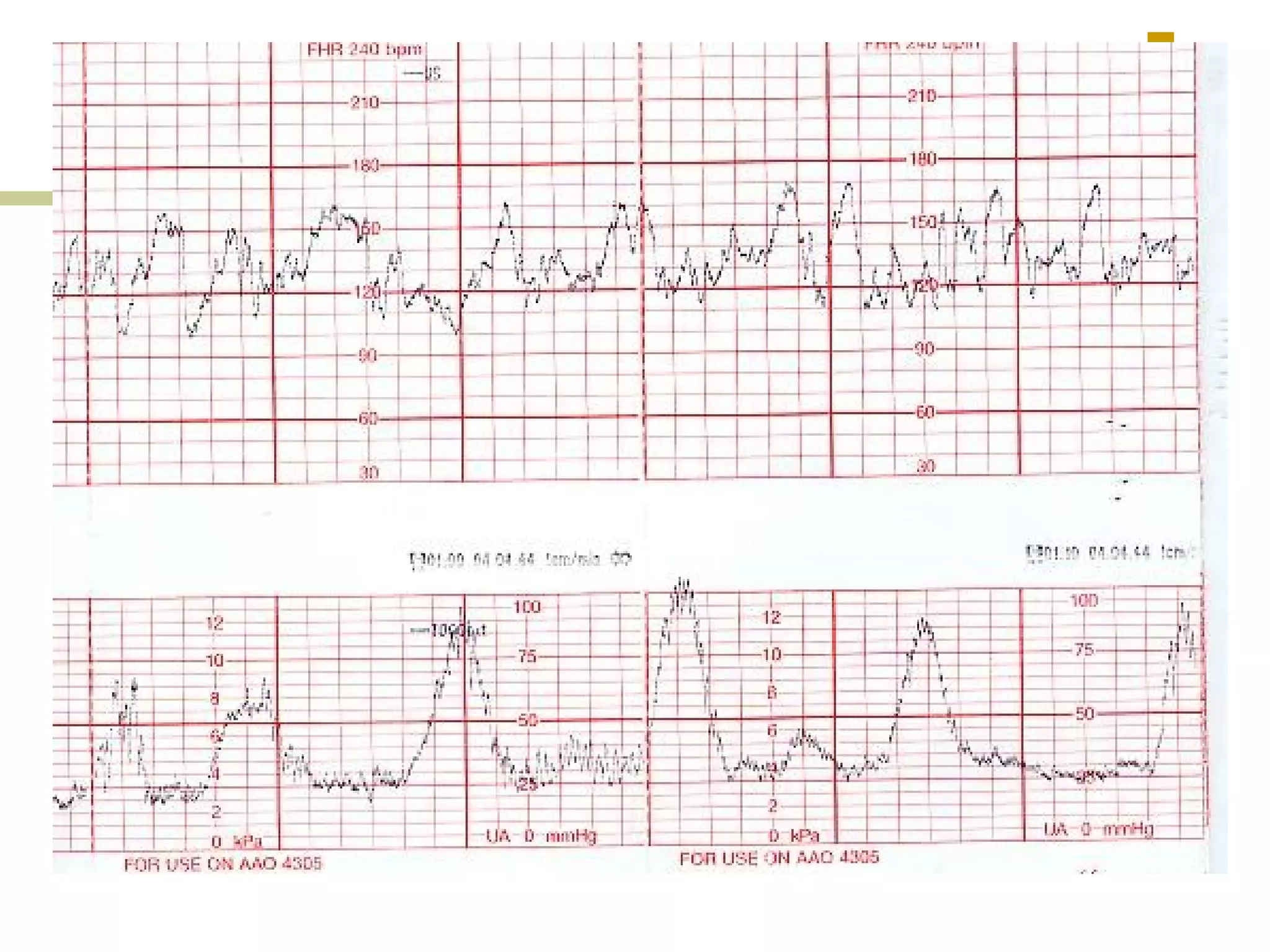
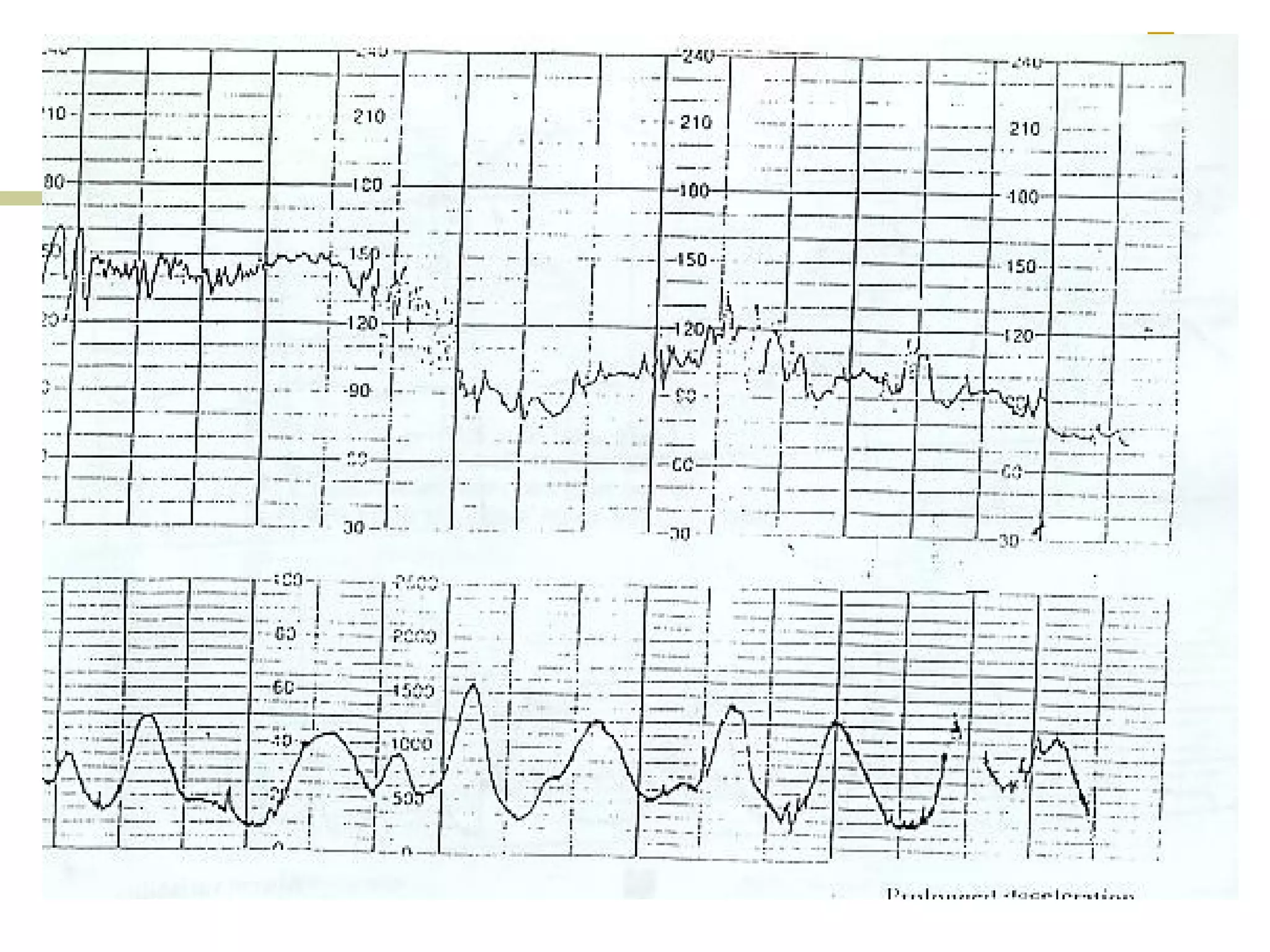
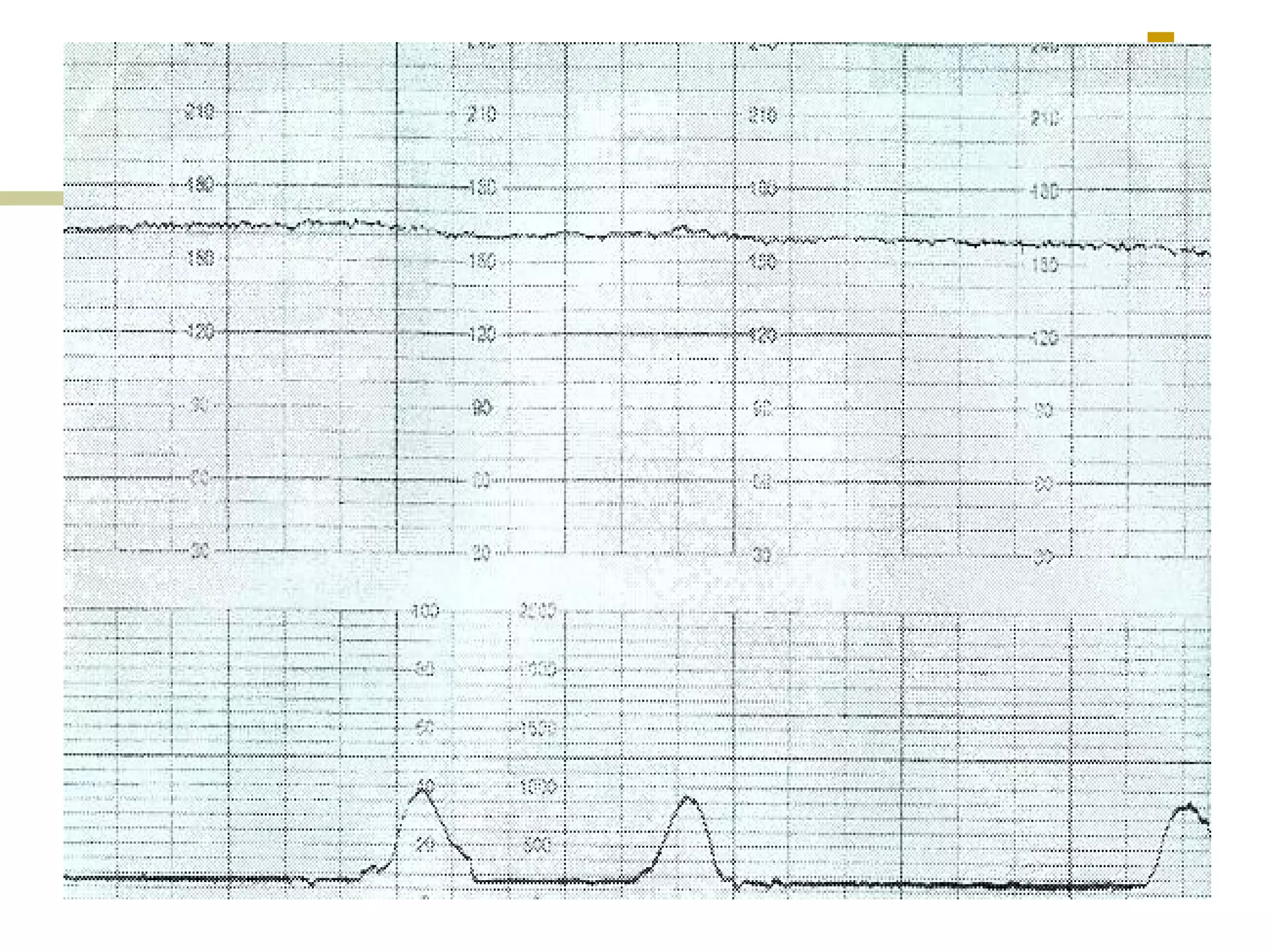
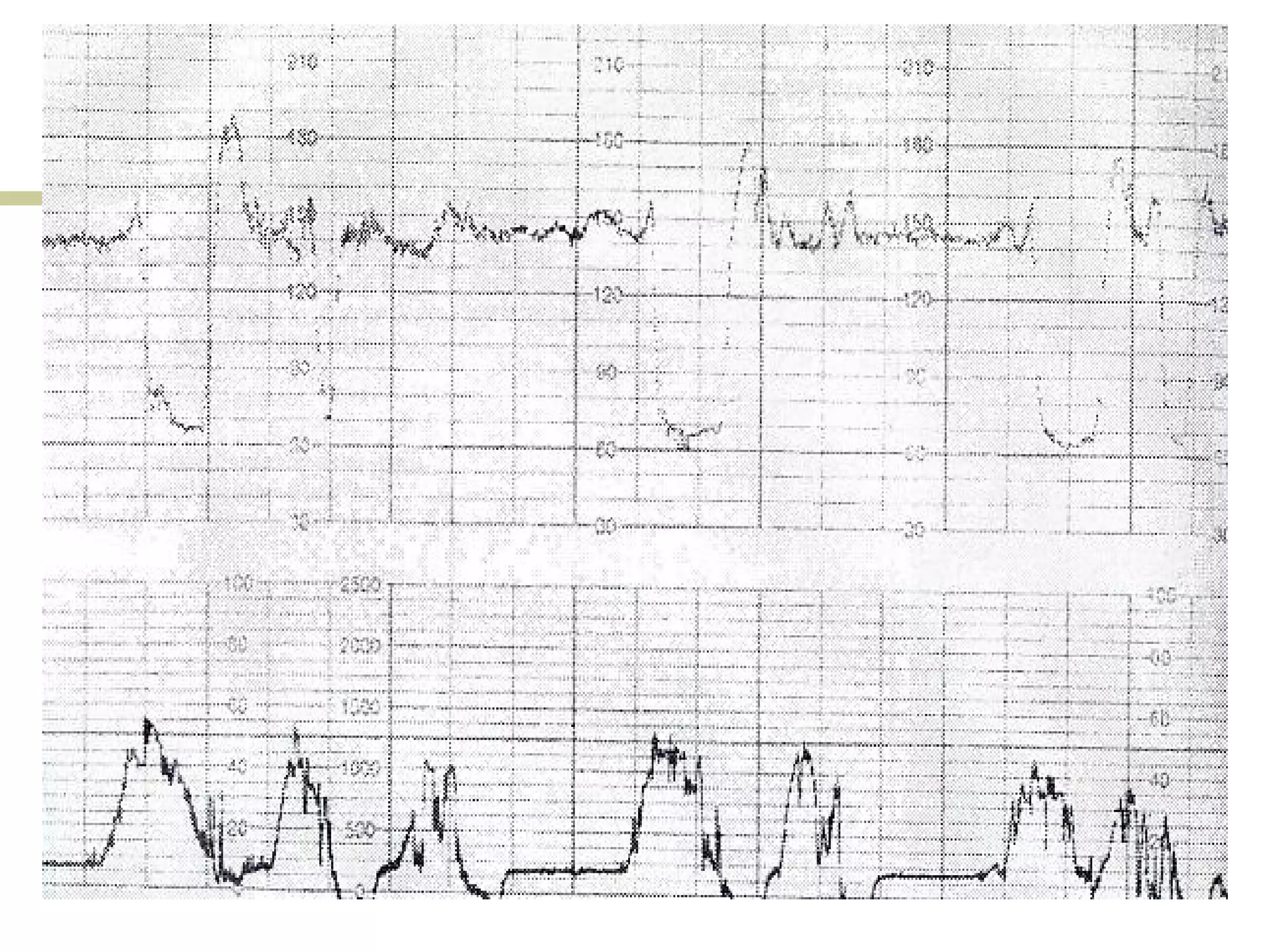
The document provides definitions and descriptions of key terms used in cardiotocography (CTG) including:
- Baseline heart rate, acceleration, deceleration, variability
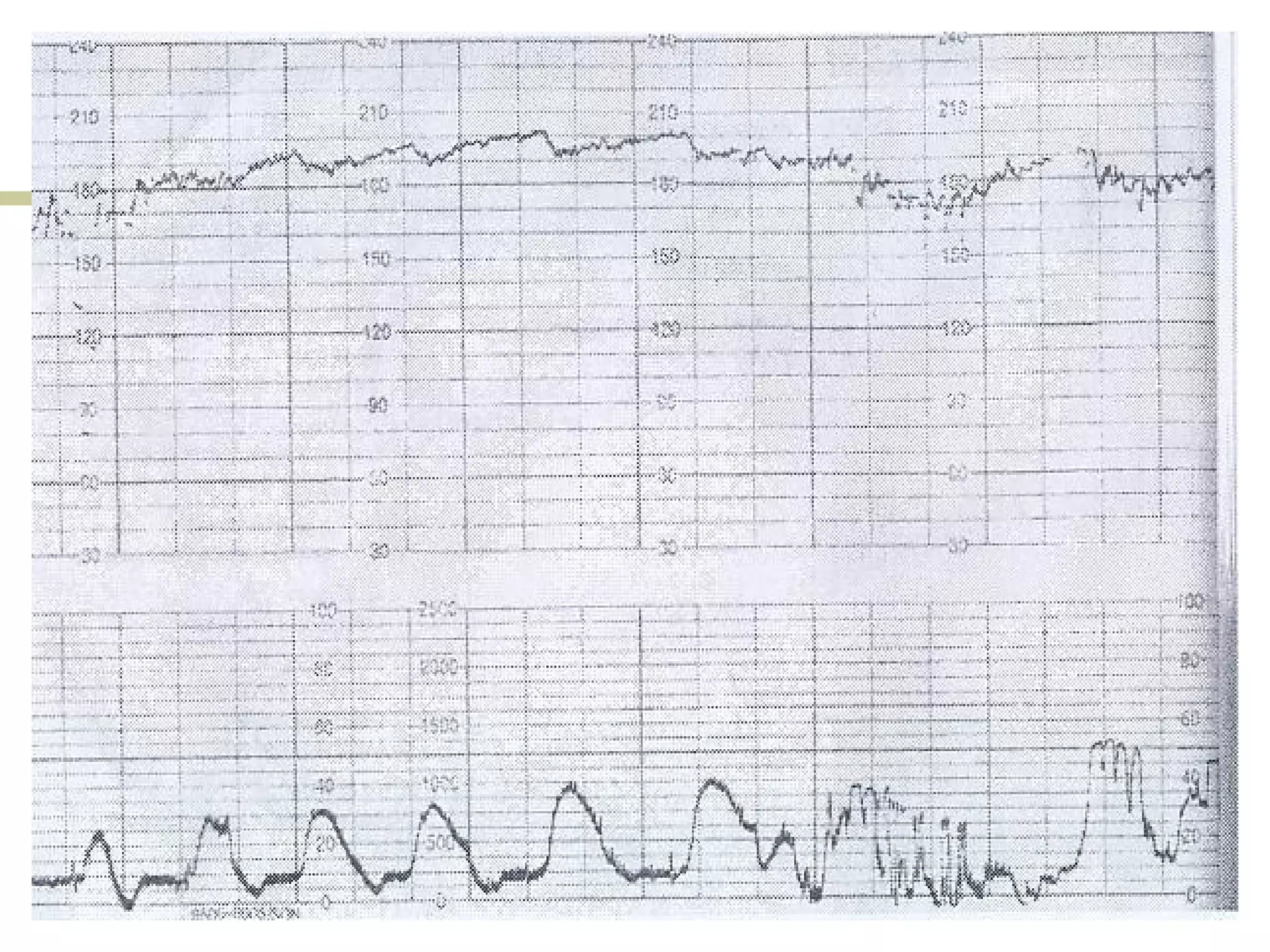
- Reactive, bradycardia, tachycardia traces
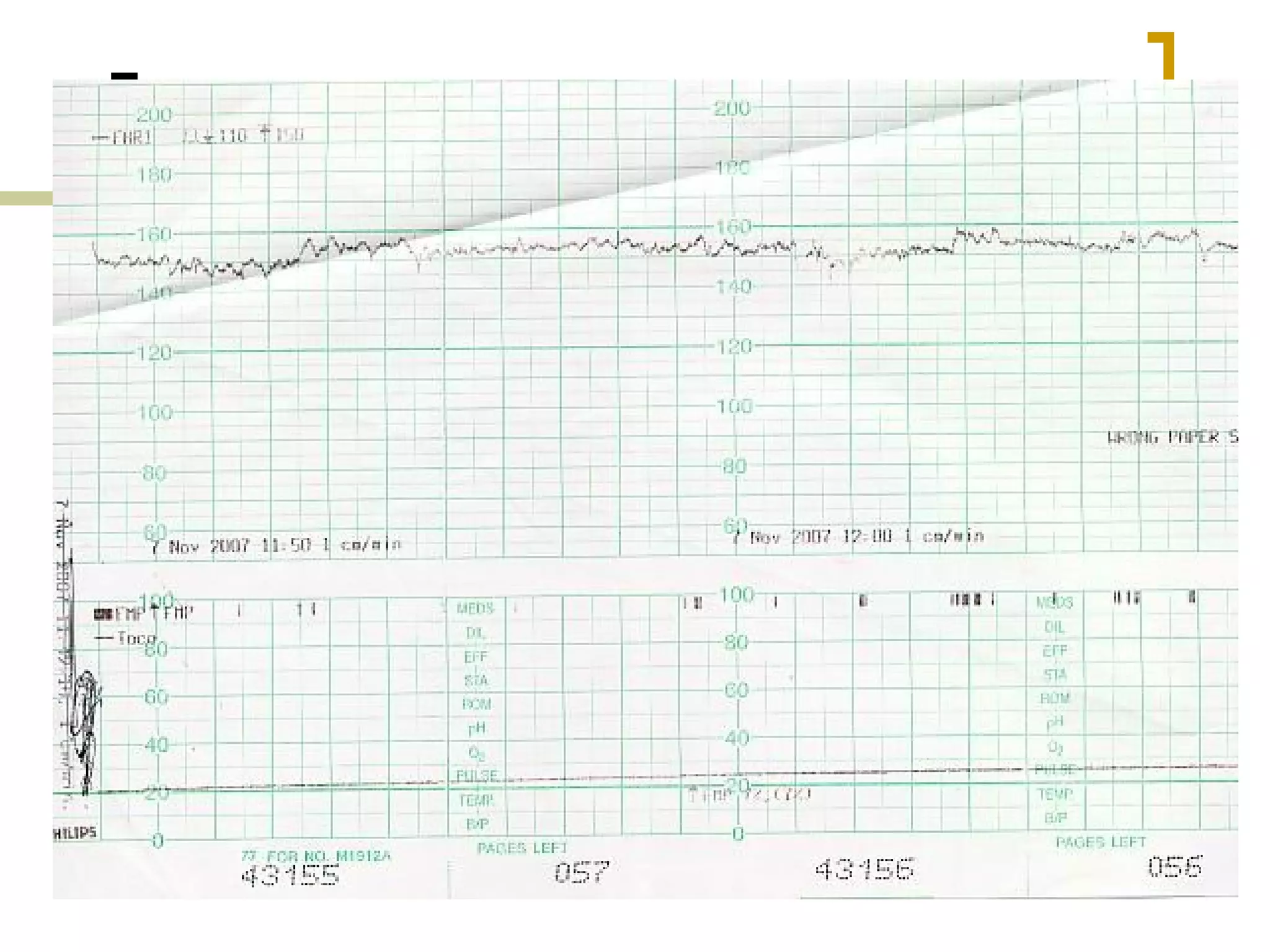
- Decreased variability, sinusoidal patterns
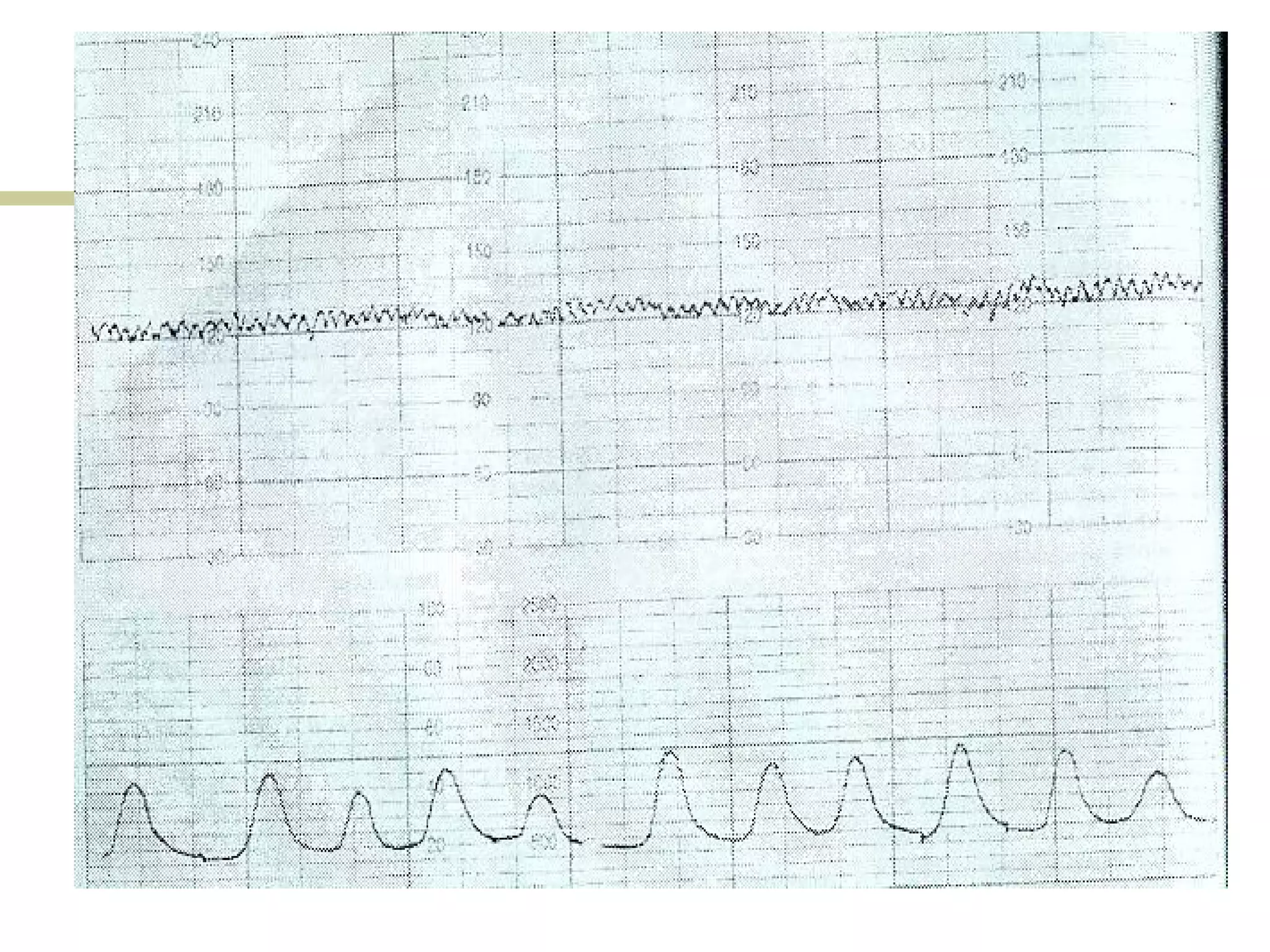
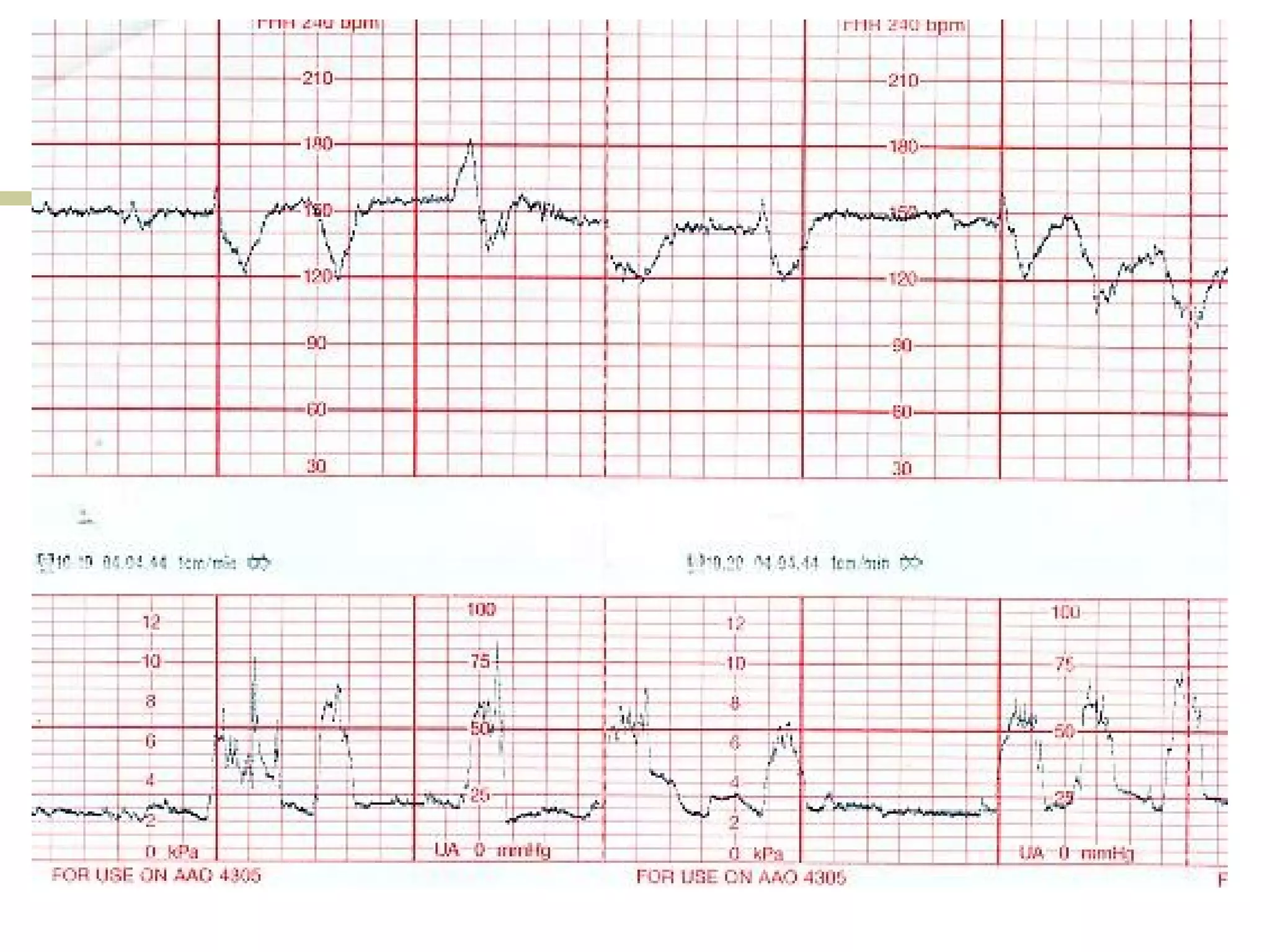
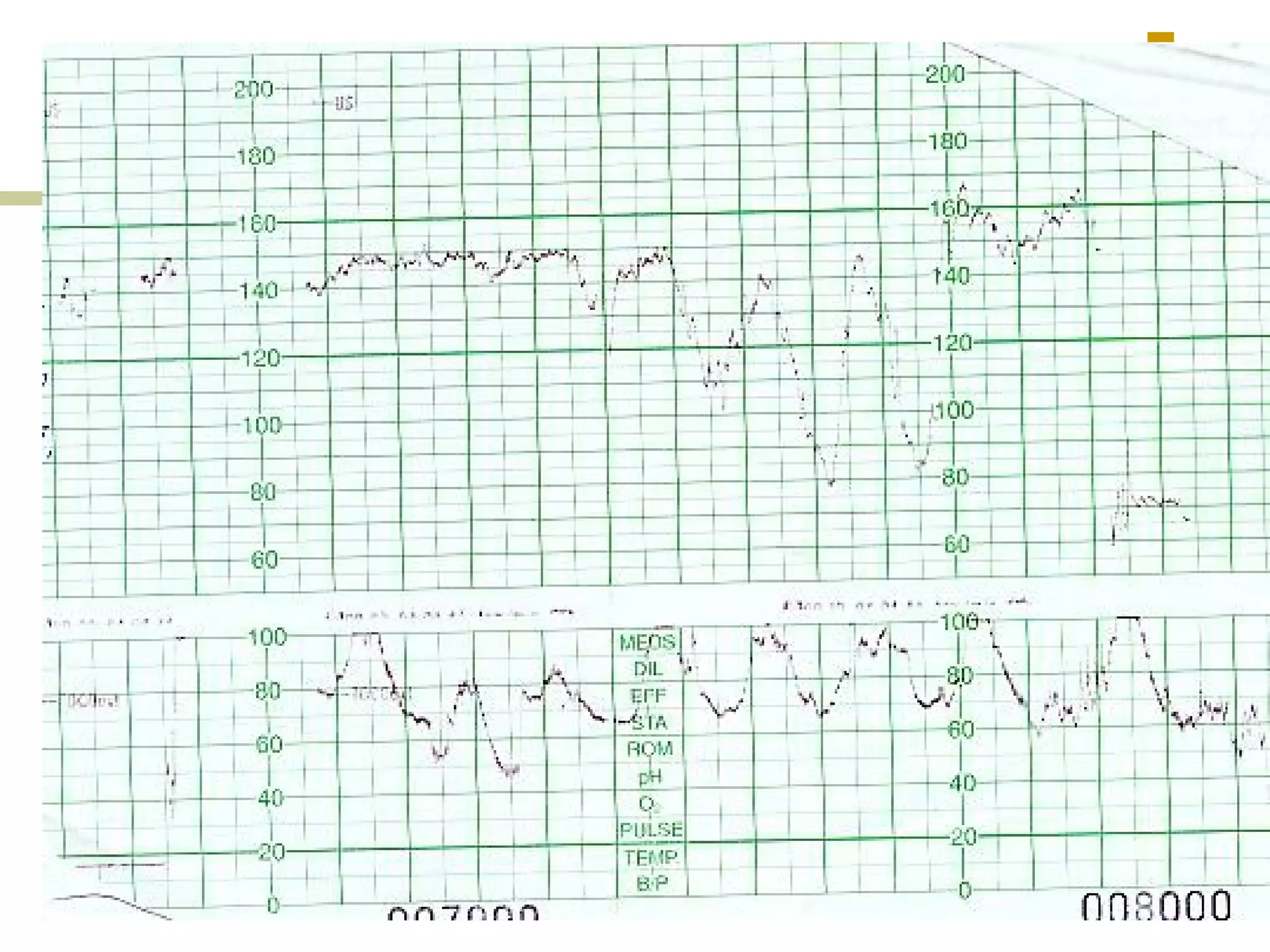
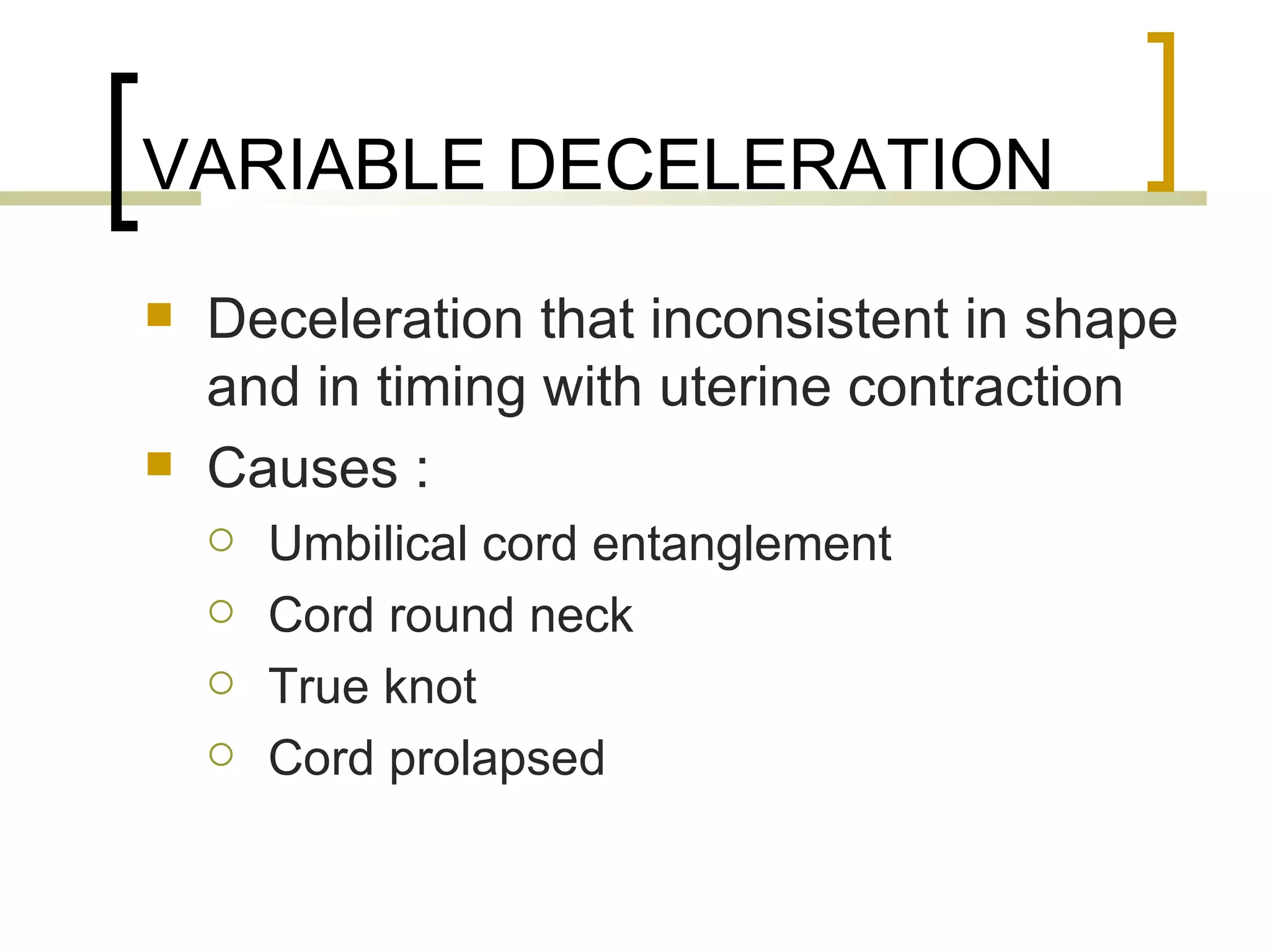
- Early, late, variable decelerations
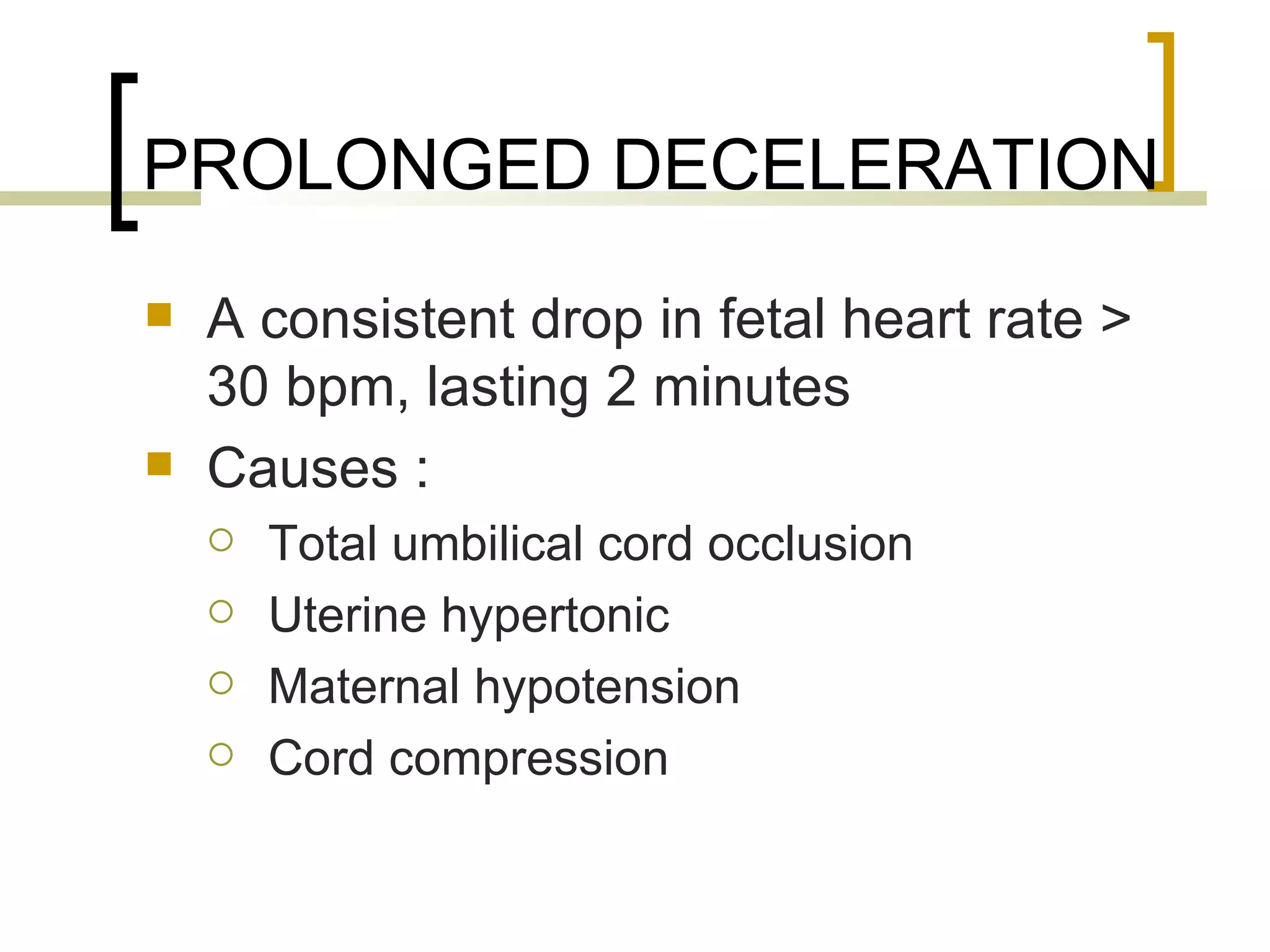
- Prolonged deceleration
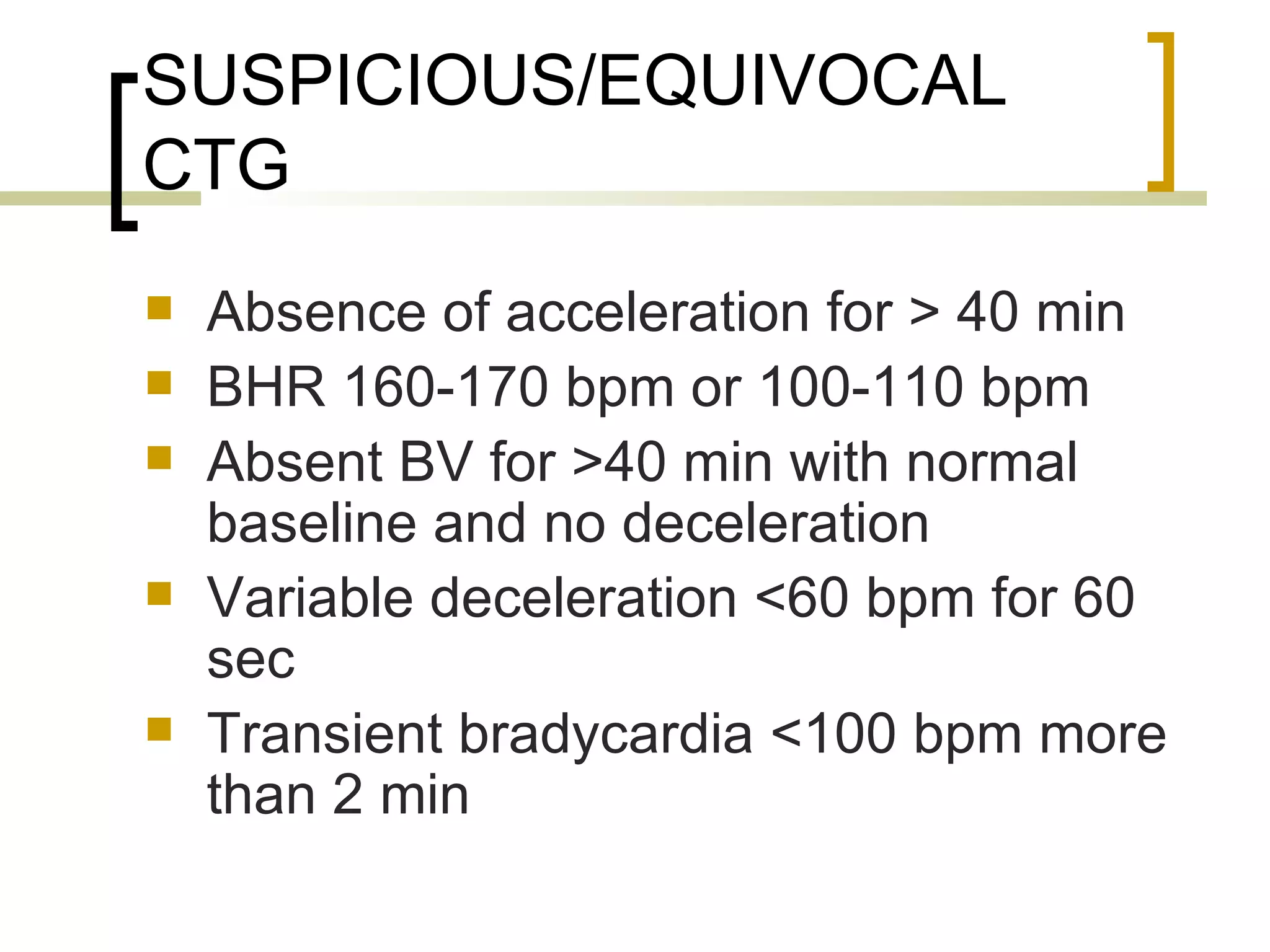
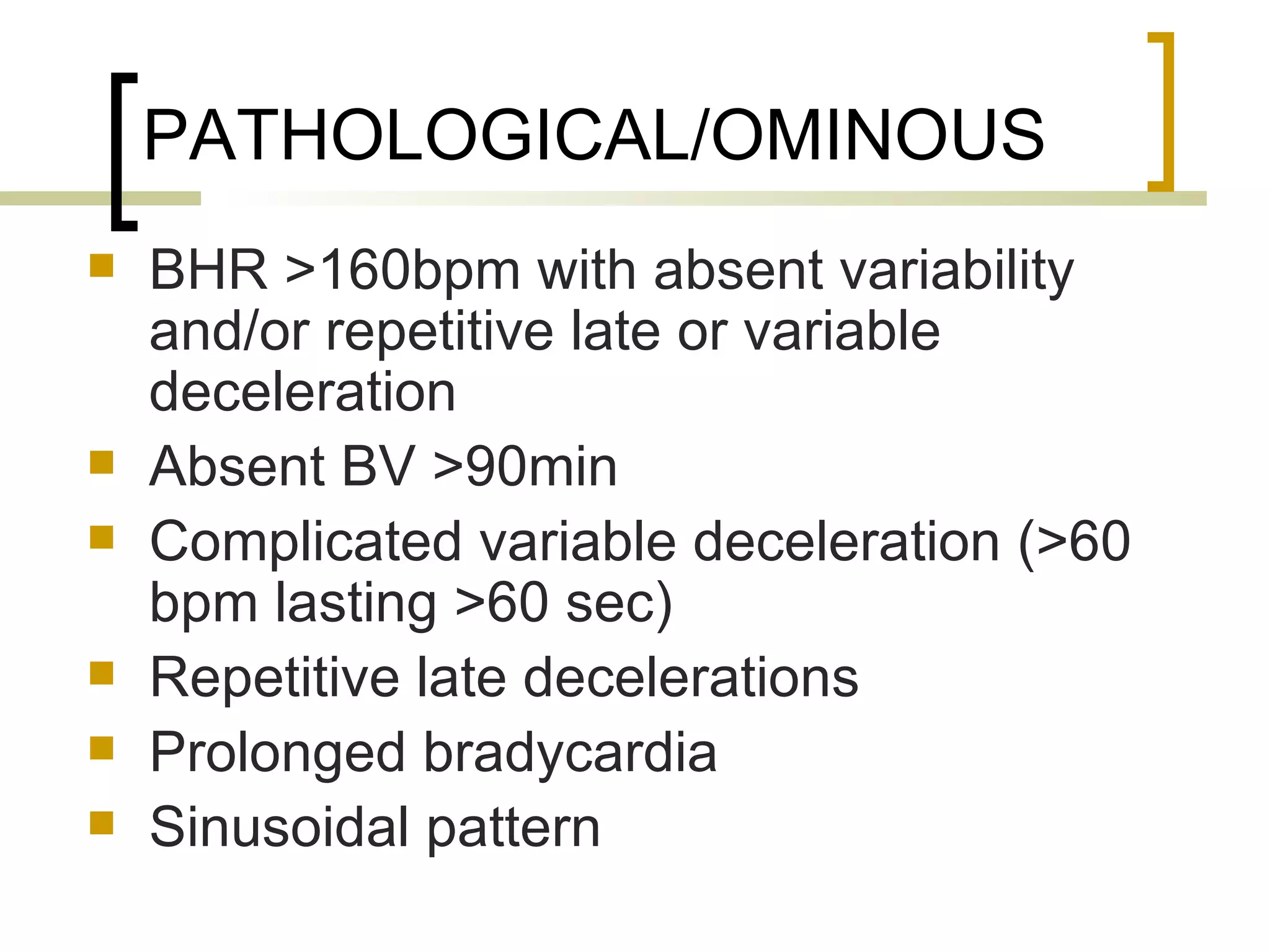
- Suspicious/equivocal and pathological/ominous CTG traces
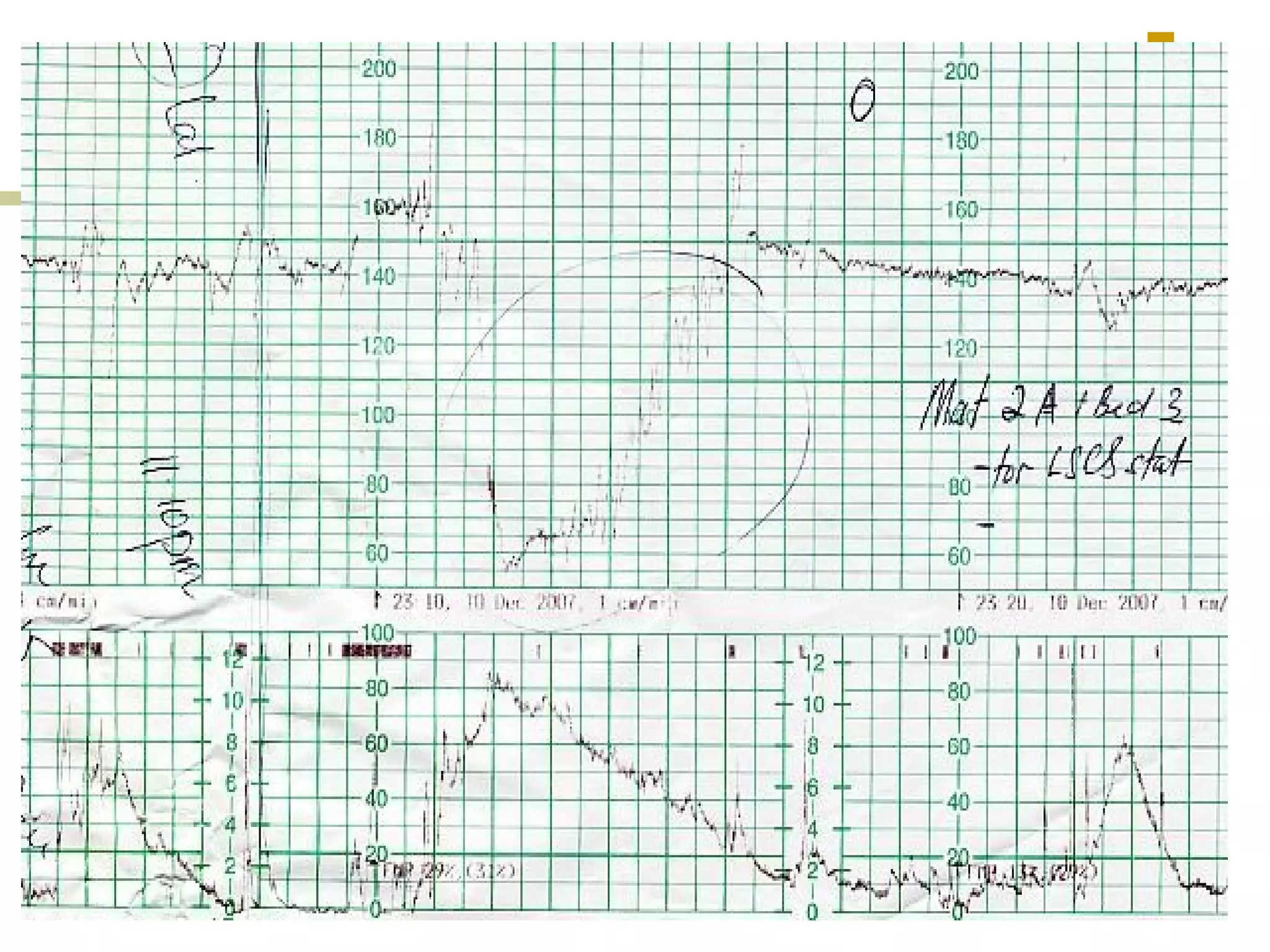
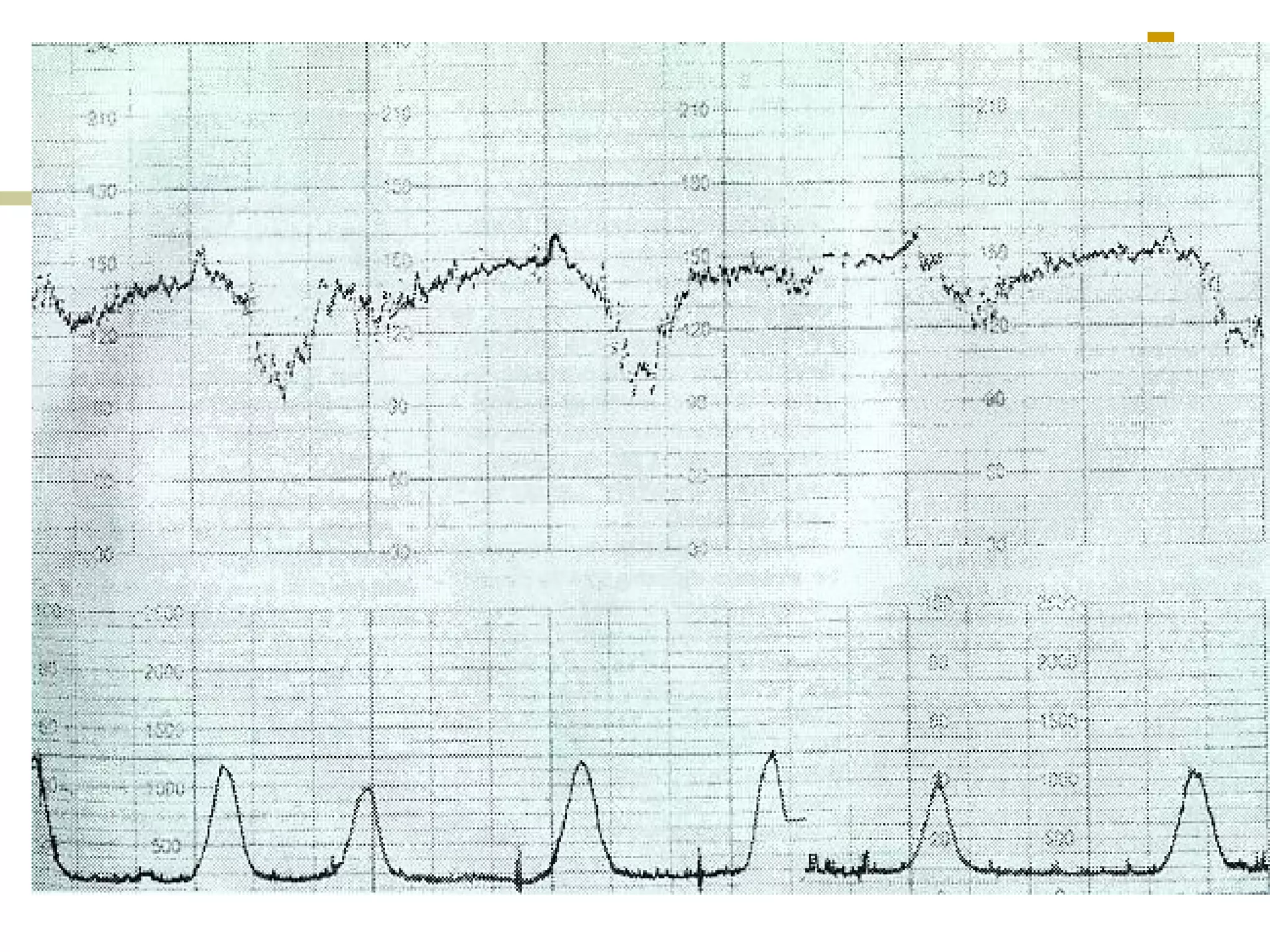
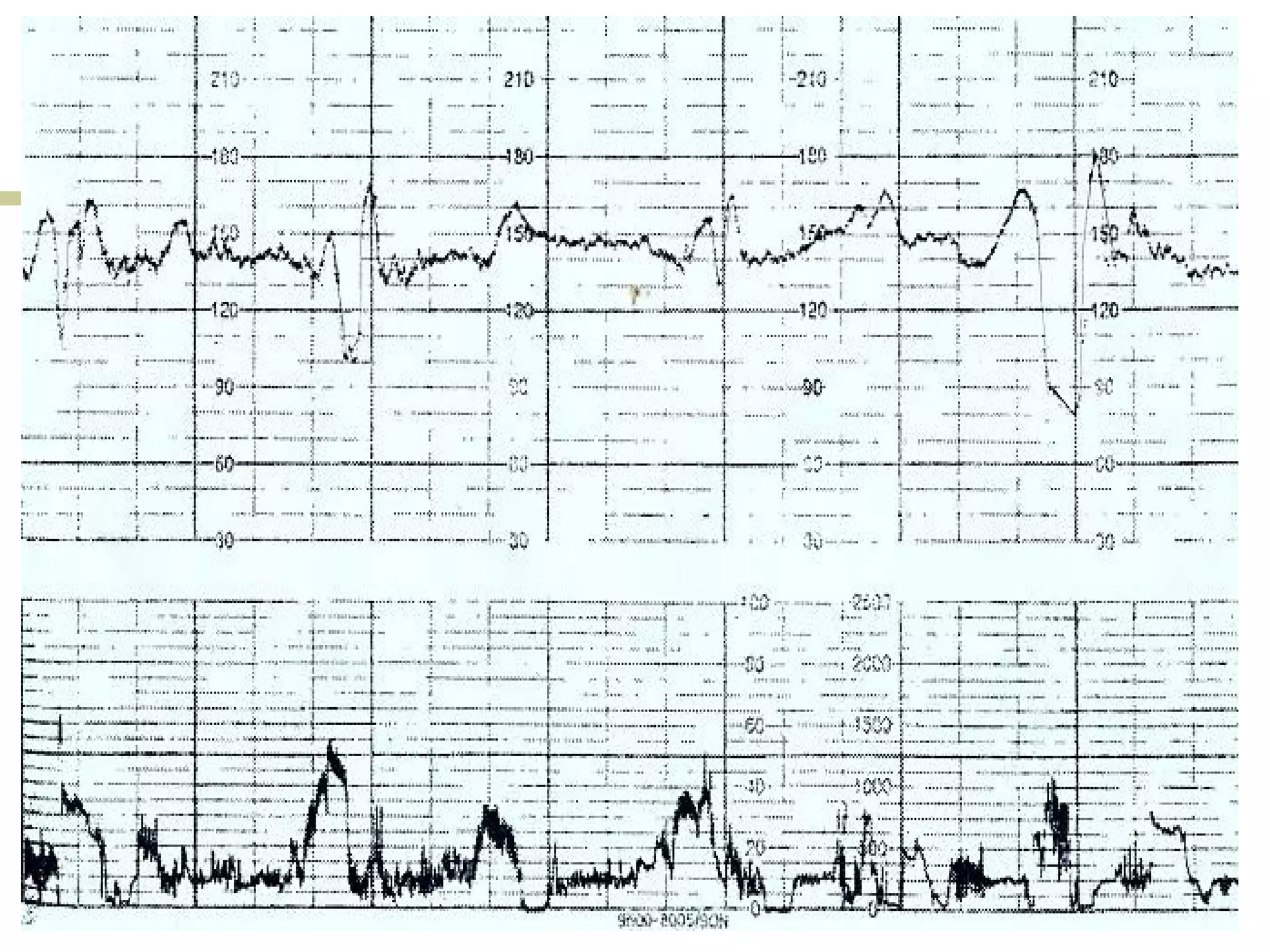
Clinical scenarios are presented involving pregnant women in labor with varying cervical dilation and fetal heart rate patterns on CTG monitoring. Uterine hyperstimulation is also defined.