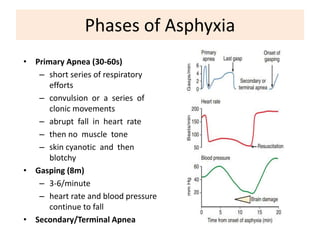
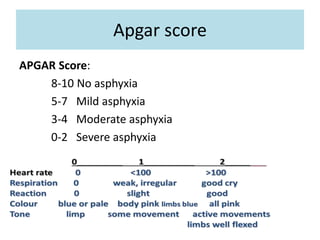
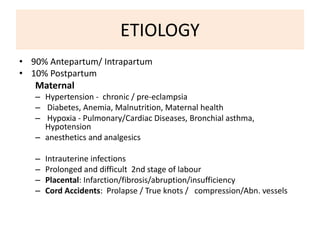
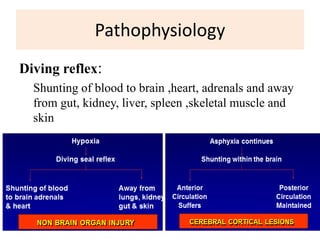
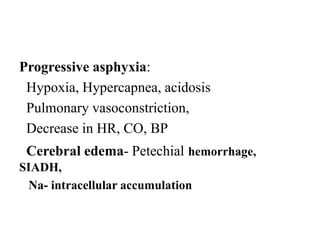
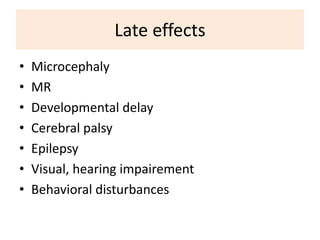
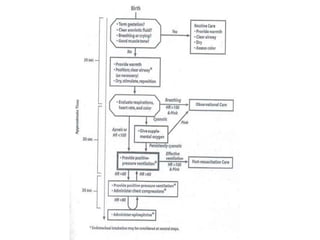
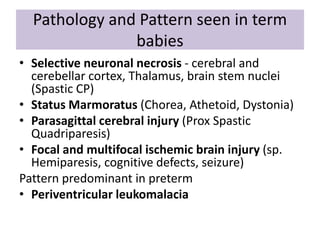
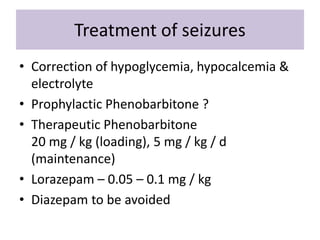
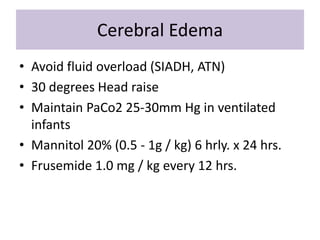
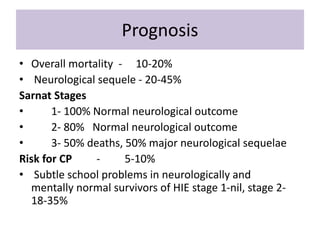
Perinatal asphyxia is caused by lack of oxygen and perfusion to organs before, during, or after birth. It can lead to hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and brain damage in newborns. Key criteria for diagnosis include low Apgar scores, metabolic acidosis in umbilical cord blood, and neurological symptoms. Management focuses on preventing further brain injury through ventilation, temperature control, seizure management, and maintaining circulation. Outcomes range from normal to death or disabilities like cerebral palsy. Prognosis depends on severity of encephalopathy.