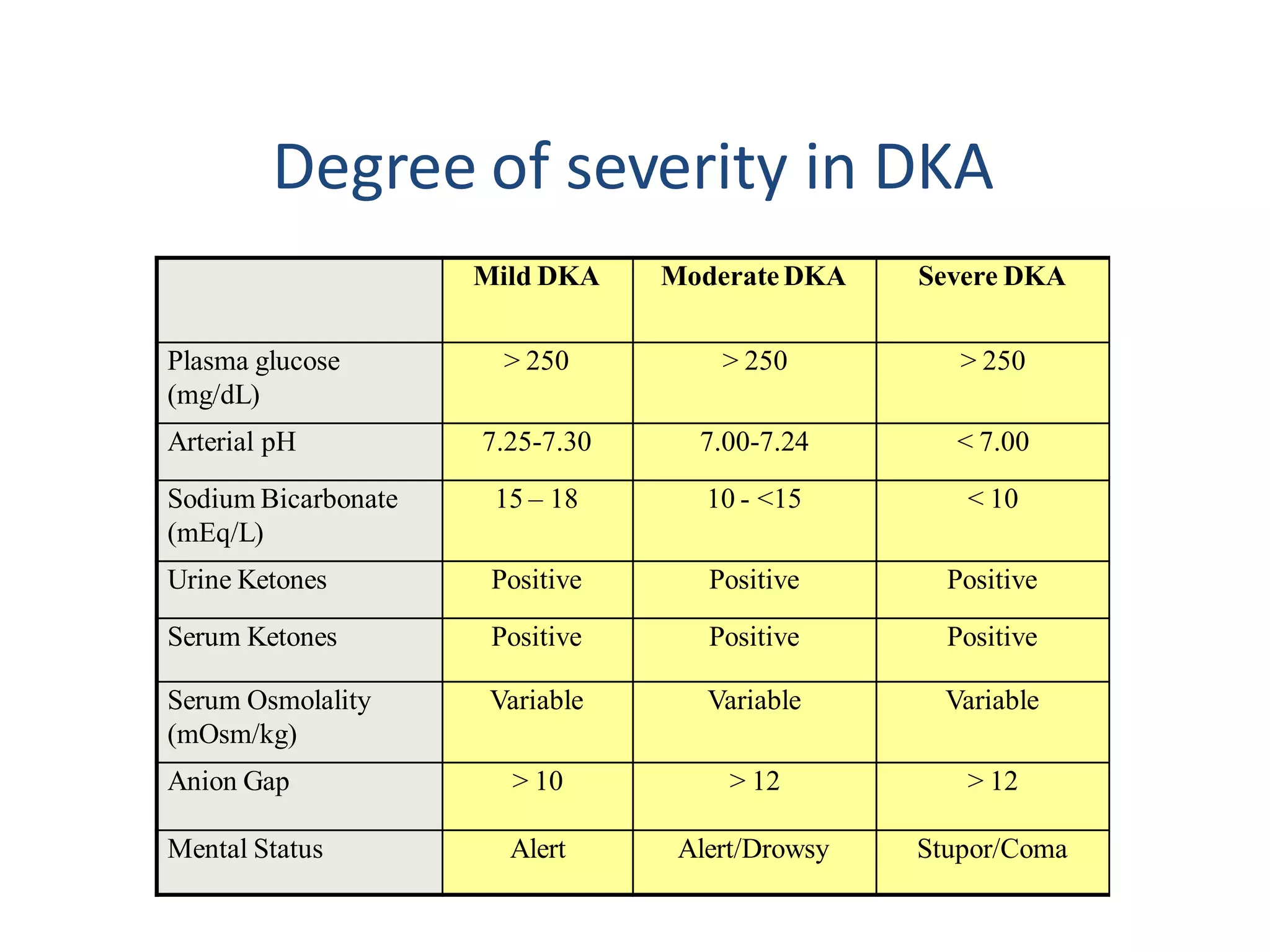
This document discusses diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), providing definitions, pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, clinical features, and management approach. DKA is characterized by hyperglycemia, dehydration, and acidosis due to insulin deficiency. It is most commonly seen in type 1 diabetics and can be life-threatening. The document outlines treatment involving fluid replacement, insulin administration, electrolyte replacement, and addressing underlying causes such as infection. Complications discussed include cerebral edema, which has high mortality. Careful management is needed to safely resolve DKA and prevent complications.